- Page 3:
Preface to the Proceedings of the E
- Page 6 and 7:
As for the Extra EURO Conference
- Page 8 and 9:
END-USERS COMMITTEE Government of A
- Page 10 and 11:
Id: 011 An activity-based systemof
- Page 12 and 13:
Id: 039 The influence of advanced t
- Page 14 and 15:
Id: 064 Strategic modelling and hie
- Page 16 and 17:
Id: 087 A stochastic approach to de
- Page 18 and 19:
Id: 112 Minimum redeployment model
- Page 20 and 21:
Id: 143 Towards mobile semantic gri
- Page 22 and 23:
21. Alessandro BALDASSARRA, Univers
- Page 24 and 25:
73. Paolo DELLE SITE, University of
- Page 26 and 27:
125. Maria Alice Prudêncio JACQUES
- Page 28 and 29:
177. Bruno MONTELLA, University of
- Page 30 and 31:
228. Domenico SASSANELLI, DVT - Tec
- Page 32 and 33:
279. Saini YANG, University of Mary
- Page 34 and 35:
To help fulfil the expectations of
- Page 36 and 37:
DO PEDESTRIANS EFFICIENTLY USE OVER
- Page 38 and 39:
The gray part in Figures 1 & 2 show
- Page 40 and 41:
INTELLIGENT TRANSPORT SYSTEMS: ROLE
- Page 42 and 43:
Figure 2. MD-200 3. Proposal 3.1. I
- Page 44 and 45:
data to be visualized in a clear an
- Page 46 and 47:
9. Would solve all the Traffic prob
- Page 48 and 49:
EFFECT OF EXTERNAL COST INTERNALISA
- Page 50 and 51:
where i ,a f is the transit user fl
- Page 52 and 53:
[7] L. D’Acierno, M. Gallo and B.
- Page 54 and 55:
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON DATA DRIVEN P
- Page 56 and 57:
Due to this uncertainty of bus arri
- Page 58 and 59:
Figure1. Flow of Data of the whole
- Page 60 and 61:
5.1. Implementation Issue: Institut
- Page 62 and 63:
A MULTINOMIAL LOGIT MODEL FOR SERVI
- Page 64 and 65:
Some Logit models were proposed by
- Page 66 and 67:
service quality attributes. The uti
- Page 68 and 69:
[4] A. Bhave. Customer Satisfaction
- Page 70 and 71:
MODELING THE IMPACT OF TRAVEL INFOR
- Page 72 and 73:
Real travel time (random generated)
- Page 74 and 75:
Our schedule engine follows this. T
- Page 76 and 77:
HOME StartTime: 0 Duration: 571 Loc
- Page 78 and 79:
[15] Sun, Z., T.A. Arentze, and H.J
- Page 80 and 81:
prevailing traffic and road conditi
- Page 82 and 83:
3.2.2. Training of the network and
- Page 84 and 85:
Error (%) Error (%) Analytical mode
- Page 86 and 87:
method should be developed to help
- Page 88 and 89:
to parking lots (T) are selected as
- Page 90 and 91:
4. Evaluation of two-phased parking
- Page 92 and 93:
[30]), in vehicle routing ([3], [19
- Page 94 and 95:
with: ∆τ t od ,l ∑ = ∆T (10)
- Page 96 and 97:
In terms of future research, we pro
- Page 98 and 99:
dell’informazione: Campi di appli
- Page 100 and 101:
Adler and Ben-Akiva are the first a
- Page 102 and 103:
Activity program Primary activity o
- Page 104 and 105:
primary activity PA in the primary
- Page 106 and 107:
A WEB BASED DATA SOURCE PLATFORM FO
- Page 108 and 109:
2.3. Process Layer The process laye
- Page 110 and 111:
DYNAMIC SELECTION OF FUZZY SIGNAL C
- Page 112 and 113:
Each of the fuzzy control strategie
- Page 114 and 115:
selection at the end of each extens
- Page 116 and 117:
PHYSICAL AND OPERATIONAL DESIGN IN
- Page 118 and 119:
∑ r∈Rw ∑ r∈R v h s l r h r
- Page 120 and 121:
As a first step in this study, the
- Page 122 and 123:
DSS FOR EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT ON MOT
- Page 124 and 125:
improve whole emergency system in t
- Page 126 and 127:
The three defined levels in the cer
- Page 128 and 129:
USING MECHANISTIC DESIGN PROCEDURES
- Page 130 and 131:
• General traffic inputs- Number
- Page 132 and 133:
Table 5 Sensitivity of the performa
