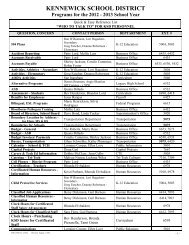
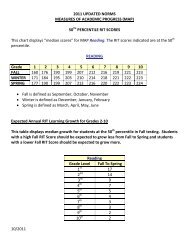
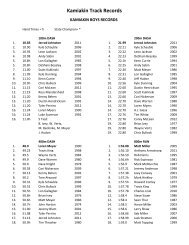
Honors Physics Chapter 17 Review 1. As a particle moves 5 m ...
Honors Physics Chapter 17 Review 1. As a particle moves 5 m ...
Honors Physics Chapter 17 Review 1. As a particle moves 5 m ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Honors</strong> <strong>Physics</strong> <strong>Chapter</strong> <strong>17</strong> <strong>Review</strong><br />
<strong>1.</strong> <strong>As</strong> a <strong>particle</strong> <strong>moves</strong> 5 m along an electric field of strength 100 N/C, its electrical<br />
potential energy decreases by 4x10 -16 J.<br />
a. What is the <strong>particle</strong>’s charge? (Answer: 8x10 -19 C)<br />
b. What is the potential difference between the initial and final locations of the<br />
<strong>particle</strong>? (Answer: -500 V)<br />
2. An electron is released from rest in a uniform electric field with a magnitude of<br />
6x10 4 V/m. The electron is displaced 0.75 m as a result.<br />
a. Find the potential difference between the electron’s initial and final positions.<br />
(Answer: -4.5x10 4 V)<br />
b. Find the change in electrical potential energy of the electron as a result of this<br />
displacement.<br />
(Answer: 7.2x10 -15 J)<br />
3. A 2 µF capacitor is connected to a 6 V battery.<br />
a. What is the charge on each place of the capacitor? (Answer: <strong>1.</strong>2x10 -5 C)<br />
b. If this same capacitor is connected to a 3 V battery, how much electrical potential<br />
energy is stored? (Answer: 9x10 -6 J)<br />
4. A parallel-place capacitor has a charge of 6 µC when charged by a potential<br />
difference of <strong>1.</strong>5 V.<br />
a. Find its capacitance. (Answer: 4x10 -6 F)<br />
b. How much electrical potential energy is stored when this capacitor is connected to<br />
a 6 V battery? (Answer: 7.2x10 -5 J)<br />
5. A capacitor has a capacitance of 4 pF.<br />
a. What potential difference would be required to store 12 pC? (Answer: 3 V)<br />
b. How much charge is stored when the potential difference is 12V? (4.8 x10 -11 C)<br />
6. You are asked to design a parallel-plate capacitor having a capacitance of 2 F and a<br />
plate separation of 1 mm. Calculate the required surface area of each plate.<br />
(Answer: 2.26x10 8 m 2 )<br />
PE<br />
PE<br />
V<br />
q<br />
V Ed<br />
I<br />
R<br />
C<br />
C<br />
PE<br />
PE<br />
PE<br />
P<br />
P<br />
charge<br />
k<br />
0<br />
Power<br />
Cost<br />
Q<br />
t<br />
V<br />
I<br />
Q<br />
V<br />
A<br />
0<br />
d<br />
1<br />
Q V<br />
2<br />
1<br />
C V<br />
2<br />
2<br />
1 Q<br />
2 C<br />
8.<br />
85x10<br />
I<br />
I<br />
2<br />
V<br />
P<br />
R<br />
Energy<br />
10<br />
V<br />
R<br />
Energy(<br />
rate)<br />
3<br />
qEd<br />
2<br />
P<br />
electron<br />
t<br />
2<br />
12<br />
Energy<br />
time<br />
2<br />
C / N m<br />
<strong>1.</strong>6x10<br />
-2<br />
7. A parallel plate capacitor has an area of 4 cm 2 , and the plates are separated by c 10<br />
-3<br />
4 mm.<br />
m 10<br />
a. What is the capacitance? (Answer: 8.85x10 -13 F)<br />
6<br />
10<br />
b. How much charge does this capacitor store when connected to an 18 V battery?<br />
-9<br />
n 10<br />
(Answer: <strong>1.</strong>6x10 -11 C)<br />
12<br />
p 10<br />
8. If a metal wire carries a current of 80 mA, how long does it take for 4x10 20 electrons to pass a given crosssectional<br />
