SNDT Women's University - Shreemati Nathibai Damodar ...
SNDT Women's University - Shreemati Nathibai Damodar ...
SNDT Women's University - Shreemati Nathibai Damodar ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
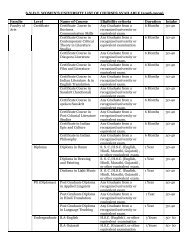
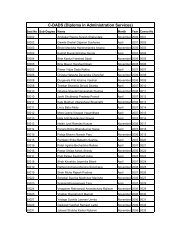
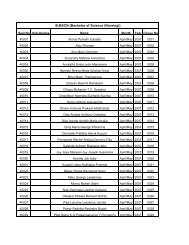
<strong>SNDT</strong> Women’s <strong>University</strong><br />
(Sndt.digitaluniversity.ac)<br />
Syllabus – M. Pharm. (Quality Assurance)<br />
<strong>SNDT</strong> Women’s <strong>University</strong><br />
1, <strong>Nathibai</strong> Thackersey Road,<br />
Mumbai 400 020<br />
1 | P a g e
C. U. SHAH COLLEGE OF PHARMACY<br />
ABOUT THE COLLEGE<br />
The S.N.D.T. Women’s <strong>University</strong> established in 1916, was founded by Maharshi<br />
Karve and nurtured by Sir Vithaldas Thackersey especially by Lady Premlila<br />
Thackersey and other dedicated social workers, who believed in women’s full<br />
participation in all spheres of life. Its expansion included offering of Graduate and<br />
Post-Graduate courses in Arts, Commerce, Home Science, Library Science, Nursing<br />
and Education, Pharmacy & Engineering, in addition to Diploma courses in various<br />
fields. A diploma course in Pharmacy was started in 1976 in P.V. Polytechnic at<br />
Juhu Campus.<br />
Befitting with the objectives of the <strong>University</strong> and due to the repaid changes taking<br />
place in society, where in more girls are opting for professional courses, a number<br />
of professional courses are introduced by the university from time to time. A full<br />
fledged degree course in Pharmacy at its C.U. SHAH College of Pharmacy was in<br />
1980, with the generous donation of Rs. 5 Lacs from C.U.SHAH Charitable Trust.<br />
The college now offers the following programmes and courses:<br />
• Four Year – Bachelor of Pharmacy (B.Pharm)<br />
• Four Semester – Master of Pharmacy (QA) (M. Pharm)<br />
Four Semester - Master of Pharmacy in Pharmaceutics (Industrial<br />
Pharmacy)<br />
• One Year P.G. Diploma in Pharm Analysis.<br />
• One Year P.G. Diploma in Cosmeticology.<br />
• Doctor of Philosophy in Pharmacy (Tech.).<br />
Facilities available to the college include.<br />
• C.U. Shah Pharmaceutical Research Centre.<br />
• Industrial Pharmacy Laboratory.<br />
• Centre for bioavailability studies.<br />
• Consultancy & Guidance to Pharmaceutical Industry.<br />
Research Projects are undertaken from Pharma Industries and State and Central<br />
government agencies like<br />
-U.G.C., M. H.R.D.<br />
-C.S.I.R., B.R.N.S., DAE, DBT.<br />
B.A.R.C. etc.<br />
2 | P a g e
The M. Pharm. (Quality Assurance) course, a very unique one was introduced in India for the<br />
FIRST TIME in 1989 at C.U. Shah College of Pharmacy, by <strong>SNDT</strong> Women’s <strong>University</strong> after<br />
due sanction from the <strong>University</strong> Grants Commission and AICTE. The course is devised with a<br />
focus on the aptitude, talents and job potential for women in pharma industry and research and<br />
development institutes.<br />
The is a four semester programme with the following specific features.<br />
1) Emphasis on modern analytical techniques like spectroflurometry, infrared<br />
spectrophotometry, NMR, Spectromentry HPLC, X-ray diffraction analysis and spectral<br />
analysis.<br />
2) Thrust on good manufacturing practices, quality audits, documentation and validation with a<br />
view to create total quality consciousness.<br />
3) Packaging and product development courses designed to teach current trends in formulation<br />
of pharmaceuticals and newer drug delivery systems.<br />
4) Students work on a research project and submit a dissertation at the end of fourth semester<br />
for which they are evaluated by experts.<br />
5) One month in plant training in industry to correlate theory with professional practice.<br />
6) Guest lectures and seminars are routinely arranged where visiting faculty impart insights in<br />
state-of-art technology and current advances in pharmaceutical sciences.<br />
HOSTEL :<br />
Very limited accommodation is available in the <strong>University</strong> Hostel, situated in the campus.<br />
ADMISSIO CRITERIA :<br />
Only Female candidates shall be admitted for the Ten open merit seats, 5 for sponsored and<br />
