Classes of Biomolecules
Classes of Biomolecules
Classes of Biomolecules
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
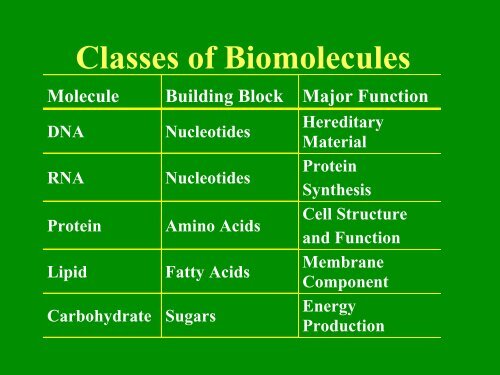
<strong>Classes</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Biomolecules</strong><br />
Molecule Building Block Major Function<br />
DNA<br />
RNA<br />
Protein<br />
Lipid<br />
Carbohydrate<br />
Nucleotides<br />
Nucleotides<br />
Amino Acids<br />
Fatty Acids<br />
Sugars<br />
Hereditary<br />
Material<br />
Protein<br />
Synthesis<br />
Cell Structure<br />
and Function<br />
Membrane<br />
Component<br />
Energy<br />
Production
The Central Dogma<br />
replication<br />
transcription processing translation<br />
• cells can make exact copies <strong>of</strong> DNA<br />
• DNA encodes all <strong>of</strong> the information necessary<br />
for cellular functions<br />
• RNA is made from a DNA template and<br />
functions in protein synthesis<br />
• proteins are translated from messenger RNA<br />
and carry out cellular functions
Lipids and Membranes<br />
The amphiphilic nature <strong>of</strong> lipids<br />
leads to the formation a bilayer.<br />
Proteins in the bilayer<br />
will provide selective<br />
permeability.
Special Features <strong>of</strong> Some<br />
Protozoan Plasma Membranes<br />
• surface coat<br />
– thick protein layer on outer surface<br />
• glycocalyx<br />
– carbohydrate layer on outer surface<br />
• protective walls<br />
– especially cyst wall<br />
• pellicle<br />
– triple membrane layer
Eukaryote vs Prokaryote<br />
Eukaryotic cells have<br />
membrane-bound<br />
compartments with<br />
specialized functions.
Prokaryotes<br />
• 1-10 µm<br />
• cellular functions<br />
in cytoplasm<br />
10X linear = 100X area = 1000X volume<br />
Eukaryotes<br />
• 10-100 µm<br />
• DNA in membrane<br />
bound nucleus<br />
• cytoskeleton<br />
• cytoplasmic organelles
Protozoan Nuclei<br />
• eukaryotes defined by staining nucleus<br />
• biological stains differentially bind DNA,<br />
RNA, protein, etc
Nucleus<br />
Lysosome<br />
ER<br />
Plasma<br />
Membrane<br />
Mitochondria<br />
Golgi
Light Microscopy Electron microscopy<br />
• image form by absorption<br />
and scattering <strong>of</strong> light<br />
• limit <strong>of</strong> resolution (~ 0.5 µm)<br />
• determined by the<br />
wavelength<br />
• based on absorption and<br />
scattering <strong>of</strong> electrons<br />
• resolutions <strong>of</strong> 2 nm (10 -9 ) or<br />
greater<br />
• wavelength = 1/velocity<br />
Sample Preparation<br />
• none, or ...<br />
• (±) fixation (preserve)<br />
• (±) section tissues<br />
• (±) stain with dyes<br />
Sample Preparation<br />
• fixation necessary<br />
• ultra-thin sections<br />
• stain with heavy metals
Microtome to Section Samples<br />
• thick samples need to be<br />
cut into thin sections