CHAPTER I: LINEAR ALGEBRA - OCW UPM
CHAPTER I: LINEAR ALGEBRA - OCW UPM
CHAPTER I: LINEAR ALGEBRA - OCW UPM
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
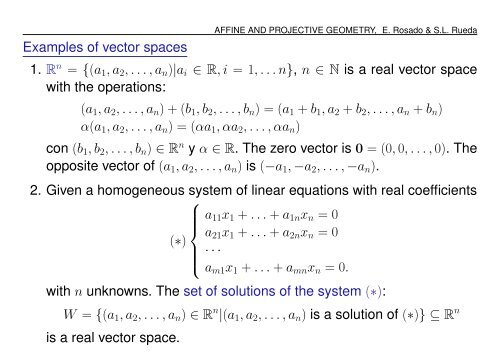
Examples of vector spaces<br />
AFFINE AND PROJECTIVE GEOMETRY, E. Rosado & S.L. Rueda<br />
1. R n = {(a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a n )|a i ∈ R, i = 1, . . . n}, n ∈ N is a real vector space<br />
with the operations:<br />
(a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a n ) + (b 1 , b 2 , . . . , b n ) = (a 1 + b 1 , a 2 + b 2 , . . . , a n + b n )<br />
α(a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a n ) = (αa 1 , αa 2 , . . . , αa n )<br />
con (b 1 , b 2 , . . . , b n ) ∈ R n y α ∈ R. The zero vector is 0 = (0, 0, . . . , 0). The<br />
opposite vector of (a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a n ) is (−a 1 , −a 2 , . . . , −a n ).<br />
2. Given a homogeneous system of linear equations with real coefficients<br />
⎧<br />
a 11 x 1 + . . . + a 1n x n = 0<br />
⎪⎨<br />
a<br />
(∗) 21 x 1 + . . . + a 2n x n = 0<br />
· · ·<br />
⎪⎩ a m1 x 1 + . . . + a mn x n = 0.<br />
with n unknowns. The set of solutions of the system (∗):<br />
W = {(a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a n ) ∈ R n |(a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a n ) is a solution of (∗)} ⊆ R n<br />
is a real vector space.