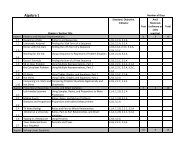
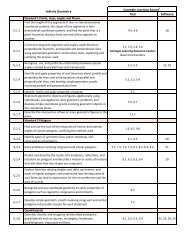
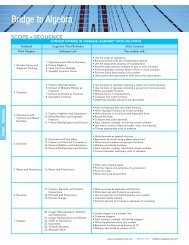
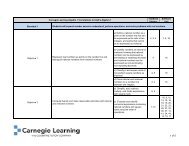
Integrated Math I Software Table of Contents – 2009‐2010
Integrated Math I Software Table of Contents – 2009‐2010
Integrated Math I Software Table of Contents – 2009‐2010
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<br />
<strong>Integrated</strong> <strong>Math</strong> I <strong>S<strong>of</strong>tware</strong> <strong>Table</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Contents</strong> <strong>–</strong> <strong>2009‐2010</strong> <br />
<br />
Unit 1 : Linear Patterns <br />
1‐1 : Finding Linear Patterns with Positive Rates <strong>of</strong> Change <br />
1‐2 : Finding Linear Patterns with Positive and Negative Rates <strong>of</strong> Change <br />
1‐3 : Finding Linear Patterns with Negative Starting Points <br />
Unit 2 : Linear Models and First Quadrant Graphs <br />
2‐1 : Graphing with Positive Rates <strong>of</strong> Change <br />
2‐2 : Graphing with Positive Rates <strong>of</strong> Change and Negative Starting Points <br />
2‐3 : Graphing with Negative Rates <strong>of</strong> Change and Positive Starting Points <br />
Unit 3 : Two‐Step Linear Equations <br />
3‐1 : Solving One‐Step Equations (Type In) <br />
3‐2 : Solving with Multiplication (No Type In) <br />
3‐3 : Solving with Multiplication (Type In) <br />
3‐4 : Solving with Division (No Type In) <br />
3‐5 : Solving with Division (Type In) <br />
3‐6 : Solving with a Variable in the Denominator (No Type In) <br />
3‐7 : Solving with a Variable in the Denominator (Type In) <br />
Unit 4 : Linear Models and Independent Variables <br />
4‐1 : Finding Independent Variables with Positive Rates <strong>of</strong> Change <br />
4‐2 : Finding Independent Variables with Starting Points <br />
4‐3 : Finding Independent Variables with Negative Rates <strong>of</strong> Change and Starting Points <br />
Unit 5 : Linear Models and Ratios <br />
5‐1 : Modeling Linear Functions with Ratios <br />
© Copyright 2009 Carnegie Learning, Inc.
<br />
Unit 6 : Linear Equations with Similar Terms <br />
6‐1 : Solving Two‐step equations (Type In) <br />
6‐2 : Solving by Combining Like Variable Terms and a Constant with Integers (No Type In) <br />
6‐3 : Solving by Combining Like Variable Terms and a Constant with Integers (Type In) <br />
6‐4 : Solving by Combining Like Variable Terms with Decimals (No Type In) <br />
6‐5 : Solving by Combining Like Variable Terms with Decimals (Type In) <br />
6‐6 : Solving by Combining Like Variable Terms and a Constant with Decimals (No Type In) <br />
6‐7 : Solving by Combining Like Variable Terms and a Constant with Decimals (Type In) <br />
Unit 7 : Linear Models and Four Quadrant Graphs <br />
7‐1 : Graphing with Positive Integer Rates <strong>of</strong> Change <br />
7‐2 : Graphing with Positive Fractional Rates <strong>of</strong> Change <br />
7‐3 : Graphing with Negative Rates <strong>of</strong> Change <br />
Unit 8 : Linear Models and Slope‐Intercept Graphs A <br />
8‐1 : Graphing given an Integer Slope and Y‐intercept <br />
8‐2 : Graphing given a Fractional Slope and Y‐intercept <br />
Unit 9 : Linear Equations and the Distributive Property <br />
9‐1 : Solving Linear Equations(Type In) <br />
9‐2 : Using Multiplication and Integers (No Type In) <br />
9‐3 : Using Multiplication and Integers (Type In) <br />
9‐4 : Using Multiplication and Decimals (No Type In) <br />
9‐5 : Using Multiplication and Decimals (Type In) <br />
9‐6 : Using Multiplication and Large Decimals (No Type In) <br />
9‐7 : Using Multiplication and Large Decimals (Type In) <br />
9‐8 : Using Division (No Type In) <br />
9‐9 : Using Division (Type In) <br />
9‐10 : Using Division with Additional Variable Term (No Type In) <br />
9‐11 : Using Division with Additional Variable Term (Type In) <br />
© Copyright 2009 Carnegie Learning, Inc.
