- Page 1 and 2: Aus dem Institut für Informationss
- Page 3 and 4: Acknowledgments I would like to tha
- Page 5 and 6: 2 CONTENTS 4 Introduction to Recent
- Page 7 and 8: 4 CONTENTS 10.3 XML Schema . . . .
- Page 9 and 10: 6 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION Due to th
- Page 11 and 12: 8 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS In contra
- Page 13 and 14: 10 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS data is
- Page 15 and 16: 12 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS XML supp
- Page 17 and 18: 14 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS 2.2 Docu
- Page 19 and 20: 16 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS be const
- Page 21 and 22: 18 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS plies th
- Page 23 and 24: 20 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS the stru
- Page 25 and 26: 22 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS 2.3 XML
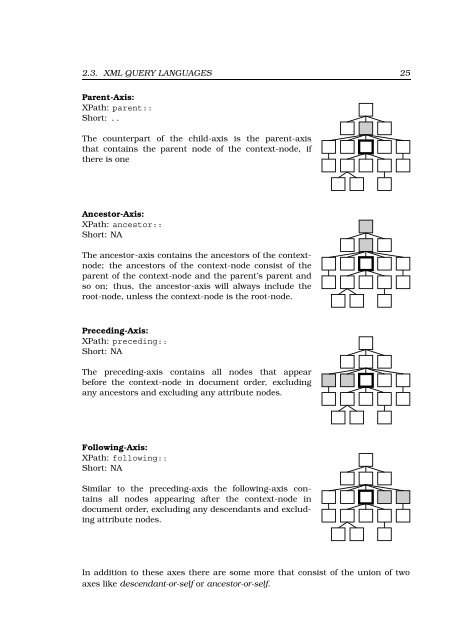
- Page 27: 24 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS Axes for
- Page 31 and 32: 28 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS //item[c
- Page 33 and 34: 30 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS 21 i f (
- Page 35 and 36: 32 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS FLWOR-Ex
- Page 37 and 38: 34 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS 21 22 {
- Page 39 and 40: 36 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS 1 2 3
- Page 41 and 42: 38 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS 2.5 XML
- Page 43 and 44: 40 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS the valu
- Page 45 and 46: 42 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS tables a
- Page 47 and 48: 44 CHAPTER 2. FUNDAMENTALS signific
- Page 49 and 50: 46 CHAPTER 3. FORMAL MODELS FOR XML
- Page 51 and 52: 48 CHAPTER 3. FORMAL MODELS FOR XML
- Page 53 and 54: 50 CHAPTER 3. FORMAL MODELS FOR XML
- Page 55 and 56: 52 CHAPTER 3. FORMAL MODELS FOR XML
- Page 57 and 58: 54 CHAPTER 3. FORMAL MODELS FOR XML
- Page 59 and 60: 56 CHAPTER 4. INTRODUCTION TO RECEN
- Page 61 and 62: 58 CHAPTER 4. INTRODUCTION TO RECEN
- Page 63 and 64: 60 CHAPTER 4. INTRODUCTION TO RECEN
- Page 65 and 66: 62 CHAPTER 4. INTRODUCTION TO RECEN
- Page 67 and 68: 64 CHAPTER 4. INTRODUCTION TO RECEN
- Page 69 and 70: 66 CHAPTER 4. INTRODUCTION TO RECEN
- Page 71 and 72: 68 CHAPTER 4. INTRODUCTION TO RECEN
- Page 73 and 74: 70 CHAPTER 4. INTRODUCTION TO RECEN
- Page 75 and 76: 72 CHAPTER 4. INTRODUCTION TO RECEN
- Page 77 and 78: 74 CHAPTER 4. INTRODUCTION TO RECEN
- Page 79 and 80:
76 CHAPTER 4. INTRODUCTION TO RECEN
- Page 81 and 82:
78 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 83 and 84:
80 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 85 and 86:
82 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 87 and 88:
