Södra annual report 2012
Södra annual report 2012
Södra annual report 2012
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Note 22<br />
Financial risk management<br />
The international and capital-intensive nature of its operations means Södra<br />
is constantly exposed to financial risks, such as market risk, credit risk and<br />
liquidity and financing risk. There are correlations between certain risk variables.<br />
According to the hedging strategy, focus shall be on hedging net exposures.<br />
The Group’s financial policy for handling financial risks is adopted by<br />
the Board and provides a framework of guidelines and rules in the form of<br />
risk mandates and limits for financial operations. Hedging measures are<br />
approved when the situation for such a measure is judged to be financially<br />
beneficial. Consideration is also taken to the current access to commercially<br />
acceptable hedging terms.<br />
Södra’s financial risk management is centralised to the Treasury function<br />
in the Parent Company. This enables economies of scale and synergy effects<br />
to be utilised and helps minimise handling risks. The overall objective is to<br />
provide cost-effective financing and liquidity administration while minimising<br />
the negative effects on consolidated income that arise from market risks.<br />
The financial risks are continuously measured and compliance with the<br />
financial policy is monitored. The key aspects of financial risk management<br />
within the Group are described below.<br />
Market risk<br />
Market risk involves the risk of the fair value of, or future cash flow from, a<br />
financial instrument changing due to fluctuating market prices. Market risk<br />
consists of foreign exchange risk, interest risk and other price risks. The<br />
market risks that primarily affect the Group are foreign exchange risk and<br />
raw material price risk.<br />
Foreign exchange risk<br />
Södra is exposed to different types of foreign exchange risk. The primary<br />
exposure arises from the Group’s sales and purchases in foreign currencies.<br />
These foreign exchange risks consist partly of the risk of fluctuations in the<br />
value of financial instruments and trade receivables and payables, and partly<br />
of foreign exchange risk in anticipated or contracted payment flows (transaction<br />
exposure).<br />
There are also foreign exchange risks in translation of the assets and liabilities<br />
of foreign subsidiaries to the functional currency of the Group (translation<br />
exposure). The Group is also exposed to foreign exchange risks attributable<br />
to investments in foreign currency (financial exposure).<br />
Consolidated income includes foreign exchange differences of negative<br />
SEK 53 million (neg: 16) in operating profit and of negative SEK 8 million<br />
(pos: 8) in finance income and expenses.<br />
Transaction exposure<br />
A substantial part of revenue is related to customers outside Sweden and most<br />
of the company’s products are invoiced in local currency or USD. Input goods<br />
are largely imported in foreign currency. These factors mean that changing foreign<br />
exchange rates have a major impact on Södra. To manage Södra’s net<br />
transaction exposure, forecast currency flow can be hedged using currency<br />
derivatives.<br />
Currency exposure is hedged in accordance with the financial policy. Temporarily<br />
attractive levels or specific factors can make it desirable to deviate<br />
from the hedging norms. The hedging interval determines the risk mandate<br />
that Södra Treasury has to follow for deviations from hedging norms. The currency<br />
hedging component of pulp hedges is included in the overall foreign<br />
exchange mandate. Under the policy, standardised forward contracts, currency<br />
swaps and acquired foreign exchange options may be used for hedging purposes.<br />
Hedge <strong>report</strong>ing is used when the demands for this are met.<br />
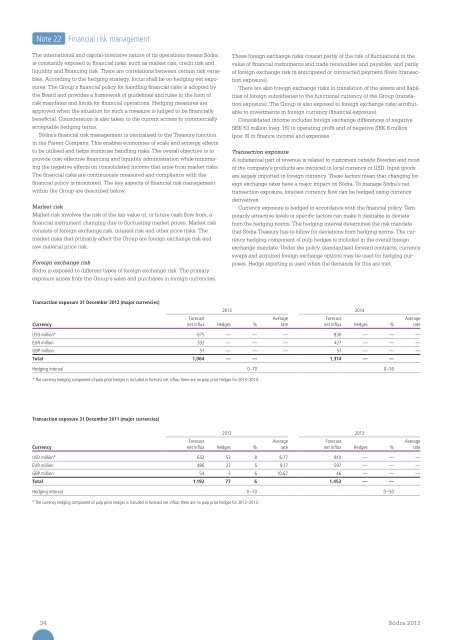
Transaction exposure 31 December <strong>2012</strong> (major currencies)<br />
Currency<br />
Forecast<br />
net influx Hedges %<br />
2013 2014<br />
Average<br />
rate<br />
Forecast<br />
net influx Hedges %<br />
Average<br />
rate<br />
USD million* 675 — — — 830 — — —<br />
EUR million 332 — — — 427 — — —<br />
GBP million 57 — — — 57 — — —<br />
Total 1,064 — — 1,314 — —<br />
Hedging interval 0–70 0–50<br />
* The currency hedging component of pulp price hedges is included in forecast net influx; there are no pulp price hedges for 2013–2014.<br />
Transaction exposure 31 December 2011 (major currencies)<br />
Currency<br />
Forecast<br />
net influx Hedges %<br />
<strong>2012</strong> 2013<br />
Average<br />
rate<br />
Forecast<br />
net influx Hedges %<br />
Average<br />
rate<br />
USD million* 652 52 8 6.77 810 — — —<br />
EUR million 486 22 5 9.17 597 — — —<br />
GBP million 54 3 6 10.67 46 — — —<br />
Total 1,192 77 6 1,453 — —<br />
Hedging interval 0–70 0–50<br />
* The currency hedging component of pulp price hedges is included in forecast net influx; there are no pulp price hedges for <strong>2012</strong>–2013.<br />
34<br />
Södra <strong>2012</strong>