Global Dialogue on Nanotechnology and the Poor ... - Nanowerk
Global Dialogue on Nanotechnology and the Poor ... - Nanowerk
Global Dialogue on Nanotechnology and the Poor ... - Nanowerk
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
nanotechnology,<br />
water, & development<br />
was added into <strong>the</strong> dead-end reactor, which was fitted with a<br />
membrane at <strong>on</strong>e end.The clean water was forced through <strong>the</strong><br />
membrane at various pressures of nitrogen gas: 5, 10, 15, <strong>and</strong> 20<br />
bars. A 5.00 cm 3 volume of permeates was collected at each<br />
pressure, <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> permeati<strong>on</strong> time was recorded.The retenti<strong>on</strong><br />
coefficient (R) of <strong>the</strong> membrane was determined by using single<br />
<strong>and</strong> binary salt soluti<strong>on</strong>s.The salts that were used were NaCl, MgCl2,<br />
<strong>and</strong> Na2SO4.The informati<strong>on</strong> from <strong>the</strong>se salt soluti<strong>on</strong>s studies was<br />
also used for <strong>the</strong> determinati<strong>on</strong> of <strong>the</strong> charge <strong>on</strong> <strong>the</strong> membrane.<br />
The rejecti<strong>on</strong> of <strong>the</strong> pollutants (i.e., nitrate, phosphate, calcium,<br />
magnesium <strong>and</strong> sodium) was tested for each membrane.The<br />
flat-sheet membranes which had good performance were noted.<br />
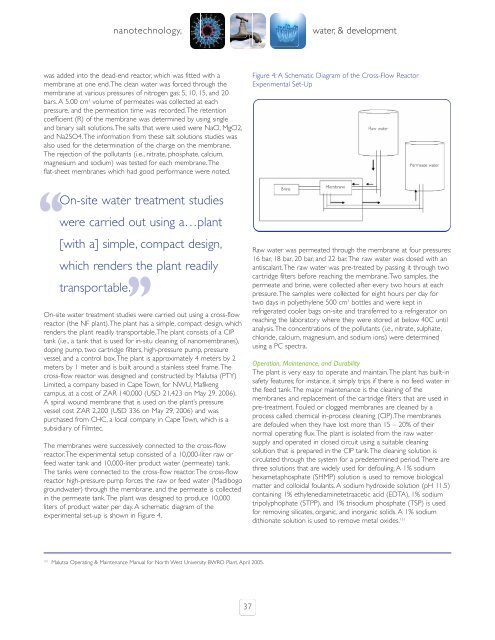
Figure 4: A Schematic Diagram of <strong>the</strong> Cross-Flow Reactor<br />
Experimental Set-Up<br />
‘‘<br />
On-site water treatment studies<br />
were carried out using a…plant<br />
[with a] simple, compact design,<br />
which renders <strong>the</strong> plant readily<br />
’’<br />
transportable.<br />
On-site water treatment studies were carried out using a cross-flow<br />
reactor (<strong>the</strong> NF plant).The plant has a simple, compact design, which<br />
renders <strong>the</strong> plant readily transportable.The plant c<strong>on</strong>sists of a CIP<br />
tank (i.e., a tank that is used for in-situ cleaning of nanomembranes),<br />
doping pump, two cartridge filters, high-pressure pump, pressure<br />
vessel, <strong>and</strong> a c<strong>on</strong>trol box.The plant is approximately 4 meters by 2<br />
meters by 1 meter <strong>and</strong> is built around a stainless steel frame.The<br />
cross-flow reactor was designed <strong>and</strong> c<strong>on</strong>structed by Malutsa (PTY)<br />
Limited, a company based in Cape Town, for NWU, Mafikeng<br />
campus, at a cost of ZAR 140,000 (USD 21,423 <strong>on</strong> May 29, 2006).<br />
A spiral wound membrane that is used <strong>on</strong> <strong>the</strong> plant’s pressure<br />
vessel cost ZAR 2,200 (USD 336 <strong>on</strong> May 29, 2006) <strong>and</strong> was<br />
purchased from CHC, a local company in Cape Town, which is a<br />
subsidiary of Filmtec.<br />
The membranes were successively c<strong>on</strong>nected to <strong>the</strong> cross-flow<br />
reactor.The experimental setup c<strong>on</strong>sisted of a 10,000-liter raw or<br />
feed water tank <strong>and</strong> 10,000-liter product water (permeate) tank.<br />
The tanks were c<strong>on</strong>nected to <strong>the</strong> cross-flow reactor.The cross-flow<br />
