The chemical behaviour of cyanide in the extraction of gold ... - saimm
The chemical behaviour of cyanide in the extraction of gold ... - saimm
The chemical behaviour of cyanide in the extraction of gold ... - saimm
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Ore<br />
Cyanide<br />
Loaded<br />
carbon<br />
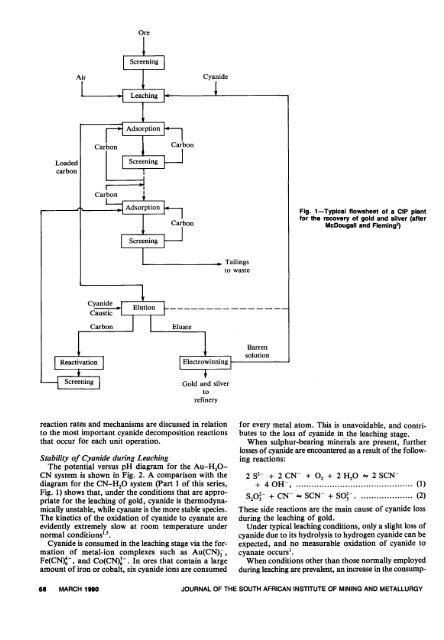
Fig. 1-Typlcal flowsheet <strong>of</strong> a CIP plant<br />
for <strong>the</strong> recovery <strong>of</strong> <strong>gold</strong> and silver (after<br />
McDougall and Flem<strong>in</strong>g~<br />
Tail<strong>in</strong>gs<br />
to waste<br />
Cyanide<br />
Caustic<br />
Carbon<br />
p-<br />
--------------.<br />
Eluate<br />
Barren<br />
solution<br />
Gold and silver<br />
to<br />
ref<strong>in</strong>ery<br />
reaction rates and mechanisms are discussed <strong>in</strong> relation<br />
to <strong>the</strong> most important <strong>cyanide</strong> decomposition reactions<br />
that occur for each unit operation.<br />
Stability ojCyanide dur<strong>in</strong>g Leach<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>The</strong> potential versus pH diagram for <strong>the</strong> Au-Hp-<br />
CN system is shown <strong>in</strong> Fig. 2. A comparison with <strong>the</strong><br />
diagram for <strong>the</strong> CN-H2O system (part 1 <strong>of</strong> this series,<br />
Fig. 1) shows that, under <strong>the</strong> conditions that are appropriate<br />
for <strong>the</strong> leach<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> <strong>gold</strong>, <strong>cyanide</strong> is <strong>the</strong>rmodynamically<br />
unstable, while cyanate is <strong>the</strong> more stable species.<br />
<strong>The</strong> k<strong>in</strong>etics <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> oxidation <strong>of</strong> <strong>cyanide</strong> to cyanate are<br />
evidently extremely slow at room temperature under<br />
normal conditionsJ.S.<br />
Cyanide is consumed <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> leach<strong>in</strong>g stage via <strong>the</strong> formation<br />
<strong>of</strong> metal-ion complexes such as Au(CN);,<br />
Fe(CN):- , and Co(CN)~-. In ores that conta<strong>in</strong> a large<br />
amount <strong>of</strong> iron or cobalt, six <strong>cyanide</strong> ions are consumed<br />
for every metal atom. This is unavoidable, and contributes<br />
to <strong>the</strong> loss <strong>of</strong> <strong>cyanide</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> leach<strong>in</strong>g stage.<br />
When sulphur-bear<strong>in</strong>g m<strong>in</strong>erals are present, fur<strong>the</strong>r<br />
losses <strong>of</strong> <strong>cyanide</strong> are encountered as a result <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> follow<strong>in</strong>g<br />
reactions:<br />
2 S2- + 2 CN- + °2 + 2 HP ~ 2 SCN-<br />
+ 4 OH-, (1)<br />
Sp~- + CN- ~ SCN- + S~-. "... (2)<br />
<strong>The</strong>se side reactions are <strong>the</strong> ma<strong>in</strong> cause <strong>of</strong> <strong>cyanide</strong> loss<br />
dur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> leach<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> <strong>gold</strong>.<br />
Under typical leach<strong>in</strong>g conditions, only a slight loss <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>cyanide</strong> due to its hydrolysis to hydrogen <strong>cyanide</strong> can be<br />
expected, and no measurable oxidation <strong>of</strong> <strong>cyanide</strong> to<br />
cyanate occursl.<br />
When conditions o<strong>the</strong>r than those normally employed<br />
dur<strong>in</strong>g leach<strong>in</strong>g are prevalent, an <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> consump-<br />
68 MARCH 1990 JOURNAL OF THE SOUTH AFRICAN INSTITUTE OF MINING AND METALLURGY