84 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 89 and 90:
86 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 91 and 92:
88 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 93 and 94:
90 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 95 and 96:
92 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 97 and 98:
94 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 99 and 100:
96 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 101 and 102:
98 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 103 and 104:
100 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 105 and 106:
102 CHAPTER 5. THE KEY-ORIENTED XML
- Page 107 and 108:
104 CHAPTER 6. THE INDEX SELECTION
- Page 109 and 110:
106 CHAPTER 6. THE INDEX SELECTION
- Page 111 and 112:
108 CHAPTER 6. THE INDEX SELECTION
- Page 113 and 114:
110 CHAPTER 6. THE INDEX SELECTION
- Page 115 and 116:
112 CHAPTER 6. THE INDEX SELECTION
- Page 117 and 118:
114 CHAPTER 6. THE INDEX SELECTION
- Page 119 and 120:
116 CHAPTER 6. THE INDEX SELECTION
- Page 121 and 122:
118 CHAPTER 6. THE INDEX SELECTION
- Page 123 and 124:
120 CHAPTER 6. THE INDEX SELECTION
- Page 125 and 126:
122 CHAPTER 6. THE INDEX SELECTION
- Page 127 and 128:
124 CHAPTER 7. THE XML INDEX UPDATE
- Page 129 and 130:
126 CHAPTER 7. THE XML INDEX UPDATE
- Page 131 and 132:
128 CHAPTER 7. THE XML INDEX UPDATE
- Page 133 and 134:
130 CHAPTER 7. THE XML INDEX UPDATE
- Page 135 and 136:
132 CHAPTER 7. THE XML INDEX UPDATE
- Page 137 and 138:
134 CHAPTER 7. THE XML INDEX UPDATE
- Page 139 and 140:
136 CHAPTER 7. THE XML INDEX UPDATE
- Page 141 and 142:
138 CHAPTER 7. THE XML INDEX UPDATE
- Page 143 and 144:
140 CHAPTER 7. THE XML INDEX UPDATE
- Page 145 and 146:
142 CHAPTER 7. THE XML INDEX UPDATE
- Page 147 and 148:
144 CHAPTER 7. THE XML INDEX UPDATE
- Page 149 and 150:
146 CHAPTER 7. THE XML INDEX UPDATE
- Page 151 and 152:
148 CHAPTER 8. KEYX IMPLEMENTATION
- Page 153 and 154:
150 CHAPTER 8. KEYX IMPLEMENTATION
- Page 155 and 156:
152 CHAPTER 8. KEYX IMPLEMENTATION
- Page 157 and 158:
154 CHAPTER 8. KEYX IMPLEMENTATION
- Page 159 and 160:
156 CHAPTER 8. KEYX IMPLEMENTATION
- Page 161 and 162:
158 CHAPTER 9. CONCLUSION AND FUTUR
- Page 163 and 164:
160 CHAPTER 9. CONCLUSION AND FUTUR
- Page 165 and 166:
162 CHAPTER 10. APPENDIX 23 relKeyP
- Page 167 and 168:
164 CHAPTER 10. APPENDIX Title: On
- Page 169 and 170:
166 CHAPTER 10. APPENDIX Title: The
- Page 171 and 172:
168 CHAPTER 10. APPENDIX
- Page 173 and 174:
170 BIBLIOGRAPHY [12] Alberto Capra
- Page 175 and 176:
172 BIBLIOGRAPHY [37] Roy Goldman a
- Page 177 and 178:
174 BIBLIOGRAPHY [59] Raghav Kaushi
- Page 179 and 180:
176 BIBLIOGRAPHY [84] David G. Mitc
- Page 181 and 182:
178 BIBLIOGRAPHY [113] W3 Schools.
- Page 183 and 184:
180 Index D, 78, 108, 110, 111, 144
- Page 185 and 186:
182 INDEX Oracle XML DB, 41 Parent,