reactor high-pressure pump forces <strong>the</strong> raw or feed water (Madibogo<br />
groundwater) through <strong>the</strong> membrane, <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> permeate is collected<br />
in <strong>the</strong> permeate tank.The plant was designed to produce 10,000<br />
liters of product water per day. A schematic diagram of <strong>the</strong><br />
experimental set-up is shown in Figure 4.<br />
Raw water was permeated through <strong>the</strong> membrane at four pressures:<br />
16 bar, 18 bar, 20 bar, <strong>and</strong> 22 bar.The raw water was dosed with an<br />
antiscalant.The raw water was pre-treated by passing it through two<br />
cartridge filters before reaching <strong>the</strong> membrane.Two samples, <strong>the</strong><br />
permeate <strong>and</strong> brine, were collected after every two hours at each<br />
pressure.The samples were collected for eight hours per day for<br />
two days in polyethylene 500 cm 3 bottles <strong>and</strong> were kept in<br />
refrigerated cooler bags <strong>on</strong>-site <strong>and</strong> transferred to a refrigerator <strong>on</strong><br />
reaching <strong>the</strong> laboratory where <strong>the</strong>y were stored at below 40C until<br />
analysis.The c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s of <strong>the</strong> pollutants (i.e., nitrate, sulphate,<br />
chloride, calcium, magnesium, <strong>and</strong> sodium i<strong>on</strong>s) were determined<br />
using a PC spectra.<br />
Operati<strong>on</strong>, Maintenance, <strong>and</strong> Durability<br />
The plant is very easy to operate <strong>and</strong> maintain.The plant has built-in<br />
safety features; for instance, it simply trips if <strong>the</strong>re is no feed water in<br />
<strong>the</strong> feed tank.The major maintenance is <strong>the</strong> cleaning of <strong>the</strong><br />
membranes <strong>and</strong> replacement of <strong>the</strong> cartridge filters that are used in<br />
pre-treatment. Fouled or clogged membranes are cleaned by a<br />
process called chemical in-process cleaning (CIP).The membranes<br />
are defouled when <strong>the</strong>y have lost more than 15 – 20% of <strong>the</strong>ir<br />
normal operating flux.The plant is isolated from <strong>the</strong> raw water<br />
supply <strong>and</strong> operated in closed circuit using a suitable cleaning<br />
soluti<strong>on</strong> that is prepared in <strong>the</strong> CIP tank.The cleaning soluti<strong>on</strong> is<br />
circulated through <strong>the</strong> system for a predetermined period.There are<br />
three soluti<strong>on</strong>s that are widely used for defouling. A 1% sodium<br />
hexametaphosphate (SHMP) soluti<strong>on</strong> is used to remove biological<br />
matter <strong>and</strong> colloidal foulants. A sodium hydroxide soluti<strong>on</strong> (pH 11.5)<br />
c<strong>on</strong>taining 1% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), 1% sodium<br />
tripolyphophate (STPP), <strong>and</strong> 1% trisodium phosphate (TSP) is used<br />
for removing silicates, organic, <strong>and</strong> inorganic solids. A 1% sodium<br />
dithi<strong>on</strong>ate soluti<strong>on</strong> is used to remove metal oxides. 131<br />
131<br />
Malutsa Operating & Maintenance Manual for North West University BWRO Plant, April 2005.<br />
37