Insulin, Subcutaneous NPO or Continuous Enteral Feeding Orders
Insulin, Subcutaneous NPO or Continuous Enteral Feeding Orders
Insulin, Subcutaneous NPO or Continuous Enteral Feeding Orders
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
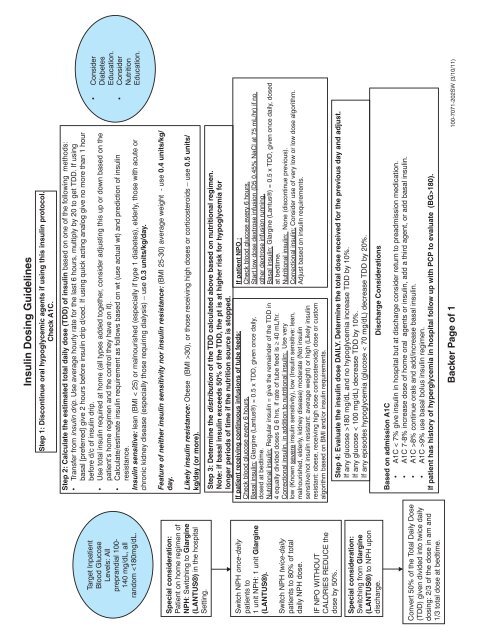
Target Inpatient<br />
Blood Glucose<br />
Levels: All<br />
preprandial 100-<br />
140 mg/dL, all<br />
random 30), <strong>or</strong> those receiving high doses <strong>or</strong> c<strong>or</strong>ticosteroids – use 0.5 units/<br />
kg/day (<strong>or</strong> m<strong>or</strong>e).<br />
Step 3: Determine the distribution of the TDD calculated above based on nutritional regimen.<br />
Note: if basal insulin exceeds 50% of the TDD, the pt is at higher risk f<strong>or</strong> hypoglycemia f<strong>or</strong><br />
longer periods of time if the nutrition source is stopped.<br />
If patient receiving continuous infusions of tube feeds:<br />
If patient <strong>NPO</strong> :<br />
Check blood glucose every 6 hours.<br />
Check blood glucose every 6 hours.<br />
Basal insulin: Glargine (Lantus®) = 0.5 x TDD, given once daily,<br />
Start low dose dextrose infusion (D5 0.45% NaCl at 75 mL/hr) if no<br />
dosed at bedtime.<br />
other dextrose infusion running.<br />
Nutritional insulin: Regular insulin = give the remainder of the TDD in Basal insulin: Glargine (Lantus®) = 0.5 x TDD, given once daily, dosed<br />
4 equally divided doses Q 6 hrs, if rate of tube feed is 40 mL/hr. at bedtime.<br />
C<strong>or</strong>rectional insulin, in addition to nutritional insulin: Use very<br />
Nutritional insulin: None (discontinue previous).<br />
low (Known severe insulin sensitivity), low (<strong>Insulin</strong> sensitive: lean, C<strong>or</strong>rectional insulin: Consider use of very low <strong>or</strong> low dose alg<strong>or</strong>ithm.<br />
malnourished, elderly, kidney disease) moderate (Not insulin<br />
Adjust based on insulin requirements.<br />
sensitive/not insulin resistant: average weight) <strong>or</strong> high (Likely insulin<br />
resistant: obese, receiving high dose c<strong>or</strong>ticosteroids) dose <strong>or</strong> custom<br />
alg<strong>or</strong>ithm based on BMI and/<strong>or</strong> insulin requirements.<br />
Step 4: Evaluate the insulin dose DAILY. Determine the total dose received f<strong>or</strong> the previous day and adjust.<br />
If any glucose >180 mg/dL and no hypoglycemia increase TDD by 10%.<br />
If any glucose < 100 mg/dL) decrease TDD by 10%.<br />
If any episodes hypoglycemia (glucose < 70 mg/dL) decrease TDD by 20%.<br />
Discharge Considerations<br />
Based on admission A1C<br />
• A1C < 7% give insulin in hospital but at discharge consider return to preadmission medication.<br />
• A1C 7-8% increase dose of home <strong>or</strong>al agents <strong>or</strong> insulin, add a third agent, <strong>or</strong> add basal insulin.<br />
• A1C >8% continue <strong>or</strong>als and add/increase basal insulin.<br />
• A1C >9% use basal bolus insulin regimen.<br />
If patient has hist<strong>or</strong>y of hyperglycemia in hospital follow up with PCP to evaluate (BG>180).<br />
Backer Page of 1 100-7071-202SW (3/10/11)