- Page 134 and 135:
Figure 1 depicts the results for th
- Page 136 and 137:
6. Concluding Remarks The sensitivi
- Page 138 and 139:
a) Distribution of activities. For
- Page 140 and 141:
Figure 2. Multi-pole structure: the
- Page 142 and 143:
TOWARDS A SECURE RAILWAY TRANSPORT
- Page 144 and 145:
There are several reasons that peop
- Page 146 and 147:
For each potential countermeasure,
- Page 148 and 149:
SECURITY MANAGEMENT PROCESS Define
- Page 150 and 151:
OPTIMAL REROUTING DURING EMERGENCY
- Page 152 and 153:
Figure 1 Ring way network consistin
- Page 154 and 155:
Figure 3 Assignment during accident
- Page 156 and 157:
50% can be attributed to the stocha
- Page 158 and 159:
some hyper-network approaches. Simu
- Page 160 and 161:
Let V smk be the systematic utility
- Page 162 and 163:
RESEARCH ON USERS’ BEHAVIOR CHANG
- Page 164 and 165:
Item Date Subjects recruitment Sep.
- Page 166 and 167:
Transferring time Commuting time Tr
- Page 168 and 169:
4.2. Future tasks Only young people
- Page 170 and 171:
Percentage of people 80 60 40 20 0
- Page 172 and 173:
particular sound level. In this sen
- Page 174 and 175:
for the airports such as runways le
- Page 176 and 177:
A NEW METHOD FOR OFFSET OPTIMIZATIO
- Page 178 and 179:
q j-1 N j-1 n j-1 Cell j-1 N j N j+
- Page 180 and 181:
4. Optimization Algorithms The obje
- Page 182 and 183:
TRANSYT-7F (+10% delay) and the man
- Page 184 and 185:
spread out non-linear utility funct
- Page 186 and 187:
3. Application example Data source
- Page 188 and 189:
PDPC model estimation In order to i
- Page 190 and 191:
surpasses the lower bound of 35 % i
- Page 192 and 193:
follower pairs are introduced and a
- Page 194 and 195:
vehicle was not intentionally follo
- Page 196 and 197:
3. Concluding remarks and research
- Page 198 and 199:
2. the path choice from the alterna
- Page 200 and 201:
2.2. Generation of choice set For t
- Page 202 and 203:
set generated with the explicit app
- Page 204 and 205:
3.2. Generation of choice set 3.2.1
- Page 206 and 207:
A generic user n , travelling betwe
- Page 208 and 209:
[2] C. R. Bhat. Recent methodologic
- Page 210 and 211:
EXPLORING A GUIDANCE PROCESS FOR US
- Page 212 and 213:
The objective is to identify a set
- Page 214 and 215:
This impact can be evaluated (step
- Page 216 and 217:
etc.) and on queue discipline. The
- Page 218 and 219:
and actuated traffic signals. The f
- Page 220 and 221:
The results of the application of t
- Page 222 and 223:
In conclusion, after comparing the
- Page 224 and 225:
guarantees the attainment of perfor
- Page 226 and 227:
having direction of opposite march,
- Page 228 and 229:
The followings models propose, resp
- Page 230 and 231:
Where V 85c is the operating speed
- Page 232 and 233:
In order to support this statement,
- Page 234 and 235:
implementation of just local initia
- Page 236 and 237:
selection of measures to implement
- Page 238 and 239:
overall favourable achievements, bu
- Page 240 and 241:
Petty et al. (1997) focus on the tr
- Page 242 and 243:
t is the travel time for the itiner
- Page 244 and 245:
Hopkin, J., D. Crawford and I. Catl
- Page 246 and 247:
MNL model has long been considered
- Page 248 and 249:
Mendell and Elston and of Tang and
- Page 250 and 251:
An interesting extension of the mod
- Page 252 and 253:
• The newly-introduced multi-late
- Page 254 and 255:
surveillance data) and thus can be
- Page 256 and 257:
targets on signal level. Figure 3 (
- Page 258 and 259:
A GIS APPROACH TO OPTIMAL LOCALIZAT
- Page 260 and 261:
It is possible to determine the opt
- Page 262 and 263:
In particular, each record holds th
- Page 264 and 265:
START-UP LOST TIME AT URBAN TRAFFIC
- Page 266 and 267:
Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 1 Phase 2 h(n
- Page 268 and 269:
n vehicles ≥6, n vehicles tot >14
- Page 270 and 271:
THE INFLUENCE OF ADVANCED TRAVELLER
- Page 272 and 273:
is very difficult to provide reliab
- Page 274 and 275:
Moreover to confirm the relative im
- Page 276 and 277:
[6] Lehtonen M., Kulmala R., Benefi
- Page 278 and 279:
0—`1u„|aM2l]^„Z€‚N\]o`buR
- Page 280 and 281:
Œ›.1]^ž#2+Qq]^`1]t0wve2Žä „
- Page 282 and 283:
a.1{À`buqN ]OR]^„3SMv[0wv‚~ a.
- Page 284 and 285:
ŒoqÞ >Ñ)%;"$oHxR]^¯¨Nlv†‘
- Page 286 and 287:
efficient transportation system, ne
- Page 288 and 289:
4. Goals Accomplished Three major g
- Page 290 and 291:
DIFFERENCES AMONG ROUTE FLOW SOLUTI
- Page 292 and 293:
Unchanged OD = 100% 90%−100% 70%
- Page 294 and 295:
EVALUATION OF ON-STREET PARKING SCH
- Page 296 and 297:
Figure 2. Virtual Reality Experimen
- Page 298 and 299:
Total 46 Gender Male: 32 Female: 14
- Page 300 and 301:
num of answers 25 20 15 10 others c
- Page 302 and 303:
part under investigation metallogra
- Page 304 and 305:
3.1. Hyperbolic filter Among differ
- Page 306 and 307:
pores shorter than a user fixed len
- Page 308 and 309:
customers are serviced exactly once
- Page 310 and 311:
problems. The interested reader is
- Page 312 and 313:
Problem Dethloff's Best Avg Soln Be
- Page 314 and 315:
[3] D.O. Casco, B.L. Golden, E.A. W
- Page 316 and 317:
work the software was tested on a
- Page 318 and 319:
v RT v P,1 Figure 2. Right-turn man
- Page 320 and 321:
where N is the number of the counte
- Page 322 and 323:
ANALYSIS ON THE MECHANISM OF CONGES
- Page 324 and 325:
3. Data Observation and Processing
- Page 326 and 327:
of the Moriguchi Line is a little s
- Page 328 and 329:
Heavy traffic volume Trigger of the
- Page 330 and 331:
ON THE CONVERGENCE OF WEIGHTING MET
- Page 332 and 333:
Ratio weighting and weighting with
- Page 334 and 335:
4.2. Hypothesis 2 HP2 is also suppo
- Page 336 and 337:
ANALYSIS OF THE PUBLIC TRANSPORT SU
- Page 338 and 339:
therefore better quality is receive
- Page 340 and 341:
Fig. 1 - Distribution of the Global
- Page 342 and 343:
chain. Then, the intermodal termina
- Page 344 and 345:
B. Processes The considered contain
- Page 346 and 347:
Figure 2 Simulation model 314
- Page 348 and 349:
[10] C. Degano, A. Di Febbraro, “
- Page 350 and 351:
and the crew duties are defined as
- Page 352 and 353:
espectively, the predicted and the
- Page 354 and 355:
WILLINGNESS TO PAY FOR ACCESS TIME
- Page 356 and 357:
Final Destination Located in Zone 1
- Page 358 and 359:
destination several discrete choice
- Page 360 and 361:
THE UNCERTAINTY OF DELAYS AT OPTIMA
- Page 362 and 363:
q ( t) = Pr( i = j+ a −d ) ∀ j
- Page 364 and 365:
The probability of having an extens
- Page 366 and 367:
TWO LANE HIGHWAYS - A MICROSCOPIC T
- Page 368 and 369:
acc un( t) un( t) un ( t + T ) = un
- Page 370 and 371:
speed (km/h) 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 20
- Page 372 and 373:
TIME WINDOWS FOR SCHEDULED TRIPS IN
- Page 374 and 375:
Station 1 1 2 a b (±2 minutes) c a
- Page 376 and 377:
Instance Time window: 1 2 3 4 5 6 S
- Page 378 and 379:
[4] ILOG. ILOG CPLEX v9.0 User’s
- Page 380 and 381:
We present here an exact optimizati
- Page 382 and 383:
To make bounding effective the algo
- Page 384 and 385:
A DYNAMIC ACTIVITY BASED TRAVEL DEM
- Page 386 and 387:
parameter vector, and a hill-climbi
- Page 388 and 389:
[2] Bowman, J.L., and Ben-Akiva. M.
