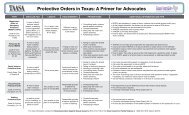
Sexual aSSault LEGAL ADVOCACY MANUAL - Texas Association ...
Sexual aSSault LEGAL ADVOCACY MANUAL - Texas Association ...
Sexual aSSault LEGAL ADVOCACY MANUAL - Texas Association ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Juvenile Offenders<br />
Introduction<br />
When the perpetrator of sexual assault is a juvenile, some special rules apply. As a general rule, the juvenile<br />
justice system is more lenient toward perpetrators than the adult system, because it has elements of both the<br />
criminal and civil legal systems. In fact, juvenile court proceedings actually are civil cases, not criminal. Even<br />
in cases involving serious offenses like sexual assault, the response to crime sometimes can be more focused<br />
on rehabilitating the child-offender than on punishment. For all those reasons, juvenile proceedings are<br />
significantly different from adult criminal proceedings.<br />
But in many ways, from the advocate’s point of view, there will be similarities. The fact that the perpetrator<br />
is a minor does not necessarily mean the advocate’s responsibilities will be drastically different than if an<br />
adult had committed the offense. For example, victims have statutory rights in juvenile proceedings, just<br />
like in adult criminal proceedings. In many respects, in fact, victims’ rights are the same in both systems.<br />
In addition, sometimes juveniles who commit felonies can be prosecuted as adults in the ordinary criminal<br />
justice system, meaning nothing would be different at all.<br />
There certainly will be differences in the juvenile system, however. The juvenile system offers many<br />
alternatives that are not available in the adult system, and the Family Code has extensive rules governing<br />
when each can apply. Thus, the bulk of this chapter will set out the various ways the state might address<br />
serious sexual offenses when committed by juveniles. Sometimes cases will result in a trial, and sometimes<br />
not. Sometimes the juvenile offender will be committed to an institution, and sometimes not. You and the<br />
survivor should know that the result of a juvenile case will depend on a lot of specific facts and details that,<br />
unfortunately, you may not have any control over.<br />
Therefore, approach this chapter with an eye toward learning what facts will be relevant to courts and<br />
prosecutors when dealing with juvenile offenders. Also, use this chapter as a foundation of knowledge—<br />
and a reference—for helping survivors understand how the juvenile justice system works in general. This<br />
chapter is not a comprehensive guide to the advocate’s role in juvenile cases; you will also need to apply the<br />
information you have learned thus far. This chapter focuses narrowly on the specific ways juvenile cases can<br />
differ from adult criminal cases, and how you should modify your advocacy.<br />
83