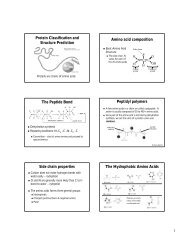
MAINCHAIN PART OF AMINO ACIDS
MAINCHAIN PART OF AMINO ACIDS
MAINCHAIN PART OF AMINO ACIDS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
What’s coming up next………no need to scribble this down!<br />
•Six hydrophilic (polar) sidechains. All possess =O, O-H<br />
or N-H groups that form hydrogen bonds with water<br />
molecules H 2 O. Often found in active sites of proteins.<br />
•Two acidic (polar) sidechains. These possess carboxyl<br />
groups COO - with a negative charge at physiological pH.<br />
Sidechain pK 3.9 (aspartate) and 4.3 (glutamate). Many<br />
roles (eg: active sites, salt bridges).<br />
•Three basic (polar) sidechains. These possess N-H<br />
groups, of which lysine and arginine are protonated at<br />
physiological pH (pK 10.5, 12.5), while histidine is a<br />
physiological buffer (pK 6.0).<br />
•Nine hydrophobic (nonpolar) sidechains. All<br />
predominantly possess C-H bonds that have little<br />
interaction with water molecules. Tendency to be found<br />
buried in core of water-soluble proteins.<br />
Hydrogen bonds with water.<br />
Usually found at protein surfaces.<br />
OH<br />
CH 2<br />
αCH<br />
αCH<br />
+<br />
NH 3 COO - +<br />
NH 3 COO -<br />
Six hydrophilic amino acid sidechains<br />
CH 3<br />
CH<br />
OH<br />
OH<br />
NH 2<br />
CO<br />
CH 2<br />
CH 2<br />
αCH<br />
αCH<br />
+<br />
NH 3 COO - +<br />
NH 3 COO -<br />
NH 2<br />
CO<br />
CH 2<br />
CH 2<br />
αCH<br />
+<br />
NH 3 COO -<br />
SH<br />
CH 2<br />
αCH<br />
+<br />
NH 3 COO -<br />
Serine Threonine Tyrosine Asparagine Glutamine Cysteine<br />
Ser, S Thr, T Tyr, Y Asn, N Gln, Q Cys, C<br />
Hydrogen bonds with water.<br />
Contain ionisable groups<br />
Two acidic amino acids<br />
NH 3<br />
+<br />
COO -<br />
CH 2<br />
αCH<br />
Aspartate<br />
Asp, D<br />
COO -<br />
NH 3<br />
+<br />
COO -<br />
CH 2<br />
CH 2<br />
αCH<br />
COO -<br />
Glutamate<br />
Glu, E<br />
NH 3<br />
+<br />
αCH<br />
Three basic amino acids<br />
NH 3<br />
+<br />
CH 2<br />
CH 2<br />
CH 2<br />
CH 2<br />
COO -<br />
NH 2 NH 2<br />
+<br />
NH 3<br />
+<br />
C<br />
NH<br />
CH 2<br />
CH 2<br />
CH 2<br />
αCH<br />
COO -<br />
NH<br />
CH<br />
NH 3<br />
+<br />
C<br />
CH 2<br />
αCH<br />
CH<br />
NH +<br />
COO -<br />
Lysine Arginine Histidine<br />
Lys, K Arg, R His, H<br />
Nine hydrophobic amino acid sidechains<br />
No hydrogen bonds<br />
with water<br />
NH 3<br />
+<br />
H<br />
αCH<br />
CH 3<br />
S<br />
CH 2<br />
CH 2<br />
αCH<br />
+<br />
NH 3<br />
COO -<br />
COO -<br />
NH 3<br />
+<br />
CH 3<br />
αCH<br />
CH 2<br />
COO -<br />
αCH<br />
+<br />
NH 3 COO -<br />
CH 3 CH 3<br />
CH<br />
CH<br />
CH<br />
CH 3<br />
αCH<br />
+<br />
NH 3<br />
CH 3<br />
COO -<br />
2<br />
αCH<br />
+<br />
NH 3 COO -<br />
NH<br />
CH 2<br />
αCH<br />
+<br />
NH 3 COO -<br />
CH 3<br />
CH 2 CH 3<br />
CH<br />
αCH<br />
+<br />
NH 3 COO -<br />
Glycine, Gly, G Alanine, Ala, A Valine, Val, V Leucine, Leu, L Isoleucine, Ile, I<br />
Methionine, Met, M Phenylalanine, Phe, F Tryptophan, Trp, W<br />
Buried in proteins.<br />
No hydrogen bonds<br />
with water<br />
CH 2 CH 2<br />
CH 2<br />
αCH<br />
+<br />
NH 2 COO -<br />
Proline, Pro, P<br />
(Note: imino acid)<br />
FUNCTIONAL DIVERSITY <strong>OF</strong> PROTEINS<br />
INTRODUCTION<br />
TO PROTEINS<br />
FIBROUS PROTEINS:<br />
Structural support Collagen (bones) Tensile strength<br />
Elastin (ligaments) Elastic strength<br />
Proteoglycans (bone) Elastic strength<br />
Keratin (hair, skin) External protection<br />
GLOBULAR PROTEINS:<br />
Enzymes Trypsin (stomach) Cleaves proteins<br />
Lysozyme (tears) Antibactericidal<br />
Transporters Haemoglobin (blood) Oxygen transport<br />
Transferrin (blood) Iron transport<br />
Protection<br />
Immunoglobulins (blood)Immune response<br />
Hormones Insulin (pancreas) Glucose regulator<br />
and DNA-binding, Storage, Toxins, Cell signalling, and many more<br />
HYBRID (MIXED) FIBROUS-GLOBULAR PROTEINS:<br />
Contractile Actin (muscle) Thin filament<br />
Myosin (muscle) Thick filament<br />
Protection Fibrinogen (blood) Clotting