three reserved category. seats Out of ten seats one is reserved for Marathwada <strong>University</strong><br />
students. The admission to these seats will be as per rules of AICTE/DTE/ <strong>University</strong>.<br />
Admission will be given on purely merit basis to candidates with valid gate score & a minimum<br />
of (60% marks at B.Pharm. Degree).<br />
Five seats are for sponsored candidates.<br />
Minimum 60% marks at B. Pharm.<br />
Reservation only for 2 S.C. + 1 S.T. Candidate is prioded.<br />
A letter from the sponsor regarding the payment of sponsorship should accompany with the<br />
application form.<br />
Preference will be given to <strong>SNDT</strong> Women’s <strong>University</strong> Students.<br />
Any additional rules prescribed by the AICTE or <strong>SNDT</strong> Women’s <strong>University</strong> will be applicable.<br />
ATTEDACE REQUIRED :<br />
(a) A candidate shall be required to attend at least 75% of the number of lectures and the<br />
number of practicals separately for each subject to study in each semester, and only then,<br />
subject to other conditions being fulfilled be eligible to appear at the <strong>University</strong><br />
Examinations.<br />
(b) The Principal of the college will have the discretion to condone 10% of the attendance in<br />
Theory and / or Practicals of any one subject or subjects if he is fully convinced of the<br />
student’s absence on ground of health or for reasons beyond his control.<br />
(c) The <strong>SNDT</strong> Women’s <strong>University</strong> however, reserves its right to condone the additional<br />
absence, if fully represented by the student and recommended by the Principal.Each student<br />
3 | P a g e
shall be required to pass theory & practical examination which will be held at the end of<br />
each semester.<br />
Semester 1 and Semester II Each will be of 15 weeks duration.<br />
Pattern of Examination :<br />
The examination at the end of Semester I & II will be conducted by the <strong>SNDT</strong> Women’s<br />
<strong>University</strong>. At the end of semester IV, a viva-voice examination based on the research project and<br />
dissertation work submitted by the student will be conducted. There will not be any examination<br />
(internal or <strong>University</strong>) for two subject heads viz practicals in computing and statistics and<br />
spectral workshop.<br />
Internal assessment :<br />
There will be an internal assessment to the tune of 20% marks in each subject separately for<br />
theory and practicals. One periodic test of 20 marks will be conducted in given subjects during<br />
each semester.<br />
No repeat unit test in theory or practicals will be GIVEN.<br />
Standard of passing :<br />
(a) A candidate shall obtain at least 50% marks (internal assessment and semester examination<br />
combined) separately in theory and practical of each subject for passing in the <strong>University</strong><br />
examination. Failure to pass the semester I examination will not disqualify a candidate for<br />
presenting herself on a subsequent occasion. On a new application being forwarded and<br />
fresh fees paid, such a candidate will be allowed to keep terms and appear for the semester<br />
II examination, not withstanding the fact that she may not have cleared the semester I<br />
examination. A candidate who has failed to pass the Semester I or II examinations may<br />
present herself on a subsequent occasion on a new application being forwarded and fresh<br />
fee paid.<br />
Every candidate is allowed to continue her research work and submit a thesis for the<br />
award of degree in accordance with the relevant regulations but the result of the thesis will not be<br />
declared until she has cleared all the examinations previous.<br />
Every candidate registered for the degree of M. Pharm. shall be required to carry out<br />
research under the supervision and guidance of a recognized <strong>University</strong> teacher. Whole or a part<br />
of the research work could also be carried out in a research institution to be approved by the<br />
Principal. The research project shall be assigned within one month of the beginning of semester<br />
I. Two type-written copies of the thesis embodying the results of research project, ordinarily not<br />
