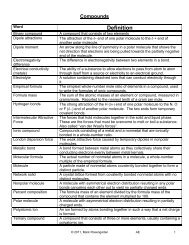
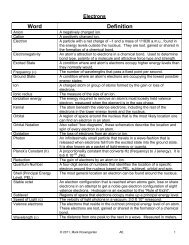
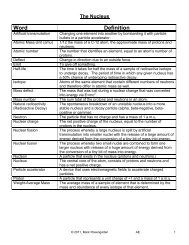
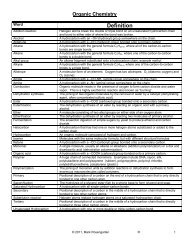
Unit 6: Periodic Table and Bonding - Mark Rosengarten
Unit 6: Periodic Table and Bonding - Mark Rosengarten
Unit 6: Periodic Table and Bonding - Mark Rosengarten
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
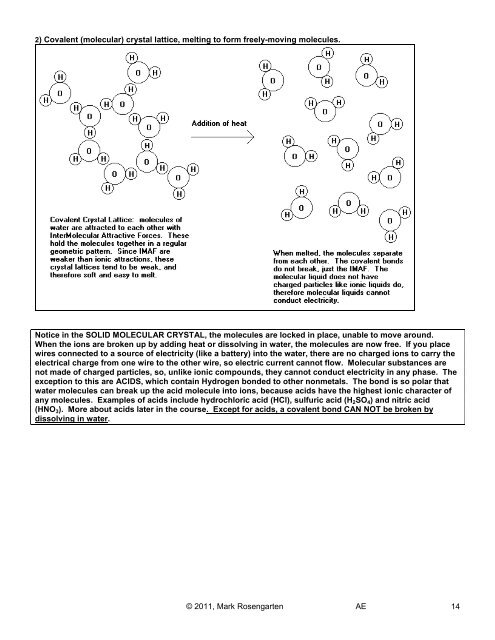
2) Covalent (molecular) crystal lattice, melting to form freely-moving molecules.<br />
Notice in the SOLID MOLECULAR CRYSTAL, the molecules are locked in place, unable to move around.<br />
When the ions are broken up by adding heat or dissolving in water, the molecules are now free. If you place<br />
wires connected to a source of electricity (like a battery) into the water, there are no charged ions to carry the<br />
electrical charge from one wire to the other wire, so electric current cannot flow. Molecular substances are<br />
not made of charged particles, so, unlike ionic compounds, they cannot conduct electricity in any phase. The<br />
exception to this are ACIDS, which contain Hydrogen bonded to other nonmetals. The bond is so polar that<br />
water molecules can break up the acid molecule into ions, because acids have the highest ionic character of<br />
any molecules. Examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4 ) <strong>and</strong> nitric acid<br />
(HNO 3 ). More about acids later in the course. Except for acids, a covalent bond CAN NOT be broken by<br />
dissolving in water.<br />
© 2011, <strong>Mark</strong> <strong>Rosengarten</strong> AE 14