BIS guide for clinicians
BIS guide for clinicians
BIS guide for clinicians
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Using <strong>BIS</strong> Monitoring to Reduce Intraoperative Awareness<br />
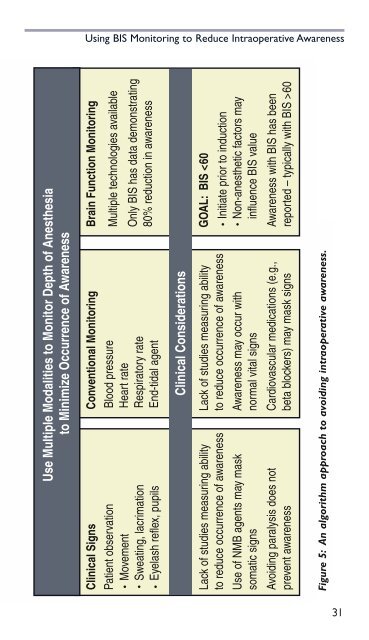
Use Multiple Modalities to Monitor Depth of Anesthesia<br />
to Minimize Occurrence of Awareness<br />
Clinical Signs<br />
Patient observation<br />
Movement<br />
Sweating, lacrimation<br />
Eyelash reflex, pupils<br />
Conventional Monitoring<br />
Blood pressure<br />
Heart rate<br />
Respiratory rate<br />
End-tidal agent<br />
Brain Function Monitoring<br />
Multiple technologies available<br />
Only <strong>BIS</strong> has data demonstrating<br />
80% reduction in awareness<br />
Clinical Considerations<br />
Lack of studies measuring ability<br />
to reduce occurrence of awareness<br />
Use of NMB agents may mask<br />
somatic signs<br />
Avoiding paralysis does not<br />
prevent awareness<br />
Lack of studies measuring ability<br />
to reduce occurrence of awareness<br />
Awareness may occur with<br />
normal vital signs<br />
Cardiovascular medications (e.g.,<br />
beta blockers) may mask signs<br />
GOAL: <strong>BIS</strong> 60<br />
Figure 5: An algorithm approach to avoiding intraoperative awareness.<br />
31