area of the wire? (Answer: 800 s)<br />
9. The compressor on an air conditioner draws 60 A when it starts up. If the start-up time is 4 s, how much<br />
charge passes a cross-sectional area of the circuit in this time? (Answer: 240 C)<br />
10. A net charge of 750 mC passes through the cross-sectional area of a wire in 25 seconds.<br />
a. What is the current in the wire? (Answer: 0.03 A)<br />
b. How many electrons pass the cross-sectional area in 3 minutes? (Answer: 3.375×10 19 electrons)<br />
19<br />
2<br />
C
1<strong>1.</strong> A color television draws 7 A of current when connected across a potential<br />
difference of 110V. What is the effective resistance of the television set?<br />
(Answer: 15.71 Ω)<br />
12. How much current is drawn by a stereo with a resistance of 25 Ω that is connected<br />
across a potential difference of 90 V? (Answer: 3.6 A)<br />
13. The current in a certain resistor is 8 A when it is connected to a potential difference<br />
of 130 V. What is the current in the same resistor if the operating potential is 120 V?<br />
(Answer: 7.38 A)<br />
14. The current in a heater is 65 A, and the resistance of the oven’s circuitry is 2 Ω.<br />
a. What is the potential difference across the wire? (Answer: 130 V)<br />
b. How much power does the heater dissipate? (Answer: 8,450 W)<br />
15. The operating potential difference of a light bulb is 90 V. The power rating of the<br />
bulb is 60 W.<br />
a. Find the bulb’s resistance. (Answer: 135 Ω)<br />
b. Find the current in the bulb. (Answer: 0.67 A)<br />
16 Calculate the cost of operating a 100 W light bulb continuously for a two weeks<br />
when electrical energy costs $0.07/kW·h. (Answer: $2.35)<br />
There will also be conceptual questions so you will need to review your notes and text.<br />
Things to know:<br />
Difference between electrical potential energy, electrical potential, and potential<br />
difference<br />
Charges gaining or losing potential energy as they move through an electric<br />
field (pg. 595)<br />
How a battery works and provides energy for charge movement (pg. 600)<br />
What capacitance is, how a capacitor stores energy, how a capacitor is made,<br />
what a dielectric is, what factors affect the amount of energy stored<br />
What electric current is, what 1 ampere is equivalent to, conventional current vs.<br />
movement of charge carriers, drift velocity vs. average speed between collisions,<br />
difference between ohmic and non-ohmic materials, factors that affect resistance<br />
Difference between batteries and generators<br />
Difference between direct and indirect current<br />
What power rating is and what is means<br />
PE<br />
I<br />
R<br />
C<br />
C<br />
PE<br />
PE<br />
PE<br />
P<br />
P<br />
charge<br />
k<br />
c<br />
m<br />
n<br />
p<br />
0<br />
Power<br />
Cost<br />
Q<br />
t<br />
V<br />
I<br />
Q<br />
V<br />
A<br />
0<br />
d<br />
1<br />
Q V<br />
2<br />
1<br />
C V<br />
2<br />
2<br />
1 Q<br />
2 C<br />
8.<br />
85x10<br />
I<br />
I<br />
2<br />
V<br />
P<br />
R<br />
Energy<br />
10<br />
10<br />
10<br />
10<br />
R<br />
3<br />
-2<br />
10<br />
10<br />
qEd<br />
PE<br />
V<br />
q<br />
V Ed<br />
V<br />
Energy(<br />
rate)<br />
-9<br />
2<br />
electron<br />
-3<br />
6<br />
12<br />
P<br />
t<br />
2<br />
12<br />
Energy<br />
time<br />
2<br />
C / N m<br />
<strong>1.</strong>6x10<br />
19<br />
2<br />
C