Prehospital trauma care systems - World Health Organization
Prehospital trauma care systems - World Health Organization
Prehospital trauma care systems - World Health Organization
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
PREHOSPITAL TRAUMA CARE SYSTEMS<br />
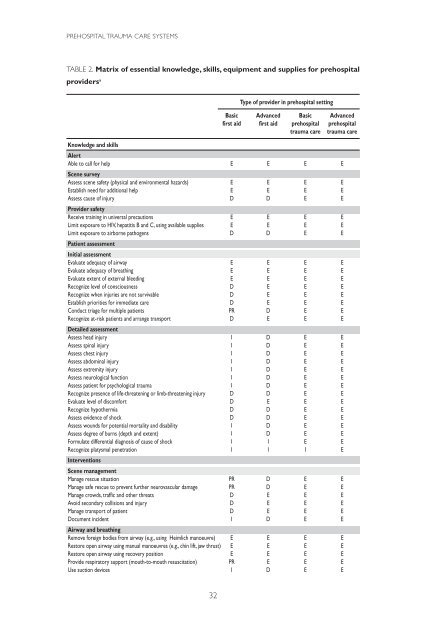
TABLE 2. Matrix of essential knowledge, skills, equipment and supplies for prehospital<br />
providers a<br />
Type of provider in prehospital setting<br />
Basic Advanced Basic Advanced<br />
first aid first aid prehospital prehospital<br />
<strong>trauma</strong> <strong>care</strong> <strong>trauma</strong> <strong>care</strong><br />
Knowledge and skills<br />
Alert<br />
Able to call for help E E E E<br />
Scene survey<br />
Assess scene safety (physical and environmental hazards) E E E E<br />
Establish need for additional help E E E E<br />
Assess cause of injury D D E E<br />
Provider safety<br />
Receive training in universal precautions E E E E<br />
Limit exposure to HIV, hepatitis B and C, using available supplies E E E E<br />
Limit exposure to airborne pathogens D D E E<br />
Patient assessment<br />
Initial assessment<br />
Evaluate adequacy of airway E E E E<br />
Evaluate adequacy of breathing E E E E<br />
Evaluate extent of external bleeding E E E E<br />
Recognize level of consciousness D E E E<br />
Recognize when injuries are not survivable D E E E<br />
Establish priorities for immediate <strong>care</strong> D E E E<br />
Conduct triage for multiple patients PR D E E<br />
Recognize at-risk patients and arrange transport D E E E<br />
Detailed assessment<br />
Assess head injury I D E E<br />
Assess spinal injury I D E E<br />
Assess chest injury I D E E<br />
Assess abdominal injury I D E E<br />
Assess extremity injury I D E E<br />
Assess neurological function I D E E<br />
Assess patient for psychological <strong>trauma</strong> I D E E<br />
Recognize presence of life-threatening or limb-threatening injury D D E E<br />
Evaluate level of discomfort D E E E<br />
Recognize hypothermia D D E E<br />
Assess evidence of shock D D E E<br />
Assess wounds for potential mortality and disability I D E E<br />
Assess degree of burns (depth and extent) I D E E<br />
Formulate differential diagnosis of cause of shock I I E E<br />
Recognize platysmal penetration I I I E<br />
Interventions<br />
Scene management<br />
Manage rescue situation PR D E E<br />
Manage safe rescue to prevent further neurovascular damage PR D E E<br />
Manage crowds, traffic and other threats D E E E<br />
Avoid secondary collisions and injury D E E E<br />
Manage transport of patient D E E E<br />
Document incident I D E E<br />
Airway and breathing<br />
Remove foreign bodies from airway (e.g., using Heimlich manoeuvre) E E E E<br />
Restore open airway using manual manoeuvres (e.g., chin lift, jaw thrust) E E E E<br />
Restore open airway using recovery position E E E E<br />
Provide respiratory support (mouth-to-mouth resuscitation) PR E E E<br />
Use suction devices I D E E<br />
32