exceeding 100 pages, together with a synopsis and a statement indicating to what extent this work<br />
is original, shall be submitted by the candidate to the principal, through her guiding teacher. The<br />
thesis shall be the candidate’s own work carried out under the guidance or supervision of her<br />
teacher and shall be submitted at the end of Semester IV. Provided further that a candidate who<br />
has submitted a synopsis of the thesis but is unable to produce the thesis under circumstances<br />
satisfying the Research Guide on the recommendation of the Research guide and the Principal,<br />
the thesis may be allowed to be submitted upto the end of the fifth term as a special case.<br />
At least two months before submitting her thesis, but not later than end of semester IV<br />
a candidate shall forward to the Principal, through the guide under whom she has worked or by<br />
whom she has been guided, a statement giving a title & synopsis of the thesis along with<br />
application form and fee prescribed by the <strong>University</strong>. In the synopsis, the candidate shall<br />
indicate the broad outline of the work carried out by her.<br />
4 | P a g e
Every candidate shall submit a certificate signed by the research guide<br />
under whom she has worked stating that there is a prime facie case for consideration<br />
of the thesis.<br />
The thesis shall be referred for examination and reported to two referees,<br />
to be appointed by the <strong>University</strong>, on the recommendation of the Ad-hoc Board of<br />
Studies in Pharmacy and one of the referees being always the guiding teacher. The<br />
referees shall jointly hold a viva-voce examination which shall be held only after<br />
the thesis has been evaluated by both the referees. The referees to whom the thesis<br />
is referred and report, shall, after evaluating the thesis and holding a joint viva-voce<br />
examination, to the <strong>University</strong> whether the thesis shall be accepted or rejected and<br />
their report shall be final. In case there is a difference of opinion between the<br />
examiners, the <strong>University</strong> shall appoint a third referee, and shall decide whether the<br />
degree is to be conferred or not after considering the reports of all the three<br />
referees.<br />
Provided that the thesis is accepted for the degree, it shall be given a<br />
grade, viz “A” ( very good ) or “B” (satisfactory). The grade to be awarded shall be<br />
decided by the referees jointly depending on the quality and the presentation of the<br />
research work and the performance at the viva-voca examination.<br />
Successful candidate shall be awarded class, as under, jointly on the basis<br />
of the results of the Semester I & II examinations and the thesis submitted by her.<br />
1 Those obtaining 65% or more marks out of the grand<br />
total at both the Semester I & Semester II examinations<br />
taken together and grade “A” in the thesis<br />
2 Those obtaining 65% or more marks out of the grand<br />
total at both the Semester I & Semester II examinations<br />
taken together and grade “B” in the thesis<br />
3 Those obtaining 55% to 64.99% marks out of the grand<br />
total at both the Semester I Semester II examinations<br />
taken together and grade “A” in the thesis<br />
1 st Class with Distinction<br />
1 st Class<br />
1 st Class.<br />
4 All other cases. IInd Class<br />
A thesis that has been rejected may be resubmitted after due revision and payment of<br />
fresh fee.<br />
5 | P a g e
Semester I<br />
SR.NO SUBJECT Exam.<br />
Dur.<br />
1 Analytical<br />
Techniques-I<br />
2 Product<br />
Development<br />
3 Biological<br />
Evaluation<br />
4 Quality<br />
Management-I<br />
5 Computing &<br />
Statistics<br />
Theory Exam. Practical<br />
Int. Ext. Total Dur. Int. Ext. Total<br />
3 20 80 100 6 20 80 100<br />
3 20 80 100 - - - -<br />
3 20 80 100 6 20 80 100<br />
3 20 80 100 - - - -<br />
3 20 80 100 - - - -<br />
Semester- II<br />
SR.NO SUBJECT Exam.<br />
Dur.<br />
1 Analytical<br />
Techniques-II<br />
2 Quality<br />
Management-II<br />
3 Product<br />
Development-II<br />
Theory Exam. Practical<br />
Int. Ext. Total Dur. Int. Ext. Total<br />
3 20 80 100 6 20 80 100<br />
3 20 80 100 - - - -<br />
3 20 80 100 6 20 80 100<br />
4 Packaging 3 20 80 100 - - - -<br />