- Page 390 and 391:
AN AGENT-BASED APPROACH TO COMBINED
- Page 392 and 393:
2.1. Environmental Model As mention
- Page 394 and 395:
mental maps. A history based heuris
- Page 396 and 397:
[5] M. Bierlaire and E. Frejinger.
- Page 398 and 399:
• to evaluate the approaches of t
- Page 400 and 401:
10 seconds. The road user has an in
- Page 402 and 403:
FOOT SWITCH (Closing) TRAIN t (s) W
- Page 404 and 405:
for the vehicles. This is done in s
- Page 406 and 407:
(IVCSP1): ∑ min d∈D ∑ ∑ yij
- Page 408 and 409:
Furthermore, we denote a set of res
- Page 410 and 411:
ON THE POTENTIAL OF SOCIAL-PSYCHOLO
- Page 412 and 413:
5. Results and discussions A prelim
- Page 414 and 415:
Individual contributions in Session
- Page 416 and 417:
exceeded then the agent relies on i
- Page 418 and 419:
Considerations have to be given to
- Page 420 and 421:
capacity changes for road or non-mo
- Page 422 and 423:
incorporated to this integration. T
- Page 424 and 425:
A CONTRIBUTION TO PREDICTING THE MO
- Page 426 and 427:
( ) ( ) ( ) PM PV X ω V = α V (h,
- Page 428 and 429:
(up to 2 decimal points), while the
- Page 430 and 431:
There are only a few studies focuse
- Page 432 and 433:
ii) changes in number and severity
- Page 434 and 435:
It can be said that when the demand
- Page 436 and 437:
[3] N. Cavill, A. Davis. Cycling an
- Page 438 and 439:
The following objections for gap-ac
- Page 440 and 441:
As the third step, multiple regress
- Page 442 and 443:
[12] T. Aydemir, and S. Tanyel. Ço
- Page 444 and 445:
2. State of the art Nowadays, the i
- Page 446 and 447:
The methodology is based firstly on
- Page 448 and 449:
The network is composed of access/e
- Page 450 and 451:
The efficiency of the computational
- Page 452 and 453:
causing delay to the vehicles behin
- Page 454 and 455:
1,6 1,5 D_PCE 1,4 1,3 1,2 1,1 1 0 2
- Page 456 and 457:
A SEQUENTIAL MODEL BASED ON THRESHO
- Page 458 and 459:
(a) (b) Fig. 1 - Diagram of the pro
- Page 460 and 461:
probability density probability den
- Page 462 and 463:
− when the cost threshold is pass
- Page 464 and 465:
[11] S. Kurauchi, T. Morikawa. An e
- Page 466 and 467:
prediction approaches tackle this p
- Page 468 and 469:
implies that for aparticular depart
- Page 470 and 471:
5. Conclusions and discussion The r
- Page 472 and 473:
Again in [4], spillback congestion
- Page 474 and 475:
scale systems, leading to a very co
- Page 476 and 477:
This situation causes not only comp
- Page 478 and 479:
The “fail-to-access probability
- Page 480 and 481:
Figure 2. Underground network of Ce
- Page 482 and 483:
2005. Available from < http://www.r
- Page 484 and 485:
sovereignty - that is, that consume
- Page 486 and 487:
2.2. Public policy approaches to bo
- Page 488 and 489:
egistering and analyzing the speed
- Page 490 and 491:
ANALYSIS OF DEMAND FLUCTUATION ON U
- Page 492 and 493:
O is { s | ≤ s ≤ t} ≥ 0 for a
- Page 494 and 495:
longer distance increase at night.