<br />
Unit 10 : Linear Models and the Distributive Property <br />
10‐1 : Modeling with Integer Rates <strong>of</strong> Change <br />
10‐2 : Modeling with Fractional Rates <strong>of</strong> Change <br />
10‐3 : Modeling using the Distributive Property over Division <br />
10‐4 : Modeling More Complex Equations <br />
Unit 11 : Linear Equations with Variables on Both Sides <br />
11‐1 : Solving Linear Equations (Type In) <br />
11‐2 : Solving with Integers (No Type In) <br />
11‐3 : Solving with Integers (Type In) <br />
11‐4 : Solving with Decimals (No Type In) <br />
11‐5 : Solving with Decimals (Type In) <br />
11‐6 : Solving with Large Decimals (No Type In) <br />
11‐7 : Solving with Large Decimals (Type In) <br />
11‐8 : Solving Linear Equations with No Solution and Infinite Solutions (No Type In) <br />
Unit 12 : Perimeter and Area <strong>of</strong> Squares and Rectangles <br />
12‐1 : Finding Perimeter and Area <strong>of</strong> Squares and Rectangles <br />
Unit 13 : Perimeter and Area <strong>of</strong> Parallelograms <br />
13‐1 : Finding Perimeter and Area <strong>of</strong> Parallelograms <br />
Unit 14 : Perimeter and Area <strong>of</strong> Triangles <br />
14‐1 : Finding Perimeter and Area <strong>of</strong> Triangles <br />
Unit 15 : Perimeter and Area <strong>of</strong> Trapezoids <br />
15‐1 : Finding Perimeter and Area <strong>of</strong> Trapezoids <br />
Unit 16 : Circumference and Area <strong>of</strong> Circles <br />
16‐1 : Finding Circumference and Area <strong>of</strong> Circles <br />
Unit 17 : Area Composition <br />
17‐1 : Finding Area <strong>of</strong> Composite Figures <br />
Unit 18 : Perimeter and Area <strong>of</strong> Regular Polygons <br />
18‐1 : Finding Perimeter and Area <strong>of</strong> Regular Polygons <br />
<br />
Unit 19 : Pythagorean Theorem <br />
19‐1 : Finding the Length <strong>of</strong> the Hypotenuse <strong>of</strong> a Right Triangle <br />
© Copyright 2009 Carnegie Learning, Inc.
19‐2 : Finding the Length <strong>of</strong> a Leg <strong>of</strong> a Right Triangle <br />
19‐3 : Using the Pythagorean Theorem <br />
Unit 20 : Special Right Triangles <br />
20‐1 : Finding the Lengths <strong>of</strong> Sides <strong>of</strong> a 45‐45‐90 Triangle <br />
20‐2 : Finding the Lengths <strong>of</strong> Sides <strong>of</strong> a 30‐60‐90 Triangle <br />
Unit 21 : Right Triangles and Trigonometric Functions <br />
21‐1 : Finding Side Lengths using a Given Trigonometric Function <br />
21‐2 : Finding Side Lengths using One Trigonometric Function <br />
21‐3 : Finding Side Lengths using Multiple Trigonometric Functions <br />
Unit 22 : Quadratic Models and Area <br />
22‐1 : Modeling Quadratic Functions as Area <br />
Unit 23 : Quadratic Expression Factoring <br />
23‐1 : Factoring Trinomials with Positive Constants and Coefficients <strong>of</strong> One <br />
23‐2 : Factoring Trinomials with Negative Constants and Coefficients <strong>of</strong> One <br />
23‐3 : Factoring Trinomials with Positive Constants and Coefficients Other than One <br />
23‐4 : Factoring Trinomials with Negative Constants and Coefficients Other than One <br />
23‐5 : Factoring using Difference <strong>of</strong> Squares <br />
23‐6 : Factoring Quadratic Expressions <br />
Unit 24 : Quadratic Equation Solving <br />
24‐1 : Solving Quadratic Equations <br />
Unit 25 : Quadratic Models and Vertical Motion <br />
25‐1 : Using the Vertical Motion Model <br />
Unit 26 : Measures <strong>of</strong> Central Tendency <br />
26‐1 : Finding Mean, Median, Mode, and Range <br />
26‐2 : Determining Appropriate Measures <br />
26‐3 : Measuring the Effects <strong>of</strong> Changing Data Sets <br />
26‐4 : Finding a Data Value Given a Mean <br />
Unit 27 : Single Event Probability <br />
27‐1 : Finding Simple Probabilities <br />
27‐2 : Finding Disjoint Probabilities <br />
27‐3 : Finding Theoretical and Experimental Probabilities <br />
© Copyright 2009 Carnegie Learning, Inc.
Unit 28 : Independent and Dependent Probabilities <br />
28‐1 : Finding the Sample Space for Independent Events <br />
28‐2 : Finding the Sample Space for Dependent Events <br />
28‐3 : Finding the Sample Space for Independent and Dependent Events <br />
28‐4 : Finding Compound Probabilities <br />
Unit 29 : Graphing Using Slope and Y‐Intercept B <br />
29‐1 : Modeling with Intercepts <strong>of</strong> Zero <br />
29‐2 : Modeling with Fractional Slopes <br />
29‐3 : Modeling with Large Numbers <br />
Unit 30 : Finding Equations <strong>of</strong> a Line <br />
30‐1 : Modeling Given Slope and a Point <br />
30‐2 : Finding Slopes <br />
30‐3 : Modeling given Two Points <br />
30‐4 : Modeling Parallel and Perpendicular Lines <br />
30‐5 : Modeling Given an Initial Point <br />
Unit 31 : Systems <strong>of</strong> Linear Equations Modeling <br />
31‐1 : Solving Linear Systems using Integers <br />
31‐2 : Solving Linear Systems using Decimals <br />
Unit 32 : Linear and Quadratic Transformations <br />
32‐1 : Shifting Vertically <br />
32‐2 : Reflecting and Dilating using Graphs <br />
32‐3 : Shifting Horizontally <br />
32‐4 : Transformations using <strong>Table</strong>s <strong>of</strong> Values <br />
32‐5 : Using Multiple Transformations <br />
© Copyright 2009 Carnegie Learning, Inc.