5 Validation 3 20 80 100 - - - -<br />
6 | P a g e
Semester-III<br />
SR.NO SUBJECT Exam.<br />
Dur.<br />
1 Spectral<br />
workshop<br />
2 Project and<br />
Dissertation<br />
work.<br />
Theory Exam. Practical<br />
Int. Ext. Total Dur. Int. Ext. Total<br />
- - - - - - - -<br />
GRADE<br />
RULES FOR REFUND OF FEES FOR M.PHARM. COURSE.<br />
AS PER GOVERNMENT DIRECTIVES<br />
7 | P a g e
Analytical Techniques-I<br />
1. UV spectrophotometry (3)<br />
2. Spectofluorimetry (5)<br />
3. Absorption and Emission spectroscopy (4)<br />
4. IR Spectrometry (9)<br />
5. ORD & CD (4)<br />
6. Phase Solubility Analysis (1)<br />
7. Termal Analysis (3)<br />
8. X-Ray diffraction Analysis (2)<br />
9. Water determination (2)<br />
10. Radiochemical method of Analysis and (5)<br />
QC of Radio-pharmaceuticals<br />
Analytical Techniques – I (Practicals) 150 hours<br />
Experiments involving the use of :<br />
1) UV<br />
2) Spectrofluorometer,<br />
3) Flame photometer,<br />
4) Atomic Absorption,<br />
5) IR Spectrometer<br />
8 | P a g e
PRODUCT DEVELOPMET-I<br />
1. Preformulation Studies: pka and solubility, kinetic pH profile, partition<br />
coefficient, crystal morphology, polymorphism, powder flow, surface<br />
characteristics, dissolution, compatibility studies, protocol for performulation<br />
studies.<br />
2. Solubilion Techniques: Determination of solubility, solubility<br />
parameters, methods of solubilization including addition of cosolvent, surface<br />
active agents, complexation, dielectric constant, hydrotrophy, chemical<br />
modification.<br />
3. Drug stability: solution stability, solid state stability, parameters for<br />
physical stability testing, programme, Acceterated studies and shelf life<br />
assignment.<br />
4. Tablets Technology: Formulation, manufacturing and evaluation with<br />
special emphasis to unit processes involved including mixing, drying, size<br />
reduction, granulation technology granulation technology, compression and<br />
compression cooling.<br />
5. Coating of solid dosage form: Aqueous and non-aqueous film coating,<br />
polymers, process controls, coating equipments, coating pans, Accela cota, Hicoater,<br />
Driacoater, fluid bed coating equipment e.g. Glatt & Kugel coating<br />
application and metering equipment, particle coating methods, pelletistion.<br />
6. Capsulation Technology: Gelatin-Physical and chemical properties,<br />
additives, substitutes, manufacture of hard gelatin capsules, printing machinery<br />
and operation involved, filling of powders, semisolids and liquids in capsules.<br />
7. Liquid Dosage forms: Formulation, stabilization and evaluation of liquid<br />
dosage forms including suspensions and emulsions, Processing and equipments<br />
used in manufacture.<br />
8. Parenteral Technology: Formulation, stabilization and manufacture of<br />
small and large volume parenterals, stabilization, evaluation and quality control,<br />
9 | P a g e
environmental controls and design considerations for parenteral production<br />
facility, freeze drying.<br />
9. Pharmacokinetic Modelling : Two compartment model for IV and<br />
extravascular administration multiple dosing regiments, statistical moment<br />
analysis.<br />
10 | P a g e
BIOLOGICAL EVALUATIO<br />
1. Microbiological limit tests. (1)<br />
2. Sterility tests : Methodology & Interpretation (2)<br />
3. Tests for effectiveness of antimicrobial preservatives. (2)<br />
4. Preclinical Drug Evaluation acute (LD50),<br />
Subacute & chronic toxicity, Evaluation of a<br />
Compound for its biological activity, and ED 50<br />
determination, special toxicity tests like teratogenecity<br />
and mutagenecity, clinical trials<br />
5. Biological standaridisation : General principles, scope (8)<br />
and limitations of bioassay, Bioassays of some officical drugs<br />
6. Radioimmunoassay: General principles, scope and limitation. (2)<br />
Radioimmunoassay of some drugs like insulin, digitalls etc.<br />
7. Pyrogens-Production, chemistry and properties of bacterial (2)<br />
pyrogens and endotoxins, Mechanism of action of pyrogens,<br />
Pharmaceuticals aspects, Pyrogen test of IP compared to that of BP & USP,<br />
Interpretation of data, comparison of LAL and official pyrogen tests. (6)<br />
PRODUCT DEVELOPMET<br />
1. Preformulation studies : general considerations.<br />