- Page 496 and 497:
3.4. Demand variation owing to comm
- Page 498 and 499:
BETTER UNDERSTANDING THE POTENTIAL
- Page 500 and 501:
them to use transit responding to t
- Page 502 and 503:
Eight factors can be defined throug
- Page 504 and 505:
egular commute, which includes ques
- Page 506 and 507:
Select References Kemp, M. A. (1973
- Page 508 and 509:
Consequently, others important rela
- Page 510 and 511:
The most general form to solve the
- Page 512 and 513:
max z od k − d z od k od k < ε I
- Page 514 and 515:
1 2 3 4 5 1 0 800 500 1000 300 2 80
- Page 516 and 517:
A part from the results obtained fo
- Page 518 and 519:
[2] Cascetta E., Russo F. (1997). C
- Page 520 and 521:
2. Transportation system of Turkey
- Page 522 and 523:
5. The public survey To investigate
- Page 524 and 525:
6. Conclusions The traffic safety i
- Page 526 and 527:
TRANSPORT NETWORK DESIGN UNDER RISK
- Page 528 and 529:
2. Formulation A general transporta
- Page 530 and 531:
[11]). According to (9), if scenari
- Page 532 and 533:
Value of Time: ψ = €0.2/min Impr
- Page 534 and 535:
References [1] J. Abadie and J. Car
- Page 536 and 537:
(SITLUM). This integrates the state
- Page 538 and 539:
2.1.1. Sub-models within DELTA The
- Page 540 and 541:
Figure 3 SITLUM study area 4.1. Dat
- Page 542 and 543:
Figures 5 and 6 show summary indica
- Page 544 and 545:
The potential geographic area for d
- Page 546 and 547:
60,0% 50,0% 52,1% 40,0% Users 30,0%
- Page 548 and 549:
known or hub-based flag company des
- Page 550 and 551:
A STUDY ON THE EFFECT OF REMOVAL OF
- Page 552 and 553:
community. The major function of tr
- Page 554 and 555:
Table 2 The difference of the numbe
- Page 556 and 557:
#" ! $ #'.60% - # $ " "
- Page 558 and 559:
## ∆ *4,!*6,*1,! " $#*&
- Page 560 and 561:
#$%&% & ! " ( $"" ##"" "#" "%
- Page 562 and 563:
! "# $ %# ! &!'! (!
- Page 564 and 565:
A B) * $$$ ! ! ) !
