poisoning of raptors with organophosphorus and carbamate ...
poisoning of raptors with organophosphorus and carbamate ...
poisoning of raptors with organophosphorus and carbamate ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
28 MINEAU Eq7 AI.. VOL. 33, NO. 1<br />
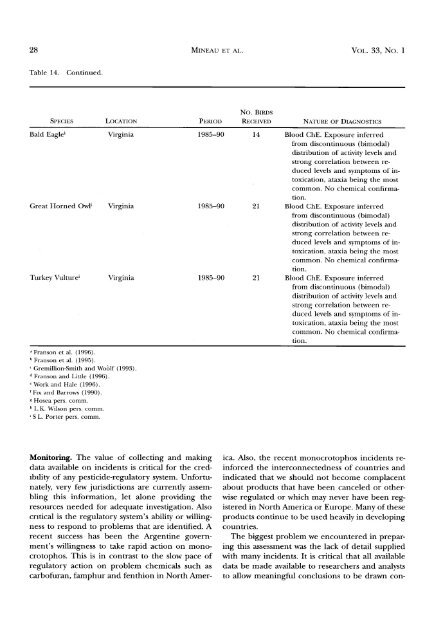
Table 14. Continued.<br />
SPECIES LOCATION PERIOD<br />
NO.<br />
BIRDS<br />
RECEIVED<br />
NATURE OF DIAGNOSTICS<br />
Bald Eagle'<br />
Great Horned Owl i<br />
Virginia<br />
Virginia<br />
1985-90<br />
1985-90<br />
14<br />
21<br />
Blood ChE. Exposure inferred<br />
from discontinuous (bimodal)<br />
distribution <strong>of</strong> activity levels <strong>and</strong><br />
strong correlation between reduced<br />
levels <strong>and</strong> symptoms <strong>of</strong> intoxication,<br />
ataxia being the most<br />
common. No chemical confirma-<br />
tion.<br />
Blood ChE. Exposure inferred<br />
from discontinuous (bimodal)<br />
distribution <strong>of</strong> activity levels <strong>and</strong><br />
strong correlation between reduced<br />
levels <strong>and</strong> symptoms <strong>of</strong> intoxication,<br />
ataxia being the most<br />
common. No chemical confirma-<br />
tion.<br />
Turkey Vulture'<br />
Virginia<br />
1985-90<br />
21<br />
Blood ChE. Exposure inferred<br />
from discontinuous (bimodal)<br />
distribution <strong>of</strong> activity levels <strong>and</strong><br />
strong correlation between reduced<br />
levels <strong>and</strong> symptoms <strong>of</strong> intoxication,<br />
ataxia being the most<br />
common. No chemical confirma-<br />
tion.<br />
Franson et al. (1996).<br />
Franson et al. (1995).<br />
Gremillion-Smith <strong>and</strong> Wo6lf (1993).<br />
Franson <strong>and</strong> Little (1996).<br />
Work <strong>and</strong> Hale (1996).<br />
F•x <strong>and</strong> Barrows (1990).<br />
Hosea pers. comm.<br />
L.K. Wilson pers. comm.<br />
S L. Porter pers. comm.<br />
Monitoring. The value <strong>of</strong> collecting <strong>and</strong> making<br />
data available on incidents is critical for the cred-<br />
•bfiity <strong>of</strong> any pesticide-regulatory system. Unfortunately,<br />
very few jurisdictions are currently assembling<br />
this information, let alone providing the<br />
resources needed for adequate investigation. Also<br />
critical is the regulatory system's ability or willingness<br />
to respond to problems that are identified. A<br />
recent success has been the Argentine government's<br />
willingness to take rapid action on monocrotophos.<br />
This is in contrast to the slow pace <strong>of</strong><br />
regulatory action on problem chemicals such as<br />
carb<strong>of</strong>uran, famphur <strong>and</strong> fenthion in North Amer-<br />
ica. Also, the recent monocrotophos incidents reinforced<br />
the interconnectedness <strong>of</strong> countries <strong>and</strong><br />
indicated that we should not become complacent<br />
about products that have been canceled or otherwise<br />
regulated or which may never have been registered<br />
in North America or Europe. Many <strong>of</strong> these<br />
products continue to be used heavily in developing<br />
countries.<br />
The biggest problem we encountered in preparing<br />
this assessment was the lack <strong>of</strong> detail supplied<br />
<strong>with</strong> many incidents. It is critical that all available<br />
data be made available to researchers <strong>and</strong> analysts<br />
to allow meaningful conclusions to be drawn con-