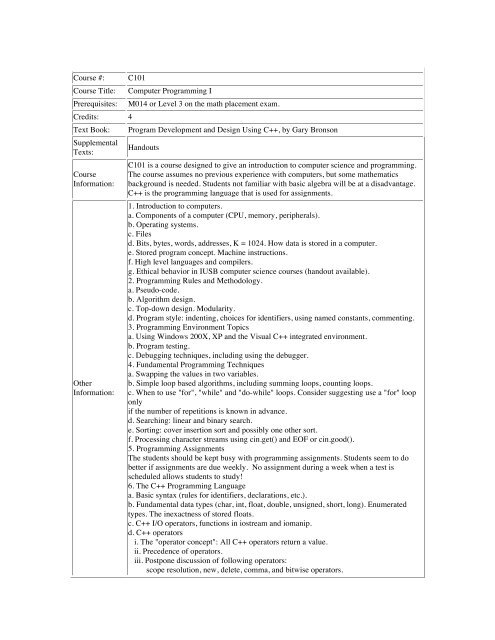
Course #: C101 Course Title: Computer Programming I ...
Course #: C101 Course Title: Computer Programming I ...
Course #: C101 Course Title: Computer Programming I ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Course</strong> #:<br />
<strong>Course</strong> <strong>Title</strong>:<br />
Prerequisites:<br />
Credits: 4<br />
Text Book:<br />
Supplemental<br />
Texts:<br />
<strong>Course</strong><br />
Information:<br />
Other<br />
Information:<br />
<strong>C101</strong><br />
<strong>Computer</strong> <strong>Programming</strong> I<br />
M014 or Level 3 on the math placement exam.<br />
Program Development and Design Using C++, by Gary Bronson<br />
Handouts<br />
<strong>C101</strong> is a course designed to give an introduction to computer science and programming.<br />
The course assumes no previous experience with computers, but some mathematics<br />
background is needed. Students not familiar with basic algebra will be at a disadvantage.<br />
C++ is the programming language that is used for assignments.<br />
1. Introduction to computers.<br />
a. Components of a computer (CPU, memory, peripherals).<br />
b. Operating systems.<br />
c. Files<br />
d. Bits, bytes, words, addresses, K = 1024. How data is stored in a computer.<br />
e. Stored program concept. Machine instructions.<br />
f. High level languages and compilers.<br />
g. Ethical behavior in IUSB computer science courses (handout available).<br />
2. <strong>Programming</strong> Rules and Methodology.<br />
a. Pseudo-code.<br />
b. Algorithm design.<br />
c. Top-down design. Modularity.<br />
d. Program style: indenting, choices for identifiers, using named constants, commenting.<br />
3. <strong>Programming</strong> Environment Topics<br />
a. Using Windows 200X, XP and the Visual C++ integrated environment.<br />
b. Program testing.<br />
c. Debugging techniques, including using the debugger.<br />
4. Fundamental <strong>Programming</strong> Techniques<br />
a. Swapping the values in two variables.<br />
b. Simple loop based algorithms, including summing loops, counting loops.<br />
c. When to use "for", "while" and "do-while" loops. Consider suggesting use a "for" loop<br />
only<br />
if the number of repetitions is known in advance.<br />
d. Searching: linear and binary search.<br />
e. Sorting: cover insertion sort and possibly one other sort.<br />
f. Processing character streams using cin.get() and EOF or cin.good().<br />
5. <strong>Programming</strong> Assignments<br />
The students should be kept busy with programming assignments. Students seem to do<br />
better if assignments are due weekly. No assignment during a week when a test is<br />
scheduled allows students to study!<br />
6. The C++ <strong>Programming</strong> Language<br />
a. Basic syntax (rules for identifiers, declarations, etc.).<br />
b. Fundamental data types (char, int, float, double, unsigned, short, long). Enumerated<br />
types. The inexactness of stored floats.<br />
c. C++ I/O operators, functions in iostream and iomanip.<br />
d. C++ operators<br />
i. The "operator concept": All C++ operators return a value.<br />
ii. Precedence of operators.<br />
iii. Postpone discussion of following operators:<br />
scope resolution, new, delete, comma, and bitwise operators.
e. Control flow statements (if, if-else, switch, break, while, do-while, for, continue).<br />
f. Functions and parameter passing; Value and reference parameters.<br />
g. Standard libraries: ctype, stdlib, string.h.<br />
h. Scope. Static and external (global) variables.<br />
i. Arrays: The relationship between pointers and arrays. "Strings".<br />
j. Preprocessor: #define and #include.