COMNET III CACI
COMNET III CACI
COMNET III CACI
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
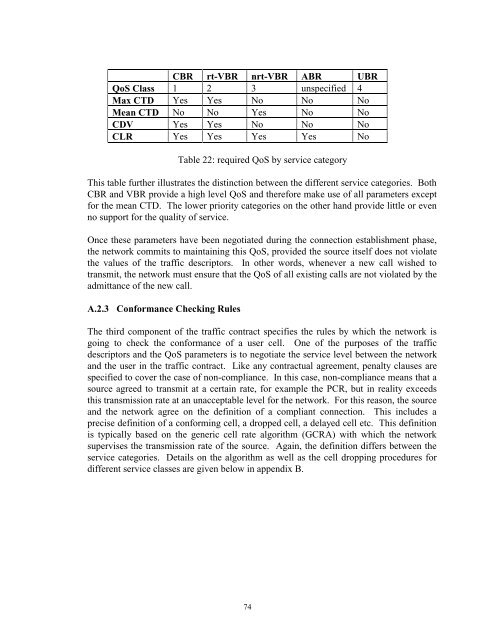
CBR rt-VBR nrt-VBR ABR UBR<br />
QoS Class 1 2 3 unspecified 4<br />
Max CTD Yes Yes No No No<br />
Mean CTD No No Yes No No<br />
CDV Yes Yes No No No<br />
CLR Yes Yes Yes Yes No<br />
Table 22: required QoS by service category<br />
This table further illustrates the distinction between the different service categories. Both<br />
CBR and VBR provide a high level QoS and therefore make use of all parameters except<br />
for the mean CTD. The lower priority categories on the other hand provide little or even<br />
no support for the quality of service.<br />
Once these parameters have been negotiated during the connection establishment phase,<br />
the network commits to maintaining this QoS, provided the source itself does not violate<br />
the values of the traffic descriptors. In other words, whenever a new call wished to<br />
transmit, the network must ensure that the QoS of all existing calls are not violated by the<br />
admittance of the new call.<br />
A.2.3<br />
Conformance Checking Rules<br />
The third component of the traffic contract specifies the rules by which the network is<br />
going to check the conformance of a user cell. One of the purposes of the traffic<br />
descriptors and the QoS parameters is to negotiate the service level between the network<br />
and the user in the traffic contract. Like any contractual agreement, penalty clauses are<br />
specified to cover the case of non-compliance. In this case, non-compliance means that a<br />
source agreed to transmit at a certain rate, for example the PCR, but in reality exceeds<br />
this transmission rate at an unacceptable level for the network. For this reason, the source<br />
and the network agree on the definition of a compliant connection. This includes a<br />
precise definition of a conforming cell, a dropped cell, a delayed cell etc. This definition<br />
is typically based on the generic cell rate algorithm (GCRA) with which the network<br />
supervises the transmission rate of the source. Again, the definition differs between the<br />
service categories. Details on the algorithm as well as the cell dropping procedures for<br />
different service classes are given below in appendix B.<br />
74