MAINCHAIN PART OF AMINO ACIDS
MAINCHAIN PART OF AMINO ACIDS
MAINCHAIN PART OF AMINO ACIDS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
How do you join up α-helices and β-strands?<br />
The need for β-turn and loop structures<br />
β- turns and loops are the two<br />
conformational extremes that<br />
exist at the surface of globular<br />
proteins to link together the<br />
individual α-helices and β-strands<br />
in the protein core. They are<br />
hydrophilic.<br />
Features:<br />
(1) A β-turn involves a SHARP reversal in the direction of a<br />
polypeptide chain over just four amino acid residues.<br />
(2) β-turns are sterically demanding, so a Gly residue is often<br />
located in the middle of a β-turn.<br />
(3) CONTRAST β-turns with loop structures which are often<br />
found at protein surfaces with as many as 10-20 amino acid<br />
residues.<br />
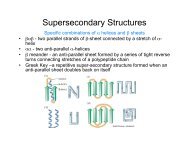
Supersecondary structures<br />
(“supersecondary” refers to all the secondary structures inside the structure)<br />
The number of ways in which α-helices and β-strands can be combined<br />
to form a protein is limited. So a number of common “folds” occur.<br />
There are three major classes of protein structures:<br />
1. All α-helix proteins eg: “globin fold” of myoglobin and haemoglobin<br />
2. All β-sheet proteins eg: “immunoglobulin fold” of antibodies<br />
3. Mixed α-helix / β-sheet proteins eg: “TIM fold” with a closed β-sheet<br />
barrel buried in the core and α-helices flanking this on the surface - or<br />
the other “fold” variant based on an open twisted β-sheet buried in the<br />
core with α-helices above and below it.<br />
Globin Immunoglobulin Open twisted α/β TIM barrel<br />
CONCLUSIONS<br />
You have now met the 20 amino acids,<br />
and seen how proteins are folded up.<br />
(1) The 20 amino acids possess very different<br />
chemical and physical properties.<br />
(2) Proteins fold up using α-helices and β-sheets.<br />
It is now down to you to read up<br />
this topic in your textbook, and do the exercises.<br />
Based on this lecture and the next, two Special<br />
Study Modules will be offered on “Structure and<br />
Function of Medically Important Proteins in<br />
Disease” which is run jointly with a clinician.