PDF (6M) - Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes - Instituto de ...
PDF (6M) - Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes - Instituto de ...
PDF (6M) - Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes - Instituto de ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
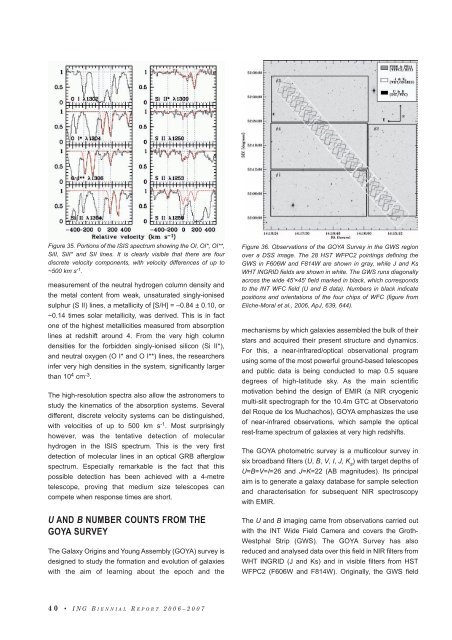
Figure 35. Portions <strong>of</strong> the ISIS spectrum showing the OI, OI*, OI**,<br />
SiII, SiII* and SII lines. It is clearly visible that there are four<br />
discrete velocity components, with velocity differences <strong>of</strong> up to<br />
~500 km s -1 .<br />
measurement <strong>of</strong> the neutral hydrogen column <strong>de</strong>nsity and<br />
the metal content from weak, unsaturated singly-ionised<br />
sulphur (S II) lines, a metallicity <strong>of</strong> [S/H] = –0.84 ± 0.10, or<br />
~0.14 times solar metallicity, was <strong>de</strong>rived. This is in fact<br />
one <strong>of</strong> the highest metallicities measured from absorption<br />
lines at redshift around 4. From the very high column<br />
<strong>de</strong>nsities for the forbid<strong>de</strong>n singly-ionised silicon (Si II*),<br />
and neutral oxygen (O I* and O I**) lines, the researchers<br />
infer very high <strong>de</strong>nsities in the system, significantly larger<br />
than 10 4 cm -3 .<br />
The high-resolution spectra also allow the astronomers to<br />
study the kinematics <strong>of</strong> the absorption systems. Several<br />
different, discrete velocity systems can be distinguished,<br />
with velocities <strong>of</strong> up to 500 km s -1 . Most surprisingly<br />
however, was the tentative <strong>de</strong>tection <strong>of</strong> molecular<br />
hydrogen in the ISIS spectrum. This is the very first<br />
<strong>de</strong>tection <strong>of</strong> molecular lines in an optical GRB afterglow<br />
spectrum. Especially remarkable is the fact that this<br />
possible <strong>de</strong>tection has been achieved with a 4-metre<br />
telescope, proving that medium size telescopes can<br />
compete when response times are short.<br />
U AND B NUMBER COUNTS FROM THE<br />
GOYA SURVEY<br />
The Galaxy Origins and Young Assembly (GOYA) survey is<br />
<strong>de</strong>signed to study the formation and evolution <strong>of</strong> galaxies<br />
with the aim <strong>of</strong> learning about the epoch and the<br />
Figure 36. Observations <strong>of</strong> the GOYA Survey in the GWS region<br />
over a DSS image. The 28 HST WFPC2 pointings <strong>de</strong>fining the<br />
GWS in F606W and F814W are shown in gray, while J and Ks<br />
WHT INGRID fields are shown in white. The GWS runs diagonally<br />
across the wi<strong>de</strong> 45'×45' field marked in black, which corresponds<br />
to the INT WFC field (U and B data). Numbers in black indicate<br />
positions and orientations <strong>of</strong> the four chips <strong>of</strong> WFC (figure from<br />
Eliche-Moral et al., 2006, ApJ, 639, 644).<br />
mechanisms by which galaxies assembled the bulk <strong>of</strong> their<br />
stars and acquired their present structure and dynamics.<br />
For this, a near-infrared/optical observational program<br />
using some <strong>of</strong> the most powerful ground-based telescopes<br />
and public data is being conducted to map 0.5 square<br />
<strong>de</strong>grees <strong>of</strong> high-latitu<strong>de</strong> sky. As the main scientific<br />
motivation behind the <strong>de</strong>sign <strong>of</strong> EMIR (a NIR cryogenic<br />
multi-slit spectrograph for the 10.4m GTC at Observatorio<br />
<strong>de</strong>l Roque <strong>de</strong> los Muchachos), GOYA emphasizes the use<br />
<strong>of</strong> near-infrared observations, which sample the optical<br />
rest-frame spectrum <strong>of</strong> galaxies at very high redshifts.<br />
The GOYA photometric survey is a multicolour survey in<br />
six broadband filters (U, B, V, I, J, K s<br />
) with target <strong>de</strong>pths <strong>of</strong><br />
U=B=V=I=26 and J=K=22 (AB magnitu<strong>de</strong>s). Its principal<br />
aim is to generate a galaxy database for sample selection<br />
and characterisation for subsequent NIR spectroscopy<br />
with EMIR.<br />
The U and B imaging came from observations carried out<br />
with the INT Wi<strong>de</strong> Field Camera and covers the Groth-<br />
Westphal Strip (GWS). The GOYA Survey has also<br />
reduced and analysed data over this field in NIR filters from<br />
WHT INGRID (J and Ks) and in visible filters from HST<br />
WFPC2 (F606W and F814W). Originally, the GWS field<br />
40 • ING BIENNIAL R EPORT 2006–2007