- Page 566 and 567:
-.10 J I & > =) D! H>==A;B&
- Page 568 and 569:
important to measure the conflict i
- Page 570 and 571:
3.3. PTTC indicator In a fixed coor
- Page 572 and 573:
(sec) 10 (km/h) (cm) 25 700 600 CON
- Page 574 and 575:
− − − framework and on the ot
- Page 576 and 577:
4. The transferability study This s
- Page 578 and 579:
stochastic aspects and it derives a
- Page 580 and 581:
δ(x) = 0 if x ≠ 0, δ(0) = ∞,
- Page 582 and 583:
queue probability x=0.833 0.14 prob
- Page 584 and 585:
and will be briefly reminded here i
- Page 586 and 587:
The integration of this equation in
- Page 588 and 589:
A COMPARISON OF MACROSCOPIC AND MIC
- Page 590 and 591:
points and simulate design scenario
- Page 592 and 593:
priorities and behavior, and events
- Page 594 and 595:
The analysis of a transportation sy
- Page 596 and 597:
transported each day. The statistic
- Page 598 and 599:
- ability to provide output data wh
- Page 600 and 601:
Currently, this aspect of safety re
- Page 602 and 603:
INTERSECTION MODELLING BASED ON THE
- Page 604 and 605:
In the heterogeneous Riemann proble
- Page 606 and 607:
Max ∑ ∑ 0 ≤ q Φ 0 ≤ q ≤
- Page 608 and 609:
4.1. Diverge node model results The
- Page 610 and 611:
Figures 6 and 7 represent the densi
- Page 612 and 613:
References [1] Lebacque J.P, Khoshy
- Page 614 and 615:
(safety index combined with a traff
- Page 616 and 617:
As regards cluster 3 (representing
- Page 618 and 619:
100 acc 13956 90 80 Occ(%), Risk In
- Page 620 and 621:
2. The model 2.1. Introduction The
- Page 622 and 623:
In other terms, the local first ord
- Page 624 and 625:
Figure 4 3. Existence and quality o
- Page 626 and 627:
A better way to approximate any pop
- Page 628 and 629:
• Calibrating motorists behaviour
- Page 630 and 631:
Let us further consider a truck dri
- Page 632 and 633:
A SHOCKWAVE-BASED METHODODLOGY FOR
- Page 634 and 635:
the problem under consideration is
- Page 636 and 637:
Solution Approach For the commuting
- Page 638 and 639:
56 52 48 44 40 36 32 28 24 20 16 12
- Page 640 and 641:
PIACON: ROBUST VEHICLE TRAJECTORY B
- Page 642 and 643:
TDS =(P, A, B): where P- denotes se
- Page 644 and 645:
3. PIACON vehicle trajectories base
- Page 646 and 647:
Table 2 .PIACON artery synchronizat
- Page 648 and 649:
MODELING ACTIVITY CHOICE DISTRIBUTI
- Page 650 and 651:
St. d d e od Min o ∑∫ fe( s, Ce
- Page 652 and 653:
1. initialize all links with small
- Page 654 and 655:
Figure 2. Evolution of quantity of
- Page 656 and 657:
ON THE FRACTAL GEOMETRY OF THE ROAD
- Page 658 and 659:
The transport network can be descri
- Page 660 and 661:
Figure 2. This network can be descr
- Page 662 and 663:
STOCHASTIC DELAY AT TRAFFIC SIGNALS
- Page 664 and 665:
The cumulative count curves method
- Page 666 and 667:
3.3. Intensity effect We compared d
- Page 668 and 669:
the average delay with the step dem
- Page 670 and 671:
References [1] R. Akçelik. HCM 200
- Page 672 and 673:
the other trips were done in SOV [1
- Page 674 and 675:
i. Hpath (i,k) is a feasible path i
- Page 676 and 677:
Objective function (LCPP): = ⎛
- Page 678 and 679:
Figure 3 - Application of the progr
- Page 680 and 681:
exceeding the maximum density. Ther
- Page 682 and 683:
Here, n i p( t) 0 j, = when j>t; s,
- Page 684 and 685:
The nodes rules component of the pr
- Page 686 and 687:
3. Validity of proposed DNL model T
- Page 688 and 689:
Under the set node configuration it
- Page 690 and 691:
A DYNAMIC NODE MODEL WITH A QUADRAT
- Page 692 and 693:
control variables such as link trav
- Page 694 and 695:
♣ FW k : The set of links that ar
- Page 696 and 697:
! ir á = 1 r" FW k (24) When the c
- Page 698 and 699:
[3] V. Astarita. A continuous time
- Page 700 and 701:
This paper focuses on the optimizat
- Page 702 and 703:
to improve the operational efficien
- Page 704 and 705:
THE 2-PERIOD PROBABILISTIC TSP: A M
- Page 706 and 707:
N variables is solved, where N is t
