the influence of linguistic factors on the expression of futurity
the influence of linguistic factors on the expression of futurity
the influence of linguistic factors on the expression of futurity
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
148<br />
NICHOLAS S. ROBERTS<br />
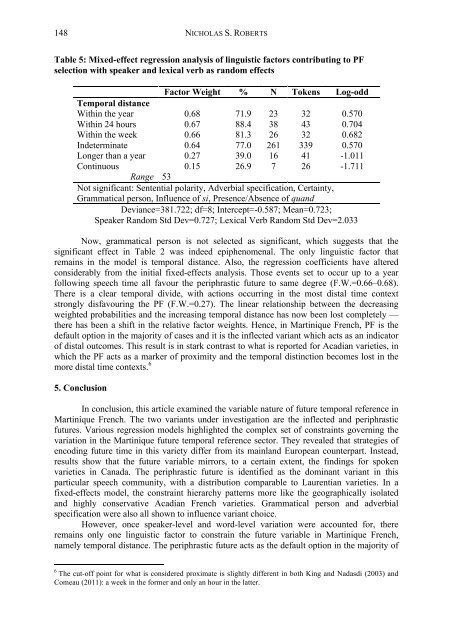
Table 5: Mixed-effect regressi<strong>on</strong> analysis <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>linguistic</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>factors</str<strong>on</strong>g> c<strong>on</strong>tributing to PF<br />
selecti<strong>on</strong> with speaker and lexical verb as random effects<br />
Factor Weight % N Tokens Log-odd<br />
Temporal distance<br />
Within <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> year 0.68 71.9 23 32 0.570<br />
Within 24 hours 0.67 88.4 38 43 0.704<br />
Within <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> week 0.66 81.3 26 32 0.682<br />
Indeterminate 0.64 77.0 261 339 0.570<br />
L<strong>on</strong>ger than a year 0.27 39.0 16 41 -1.011<br />
C<strong>on</strong>tinuous 0.15 26.9 7 26 -1.711<br />
Range 53<br />
Not significant: Sentential polarity, Adverbial specificati<strong>on</strong>, Certainty,<br />
Grammatical pers<strong>on</strong>, Influence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> si, Presence/Absence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> quand<br />
Deviance=381.722; df=8; Intercept=-0.587; Mean=0.723;<br />
Speaker Random Std Dev=0.727; Lexical Verb Random Std Dev=2.033<br />
Now, grammatical pers<strong>on</strong> is not selected as significant, which suggests that <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
significant effect in Table 2 was indeed epiphenomenal. The <strong>on</strong>ly <str<strong>on</strong>g>linguistic</str<strong>on</strong>g> factor that<br />
remains in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> model is temporal distance. Also, <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> regressi<strong>on</strong> coefficients have altered<br />
c<strong>on</strong>siderably from <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> initial fixed-effects analysis. Those events set to occur up to a year<br />
following speech time all favour <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> periphrastic future to same degree (F.W.=0.66–0.68).<br />
There is a clear temporal divide, with acti<strong>on</strong>s occurring in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> most distal time c<strong>on</strong>text<br />
str<strong>on</strong>gly disfavouring <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> PF (F.W.=0.27). The linear relati<strong>on</strong>ship between <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> decreasing<br />
weighted probabilities and <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> increasing temporal distance has now been lost completely —<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>re has been a shift in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> relative factor weights. Hence, in Martinique French, PF is <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
default opti<strong>on</strong> in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> majority <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> cases and it is <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> inflected variant which acts as an indicator<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> distal outcomes. This result is in stark c<strong>on</strong>trast to what is reported for Acadian varieties, in<br />
which <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> PF acts as a marker <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> proximity and <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> temporal distincti<strong>on</strong> becomes lost in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
more distal time c<strong>on</strong>texts. 6<br />
5. C<strong>on</strong>clusi<strong>on</strong><br />
In c<strong>on</strong>clusi<strong>on</strong>, this article examined <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> variable nature <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> future temporal reference in<br />
Martinique French. The two variants under investigati<strong>on</strong> are <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> inflected and periphrastic<br />
futures. Various regressi<strong>on</strong> models highlighted <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> complex set <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> c<strong>on</strong>straints governing <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
variati<strong>on</strong> in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> Martinique future temporal reference sector. They revealed that strategies <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
encoding future time in this variety differ from its mainland European counterpart. Instead,<br />
results show that <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> future variable mirrors, to a certain extent, <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> findings for spoken<br />
varieties in Canada. The periphrastic future is identified as <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> dominant variant in this<br />
particular speech community, with a distributi<strong>on</strong> comparable to Laurentian varieties. In a<br />
fixed-effects model, <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> c<strong>on</strong>straint hierarchy patterns more like <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> geographically isolated<br />
and highly c<strong>on</strong>servative Acadian French varieties. Grammatical pers<strong>on</strong> and adverbial<br />
specificati<strong>on</strong> were also all shown to <str<strong>on</strong>g>influence</str<strong>on</strong>g> variant choice.<br />
However, <strong>on</strong>ce speaker-level and word-level variati<strong>on</strong> were accounted for, <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>re<br />
remains <strong>on</strong>ly <strong>on</strong>e <str<strong>on</strong>g>linguistic</str<strong>on</strong>g> factor to c<strong>on</strong>strain <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> future variable in Martinique French,<br />
namely temporal distance. The periphrastic future acts as <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> default opti<strong>on</strong> in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> majority <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
6 The cut-<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g>f point for what is c<strong>on</strong>sidered proximate is slightly different in both King and Nadasdi (2003) and<br />
Comeau (2011): a week in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> former and <strong>on</strong>ly an hour in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> latter.