Inhibition of Bacterial Growth In Vitro Following ... - Physical Therapy
Inhibition of Bacterial Growth In Vitro Following ... - Physical Therapy
Inhibition of Bacterial Growth In Vitro Following ... - Physical Therapy
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Method<br />
Organisms Tested<br />
Three bacterial species commonly<br />
isolated from wounds were used as<br />
test organisms. 17 Isolates <strong>of</strong> Staphylococcus<br />
aureus (gram-positive cocci)<br />
and Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas<br />
aeruginosa (both gram-negative<br />
rods) were obtained from American<br />
Type Culture Collection † stocks.<br />
Procedure and <strong>In</strong>strumentation<br />
Our procedure was a slight modification<br />
<strong>of</strong> the procedure used by Barranco<br />
et al to test the in vitro effect <strong>of</strong><br />
weak direct current on S aureus. 14<br />
Sterile disposable plastic petri dishes<br />
were used throughout the experiment.<br />
Stainless-steel wires ‡ (0.035<br />
gauge) used as electrodes were positioned<br />
parallel 50 mm apart and covered<br />
with growth medium containing<br />
the test organisms. With a heated<br />
wire, four holes were melted 3 mm<br />
from the bottom edge <strong>of</strong> the dish.<br />
The holes allowed parallel placement<br />
<strong>of</strong> two 15-cm pieces <strong>of</strong> sterile<br />
stainless-steel wire extending across<br />
the entire width <strong>of</strong> the dish with the<br />
ends bent to prevent the wires from<br />
rolling and breaking contact with the<br />
medium.<br />
Test organisms were grown in trypticase<br />
soy broth § overnight at 37°C in a<br />
shaking water bath, and enough culture<br />
was added to the test medium to<br />
reach a final concentration <strong>of</strong> 1 ×10 7<br />
colony-forming units per milliliter, as<br />
determined by standard use <strong>of</strong> a<br />
hemocytometer.<br />
The test medium selected was<br />
Mueller-Hinton agar, § which is used<br />
in the semiquantitative Kirby-Bauer<br />
technique for determining effectiveness<br />
<strong>of</strong> antibiotics, because <strong>of</strong> the<br />
consistency <strong>of</strong> the widths <strong>of</strong> zones<br />
indicating inhibition <strong>of</strong> bacterial<br />
Fig. 1. Comparison <strong>of</strong> waveforms <strong>of</strong><br />
(a) low-intensity direct current (LIDC)<br />
and (b) high voltage pulsed current<br />
(HVPC) stimulation.<br />
growth. 18 A sufficient quantity <strong>of</strong><br />
medium inoculated with the test organism<br />
was poured into the prepared<br />
petri dishes to completely cover the<br />
wire electrodes, covered, and allowed<br />
to solidify. Plates were refrigerated for<br />
use within 24 hours <strong>of</strong> preparation.<br />
For test runs, wires in the petri dishes<br />
were connected by alligator-clip leads<br />
to a HVPC stimulator. The experimental<br />
setup is shown in Figure 3. The<br />
pulse rate was set at 120 pulses per<br />
second (pps) and the interpulse interval<br />
(measured at 50% <strong>of</strong> peak pulse<br />
amplitude) at 55 µsec. Voltages <strong>of</strong><br />
150, 200, 250, and 300 V were applied<br />
to the test organisms for 1, 2, 3, and 4<br />
hours' duration. According to Roberta<br />
A Newton (RA Newton, PhD; unpublished<br />
data), these voltages are within<br />
the normal therapeutic range for<br />
motor effect. Exposure durations were<br />
chosen based on the results <strong>of</strong> a pilot<br />
study that showed no bactericidal<br />
effect <strong>of</strong> HVPC at these voltages with<br />
shorter exposure duration. Each petri<br />
dish was incubated at 37°C for 24<br />
hours following exposure to HVPC.<br />
† American Type Culture Collection, 12301 Parklawn Dr, Rockville, MD 20852.<br />
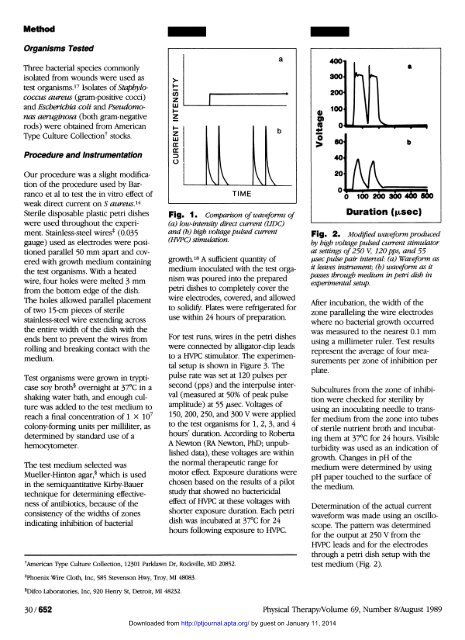
Fig. 2. Modified waveform produced<br />
by high voltage pulsed current stimulator<br />
at settings <strong>of</strong> 250 V, 120 pps, and 55<br />
µsec pulse pair interval: (a) Waveform as<br />
it leaves instrument; (b) waveform as it<br />
passes through medium in petri dish in<br />
experimental setup.<br />
After incubation, the width <strong>of</strong> the<br />
zone paralleling the wire electrodes<br />
where no bacterial growth occurred<br />
was measured to the nearest 0.1 mm<br />
using a millimeter ruler. Test results<br />
represent the average <strong>of</strong> four measurements<br />
per zone <strong>of</strong> inhibition per<br />
plate.<br />
Subcultures from the zone <strong>of</strong> inhibition<br />
were checked for sterility by<br />
using an inoculating needle to transfer<br />
medium from the zone into tubes<br />
<strong>of</strong> sterile nutrient broth and incubating<br />
them at 37°C for 24 hours. Visible<br />
turbidity was used as an indication <strong>of</strong><br />
growth. Changes in pH <strong>of</strong> the<br />
medium were determined by using<br />
pH paper touched to the surface <strong>of</strong><br />
the medium.<br />
Determination <strong>of</strong> the actual current<br />
waveform was made using an oscilloscope.<br />
The pattern was determined<br />
for the output at 250 V from the<br />
HVPC leads and for the electrodes<br />
through a petri dish setup with the<br />
test medium (Fig. 2).<br />
‡ Phoenix Wire Cloth, <strong>In</strong>c, 585 Stevenson Hwy, Troy, MI 48083.<br />
§ Difco Laboratories, <strong>In</strong>c, 920 Henry St, Detroit, MI 48232.<br />
30/652 <strong>Physical</strong> <strong>Therapy</strong>/Volume 69, Number 8/August 1989<br />
Downloaded from http://ptjournal.apta.org/ by guest on January 11, 2014