Elastic Registration of 3D Deformable Objects
Elastic Registration of 3D Deformable Objects
Elastic Registration of 3D Deformable Objects
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Delta errors (%)<br />
Delta errors (%)<br />
Delta errors (%)<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
Proposed<br />
GMMREG 2.5<br />
Proposed<br />
GMMREG 2.5<br />
Proposed<br />
GMMREG 2.5<br />
20 40 60 80 100<br />
15%<br />
20 40 60 80 100<br />
22%<br />
20 40 60 80 100<br />
30%<br />
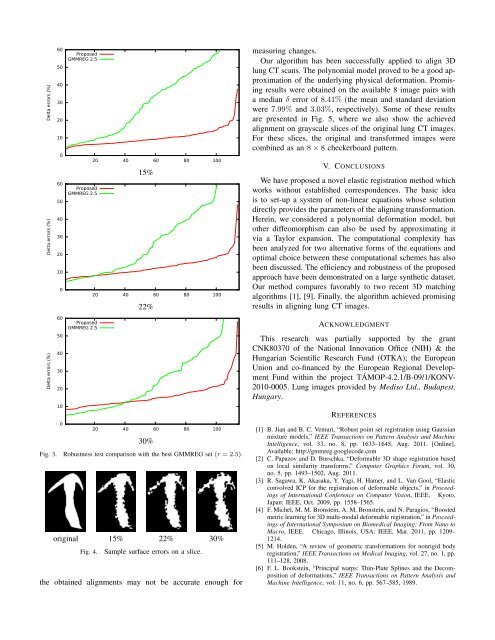
Fig. 3. Robustness test comparison with the best GMMREG set (r = 2.5).<br />
original 15% 22% 30%<br />
Fig. 4.<br />
Sample surface errors on a slice.<br />
the obtained alignments may not be accurate enough for<br />
measuring changes.<br />
Our algorithm has been successfully applied to align <strong>3D</strong><br />
lung CT scans. The polynomial model proved to be a good approximation<br />
<strong>of</strong> the underlying physical deformation. Promising<br />
results were obtained on the available 8 image pairs with<br />
a median δ error <strong>of</strong> 8.41% (the mean and standard deviation<br />
were 7.99% and 3.03%, respectively). Some <strong>of</strong> these results<br />
are presented in Fig. 5, where we also show the achieved<br />
alignment on grayscale slices <strong>of</strong> the original lung CT images.<br />
For these slices, the original and transformed images were<br />
combined as an 8 × 8 checkerboard pattern.<br />
V. CONCLUSIONS<br />
We have proposed a novel elastic registration method which<br />
works without established correspondences. The basic idea<br />
is to set-up a system <strong>of</strong> non-linear equations whose solution<br />
directly provides the parameters <strong>of</strong> the aligning transformation.<br />
Herein, we considered a polynomial deformation model, but<br />
other diffeomorphism can also be used by approximating it<br />
via a Taylor expansion. The computational complexity has<br />
been analyzed for two alternative forms <strong>of</strong> the equations and<br />
optimal choice between these computational schemes has also<br />
been discussed. The efficiency and robustness <strong>of</strong> the proposed<br />
approach have been demonstrated on a large synthetic dataset.<br />
Our method compares favorably to two recent <strong>3D</strong> matching<br />
algorithms [1], [9]. Finally, the algorithm achieved promising<br />
results in aligning lung CT images.<br />
ACKNOWLEDGMENT<br />
This research was partially supported by the grant<br />
CNK80370 <strong>of</strong> the National Innovation Office (NIH) & the<br />
Hungarian Scientific Research Fund (OTKA); the European<br />
Union and co-financed by the European Regional Development<br />
Fund within the project TÁMOP-4.2.1/B-09/1/KONV-<br />
2010-0005. Lung images provided by Mediso Ltd., Budapest,<br />
Hungary.<br />
REFERENCES<br />
[1] B. Jian and B. C. Vemuri, “Robust point set registration using Gaussian<br />
mixture models,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine<br />
Intelligence, vol. 33, no. 8, pp. 1633–1645, Aug. 2011. [Online].<br />
Available: http://gmmreg.googlecode.com<br />
[2] C. Papazov and D. Burschka, “<strong>Deformable</strong> <strong>3D</strong> shape registration based<br />
on local similarity transforms,” Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 30,<br />
no. 5, pp. 1493–1502, Aug. 2011.<br />
[3] R. Sagawa, K. Akasaka, Y. Yagi, H. Hamer, and L. Van Gool, “<strong>Elastic</strong><br />
convolved ICP for the registration <strong>of</strong> deformable objects,” in Proceedings<br />
<strong>of</strong> International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE. Kyoto,<br />
Japan: IEEE, Oct. 2009, pp. 1558–1565.<br />
[4] F. Michel, M. M. Bronstein, A. M. Bronstein, and N. Paragios, “Boosted<br />
metric learning for <strong>3D</strong> multi-modal deformable registration,” in Proceedings<br />
<strong>of</strong> International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to<br />
Macro, IEEE. Chicago, Illinois, USA: IEEE, Mar. 2011, pp. 1209–<br />
1214.<br />
[5] M. Holden, “A review <strong>of</strong> geometric transformations for nonrigid body<br />
registration,” IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 27, no. 1, pp.<br />
111–128, 2008.<br />
[6] F. L. Bookstein, “Principal warps: Thin-Plate Splines and the Decomposition<br />
<strong>of</strong> deformations,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and<br />
Machine Intelligence, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 567–585, 1989.