2. Stability : accelerated studies; shelf-life assignment<br />
3. Animal studies<br />
4. Drug approval<br />
11 | P a g e
QUALITY MAAGEMET I<br />
1. Concept of Total Quality Management, Philosophy of GMP’S and GLPS,<br />
ISO9000.<br />
2. Organisation and personnel, responsibilities, training hygene, personnel<br />
records.<br />
3. Premises : Location, design, plant layout, construction, maintenance of<br />
sterilite areas, control of contamination.<br />
4. Equipment, selection, purchase specifications, maintenance clean in place<br />
and sterilize in place.<br />
5. Raw materials; purchase specifications, stores selection of vendors,<br />
controls on raw materials.<br />
6. Manufacture of and controls on various dosage forms, Manufacturing<br />
documents, Master Formula, Batch formula records, Standard Operation<br />
Procedure, Quality audits of manufacturing processes and facilities.<br />
7. In process quality controls on various dosage forms sterile and nonsterile.<br />
Standard Operation Producers for various operation like cleaning, filling,<br />
drying compression, coating, disinfection, fumigation, sterilization,<br />
membrane filteration etc.<br />
8. Packaging and labeling controls, line clearance and other packaging<br />
material.<br />
12 | P a g e
COMPUTIG & STATISTICS<br />
PART I<br />
1. Application of computers in pharmaceutical sciences, Stores<br />
Management and inventory control.<br />
2. Data processing : Systems analysis, development and creation of<br />
databse useful in pharmacy practice.<br />
3. Writing programmes in Basic for pharmaceutical calculations.<br />
4. Information acquisition and retrieval systems, abstracting services,<br />
Drug Information Systems, Hospital Information Systems.<br />
5. Statistics in Computing : Statistical data anlaysis, Quality Control<br />
charts using computers.<br />
6. Use of application software like Harvard graphics, Nonllin, Windows<br />
etc.<br />
7. Introduction to expert systems : Medical diagnosis aid systems.<br />
8. Computer modeling and simulation : Application in drug design and<br />
Quantitative Structure Activity Relationships.<br />
PART 2<br />
1. Probability and exectations, standard error of mean, confidence limits,<br />
hypothesis testing, T-Test, chi square test, analysis of variance, F-Test,<br />
standard error of estimates, least squares method. Correlation and<br />
regression coefficients. Coefficient of determination. Prediction of X.<br />
2. Application of statistics in pharmaceutical technology, statistical<br />
quality control and control of analytical methods.<br />
3. Biostatics and statistics in clinical research.<br />
13 | P a g e
M.Pharm. SEM II<br />
AALYTICAL TECHIQUES-II<br />
1. Chromatography:<br />
(a) TLC (B) Paper (c) GC (d) HPLC (e) HPTLC<br />
(f) Size exclusion Chromatography (g) Ion-pair chromatography<br />
2. ‘H’ & 13C NMR Spectrometry<br />
3. Mass Spectrometry<br />
AALYTICAL TECHICS – II (PRACTICALS)<br />
Experiments involving the use of :<br />
1. TLC<br />
2. GC<br />
3. HPLC<br />
4. HPTLC<br />
14 | P a g e
PACKAGIG DEVELOPMET<br />
1. Glass containers for Pharmaceuticals: Glass types, their manufacture, chemical<br />
performance, testing and quality control.<br />
2. Plastics containers for pharmaceuticals : Classification of plastics, plastic<br />
polymers and their physico-chemical, mechanical and biological properties;<br />
Additives and fabrication processes. Plastic container for parentrals and<br />
transfusion sterile drip kits. Quality control testing and biological toxicity.<br />
3. Paper and paper board : Types of paper, folding cartons, quality control testing<br />
of paper and paper board.<br />
4. Metal containers: Aluminium and timplate, Drums, collapsible tubes and<br />
Aerosol containers, Lacquering, coating and lining.<br />
5. Caps and Closures : Types caps closure liners, childresistant caps. Elastomeric<br />
closures for parenterals, classification of elastomers, physical, chemical and<br />
biological properties and their quality control.<br />
6. Labels and labeling : Types of labels, adhesives, inject and barcoding.<br />
7. Flexible packaging : Types of films, Co-extruded films, foils, coating and<br />
laminates, shrink and stretch films.<br />
8. Corrugated and solid fibre boards and boxes : Type of corrugation methods.<br />
