combustion process in si engines - National Institute of Technology
combustion process in si engines - National Institute of Technology
combustion process in si engines - National Institute of Technology
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
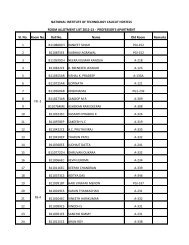
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES (ELECTIVE) (ME667)<br />
SIXTH SEMESTER<br />
propagation and prolongs the ignition lag. . This is the reason, the advance mechanism is<br />
also provided with change <strong>in</strong> load on the eng<strong>in</strong>e. This difficulty can be partly overcome<br />
by provid<strong>in</strong>g rich mixture at part loads but this def<strong>in</strong>itely <strong>in</strong>creases the chances <strong>of</strong> after-<br />
burn<strong>in</strong>g. The after burn<strong>in</strong>g is prolonged with richer mixture. In fact, poor <strong>combustion</strong> at<br />
part loads and neces<strong>si</strong>ty <strong>of</strong> provid<strong>in</strong>g richer mixture are the ma<strong>in</strong> disadvantages <strong>of</strong> S,I.<br />
eng<strong>in</strong>es which causes wastage <strong>of</strong> fuel and discharge <strong>of</strong> large amount <strong>of</strong> CO with<br />
exhaust gases.<br />
4. Turbulence : Turbulence plays very important role <strong>in</strong> <strong>combustion</strong> <strong>of</strong> fuel as the flame<br />
speed is directly proportional to the turbulence <strong>of</strong> the mixture. This is because, the<br />
turbulence <strong>in</strong>creases the mix<strong>in</strong>g and heat transfer coefficient or heat transfer rate<br />
between the burned and unburned mixture. The turbulence <strong>of</strong> the mixture can be<br />
<strong>in</strong>creased at the end <strong>of</strong> compres<strong>si</strong>on by suitable de<strong>si</strong>gn <strong>of</strong> the <strong>combustion</strong> chamber<br />
(geometry <strong>of</strong> cyl<strong>in</strong>der head and piston crown).<br />
Insufficient turbulence provides low flame velocity and <strong>in</strong>complete <strong>combustion</strong> and<br />
reduces the power output. But exces<strong>si</strong>ve turbulence is also not de<strong>si</strong>rable as it <strong>in</strong>creases<br />
the <strong>combustion</strong> rapidly and leads to detonation. Exces<strong>si</strong>ve turbulence causes to cool<br />
the flame generated and flame propagation is reduced.<br />
Moderate turbulence is always de<strong>si</strong>rable as it accelerates the chemical reaction,<br />
reduces ignition lag, <strong>in</strong>creases flame propagation and even allows weak mixture to burn<br />
efficiently.<br />
Eng<strong>in</strong>e Speed<br />
The turbulence <strong>of</strong> the mixture <strong>in</strong>creases with an <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> eng<strong>in</strong>e speed. For this<br />
reason the flame speed almost <strong>in</strong>creases l<strong>in</strong>early with eng<strong>in</strong>e speed. If the eng<strong>in</strong>e<br />
speed is doubled, flame to traverse the <strong>combustion</strong> chamber is halved. Double the<br />
orig<strong>in</strong>al speed and half the orig<strong>in</strong>al time give the same number <strong>of</strong> crank degrees for<br />
flame propagation. The crank angle required for the flame propagation , which is ma<strong>in</strong><br />
phase <strong>of</strong> <strong>combustion</strong> will rema<strong>in</strong> almost constant at all speeds. This is an important<br />
characteristics <strong>of</strong> all petrol eng<strong>in</strong>es.<br />
Jagadeesha T, As<strong>si</strong>stant Pr<strong>of</strong>essor, Department <strong>of</strong> Mechanical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Adichunchanagiri <strong>Institute</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Technology</strong>, Chikmagalur