- Page 708 and 709:
approximating future costs using th
- Page 710 and 711:
develop a MILP formulation and a br
- Page 712 and 713:
one arc from each alternative pair,
- Page 714 and 715:
URBAN TRANSPORT: EUROPEAN EXPERIENC
- Page 716 and 717:
Well-developed and efficient public
- Page 718 and 719:
In addition to these public systems
- Page 720 and 721:
AUCTION BASED CONGESTION PRICING: T
- Page 722 and 723:
3. Auction based congestion pricing
- Page 724 and 725:
issues, and potential benefits of t
- Page 726 and 727:
DEALING WITH UNCERTAINTIES IN TRANS
- Page 728 and 729:
Figure 1 The policy analysis framew
- Page 730 and 731:
uncertainties in the output of demo
- Page 732 and 733:
• Pattern of system performance:
- Page 734 and 735:
PROVIDING PUBLIC PARTICIPATION IN T
- Page 736 and 737:
have 14, 13 and 6 criterions respec
- Page 738 and 739:
6 Results of iterations Alternative
- Page 740 and 741:
MINIMUM REDEPLOYMENT MODEL FOR DYNA
- Page 742 and 743:
demand and unit busy probabilities,
- Page 744 and 745:
3. The algorithm There have been va
- Page 746 and 747:
DYNAMIC SET PARTITIONING APPLICATIO
- Page 748 and 749:
4. The dynamic solution approach In
- Page 750 and 751:
In Table 2 our in progress numerica
- Page 752 and 753:
HANDLING DEMAND AND NETWORK CAPACIT
- Page 754 and 755:
evacuation study may change the fin
- Page 756 and 757:
3.1.1. P-Level Efficient Points Def
- Page 758 and 759:
(Cell # 7 and #8) in the network ar
- Page 760 and 761:
VALIDATION AND COMPARISON OF CHOICE
- Page 762 and 763:
From the above, results of calibrat
- Page 764 and 765:
50.0% 45.0% 40.0% ASA BUS = 1,770 3
- Page 766 and 767:
2. Taxi planning model TP is modell
- Page 768 and 769:
Where the “Node flow conservation
- Page 770 and 771:
k Where θ is the step size in this
- Page 772 and 773:
ALLOCATION PLANNING OF HANDLING DEV
- Page 774 and 775:
and handling devices transfer times
- Page 776 and 777:
3. Solution approach In order to so
- Page 778 and 779:
From the previous calculation, orde
- Page 780 and 781:
UNIVARIATE AND MULTIVARIATE ARIMA M
- Page 782 and 783:
the portmanteau test statistic can
- Page 784 and 785:
provides a value of 0,11, i.e. acce
- Page 786 and 787:
emaining months have the same numbe
- Page 788 and 789:
CROSSING TIME MICRO-ANALYSIS: DIFFE
- Page 790 and 791:
The main characteristic of a zone i
- Page 792 and 793:
LEGENDA PERCORSI DI CALCOLO IN FUNZ
- Page 794 and 795:
Fig. 7 - Tempo di attraversamento v
- Page 796 and 797:
SIMULATION AND VALIDATION OF PARKIN
- Page 798 and 799:
is based on fuzzy logic. In fuzzy l
- Page 800 and 801:
2.1.3. Models for parking off stree
- Page 802 and 803:
described as a S shape Wiebe functi
- Page 804 and 805:
The validation of searching models
- Page 806 and 807:
Next step will regard the calibrati
- Page 808 and 809:
COLLABORATIVE DEMAND AND SUPPLY NET
- Page 810 and 811:
area, and an accurate overview of m
- Page 812 and 813:
6. Conclusions Current scenario in
- Page 814 and 815:
[20] Villa, A. Emerging trends in l
- Page 816 and 817:
L eq is widely used since it allows
- Page 818 and 819:
[4] Beruard B. (1986) Environmental
- Page 820 and 821:
MODELLING URBAN TRAFFIC NETWORKS BY
- Page 822 and 823:
uffer entity implementing an event-
- Page 824 and 825:
3. Conclusion and further research
- Page 826 and 827:
ased on such models. Various formul
- Page 828 and 829:
Theory is said to be amenable to th
- Page 830 and 831:
possibility distribution should be
- Page 832 and 833:
What we see above is the possibilis
- Page 834 and 835:
Williams, H. C. W. L. On the format
- Page 836 and 837:
PETRI NET MODEL OF TRANSHIPMENT ACT
- Page 838 and 839:
Activities in the yard area and the
- Page 840 and 841:
conditions consequent to the event,
- Page 842 and 843: normal supervision of loading/unloa
- Page 844 and 845: When loading containers, Ch2 verifi
- Page 846 and 847: [10] G. Crainic, M. Gendreau and P.