9. Tranist worthiness of package.<br />
10. Packaging Machinery Including strip packaging, form, fill and seal machines,<br />
liquid and solid filling machines, capping machines.<br />
11. Product-Package compatibility,: stability of product, packaging selection and<br />
development criteri.<br />
12.Tamper evident packaging systems.<br />
15 | P a g e
VALIDATIO<br />
1. Qualification, Validation and calibration of equipment.<br />
2. Validation of process like mixing, granulation, drying, compression<br />
filtration filling etc.<br />
3. Validation of sterilization methods and equipment, Dry heat sterilization,<br />
Autoclaving, membrane filteration.<br />
4. Validation and audits of analytical procedures.<br />
5. Validation and personnel.<br />
6. Validation of air handling equipment in sterile and non-sterile areas.<br />
7. Validation of water supply system, dematerialized, distilled water for<br />
injection.<br />
8. Validation and security measures for electronic data processing.<br />
16 | P a g e
QUALITY MAAGEMET-II<br />
1. Quality control laboratory responsibilities, good laboratory practices,<br />
routine controls, instruments, sampling plans, standard test producers,<br />
non-clinical testing, controls on animal house, Data generation and<br />
storage, Quality control<br />
Documentation, retention samples, records, Audits of quality control<br />
facilities.<br />
2. Finished product release, Quality review, Quality audit. Batch release<br />
documents.<br />
3. Warehousing, good warehousing practices materials management.<br />
4. Distribution and distribution records. Handling of returned goods.<br />
Recovered materials and reprocessing.<br />
5. Complaints and recalls, evaluation of complaints, recall procedures,<br />
related records and documents.<br />
6. Waste disposal, scrap disposal producers and records.<br />
7. Regulatory aspects of pharmaceutical and bulk drug manufacture.<br />
Regulatory drug analysis.<br />
8. Loan license (contract manufacture) audits of.<br />
9. Recent amendmends to Drugs and Cosmetics Act and other relevant<br />
rules. Consumer protection Environmental Protection Act, Certification<br />
and licensing procedures.<br />
10. WHO certification, Globalization of drug industry. Introduction to export<br />
of drugs and import policy.<br />
11. Present status and scope of pharmaceutical industry in India.<br />
17 | P a g e
PRODUCT DEVELOPMET—II<br />
1. Dissolution Technology: Dissolution testing devices viz forced<br />
convection, non sink and sink devices, continuous flow through<br />
methods, effect of environmental factors during dissolution testing,<br />
dissolution rate test apparatus for suspensions, topical and transdermal<br />
products, suppositories and controlled release products, in-vitro-In-vivo<br />
correlations.<br />
2. Concepts and systems design for rate controlled delivery : Rate<br />
preprogrammed, activation modulated and feed back regulated drug<br />
delivery system,<br />
3. Oral Drug Delivery Systems : O smotic pressure controlled, membrane<br />
permeationv controlled pH controlled, Ion-exchange controlled, gel<br />
diffusion controlled and hydro dynamically.<br />
Balanced systems, modulation of gastro intestinal transit time.<br />
4. Mucosal drug delivery systems : Mechanism of transmucosal<br />
permeation and mucosal membrane models, Buccal, Nasal, pulmonary,<br />
rectal and vaginal drug delivery systems, delivery of peptide based<br />
pharmaceutical.<br />
5. Ocular delivery of drug : Ocular delivery of drugs, development of<br />
ocular controlled release therapeutic systems.<br />
6. Transdermal drug delivery: Premeation through skin, permeation<br />
enhancers, gel, technologies for developing transdermal drug delivery,<br />
systems and evaluation there of.<br />
7. Parenteral drug delivery systems: Injectable controlled released<br />
formulations, long acting contraceptive formulations, implantable drug<br />
delivery.<br />
8. Intrauterine drug delivery systems: Medicated IUDS, copper IUD,<br />
Homone releasing IUD.<br />
9. Site specific drug delivery: Active and passive targeting, monoclonal<br />
antibiodies for drug targeting particulate carrier systems, microphases,<br />
liposomes and nanoparticles.<br />
10. Drug Approval and preparation of documents.<br />
18 | P a g e