- Page 848 and 849: transportation network instead of c
- Page 850 and 851: A crucial role in the evaluation of
- Page 852 and 853: Tv P Tv I Tr P Tc P Tr I Tc I (1) (
- Page 854 and 855: References [1] D. Ambrosino, A. Sci
- Page 856 and 857: private transportation on paths dev
- Page 858 and 859: 2. Research Program The work progra
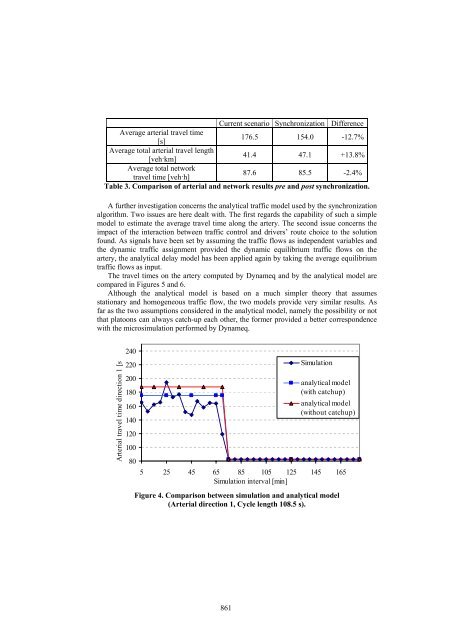
- Page 860 and 861: Starting from the availability of t
- Page 862 and 863: INFOMOBILITY AND LOGISTICS ON URBAN
- Page 864 and 865: - New algorithms for the optimal ma
- Page 866 and 867: of Milan), ATENA (Environment, Traf
- Page 868 and 869: flows. These are typically binary i
- Page 870 and 871: References [1] D. Ambrosino, A. Sci
- Page 872 and 873: [29] P. Dell'Olmo, and P.B. Mirchan
- Page 874 and 875: AN INTEGRATED INFORMATION AND MANAG
- Page 876 and 877: Transversally at the above-stated r
- Page 878 and 879: are generally “soft” measures t
- Page 880 and 881: At the moment, the CP software mana
- Page 882 and 883: L=25 km T=30’ C=4.5 € L=31 km T
- Page 884 and 885: The object of the research is to de
- Page 886 and 887: 2.3. Microscopic simulation of traf
- Page 888 and 889: 3.1. Pre-timed synchronization Sign
- Page 890 and 891: 120 100 Delay [s/veh] 80 60 40 20 0
- Page 894 and 895: Arterial travel time direction 2 [s
- Page 896 and 897: [15] Hunt P.B., Robertson D.I., Bre
- Page 898 and 899: That is, transit does not seem to b
- Page 900 and 901: The speed computed on the whole doo
- Page 902 and 903: RAIL STOP RAIL STOP Low density Hig
- Page 904 and 905: step requires not only the definiti
- Page 906 and 907: In Polish conditions Park and Ride
- Page 908 and 909: linguistic variable [4]. Values of
- Page 910 and 911: 4.1. Section off P&R users among pr
- Page 912 and 913: Fig.4 Results of FIS - share of P&R
- Page 914 and 915: Number of potential P&R users: Volu
- Page 916 and 917: ITS FRAMEWORK ARCHITECTURE IN A MUL
- Page 918 and 919: made of several functional data flo
- Page 920 and 921: Functional Areas Acronyms 1 Provide
- Page 922 and 923: TOWARDS MOBILE SEMANTIC GRID FOR IN
- Page 924 and 925: esources and services become machin
- Page 926 and 927: dissemination as well as a semantic