Integrated Math II Software Table of Contents – 2009‐2010
Integrated Math II Software Table of Contents – 2009‐2010
Integrated Math II Software Table of Contents – 2009‐2010
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<br />
<strong>Integrated</strong> <strong>Math</strong> <strong>II</strong> <strong>S<strong>of</strong>tware</strong> <strong>Table</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Contents</strong> <strong>–</strong> <strong>2009‐2010</strong> <br />
<br />
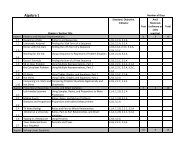
Unit 1 : Single Event Probability <br />
1‐1 : Finding Simple Probabilities <br />
1‐2 : Finding Disjoint Probabilities <br />
1‐3 : Finding Theoretical and Experimental Probabilities <br />
Unit 2 : Independent and Dependent Probabilities <br />
2‐1 : Finding the Sample Space for Independent Events <br />
2‐2 : Finding the Sample Space for Dependent Events <br />
2‐3 : Finding the Sample Space for Independent and Dependent Events <br />
2‐4 : Finding Compound Probabilities <br />
Unit 3 : Systems <strong>of</strong> Linear Equations Modeling <br />
3‐1 : Solving Linear Systems using Integers <br />
3‐2 : Solving Linear Systems using Decimals <br />
Unit 4 : Linear Models in General Form <br />
4‐1 : Modeling with Linear Inequalities <br />
4‐2 : Modeling Linear Equations in General Form <br />
Unit 5 : Graphs <strong>of</strong> Linear Equations in Two Variables <br />
5‐1 : Graphing Linear Equation Using a Given Method <br />
5‐2 : Graphing Linear Equation Using a Chosen Method <br />
Unit 6 : Systems <strong>of</strong> Linear Equations <br />
6‐1 : Solving Simple Systems <strong>of</strong> Linear Equations <br />
6‐2 : Solving Systems <strong>of</strong> Linear Equations <br />
Unit 7 : Graphs <strong>of</strong> Linear Inequalities in Two Variables <br />
7‐1 : Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables <br />
Unit 8 : Systems <strong>of</strong> Linear Inequalities <br />
8‐1 : Systems <strong>of</strong> Linear Inequalities <br />
© Copyright 2009 Carnegie Learning, Inc.
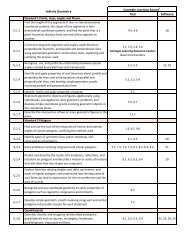
Unit 9 : Angles and Angle Pairs <br />
9‐1 : Measuring Angles <br />
9‐2 : Classifying Angles <br />
9‐3 : Classifying Angle Pairs <br />
9‐4 : Measuring Angles in a Triangle <br />
Unit 10 : Angle Relationships in a Triangle <br />
10‐1 : Finding Measures <strong>of</strong> Angles in Triangles <br />
Unit 11 : Angles Formed by Parallel Lines <br />
11‐1 : Finding Measures <strong>of</strong> Angles Formed with Parallel Lines <br />
Unit 12 : Similar Triangles <br />
12‐1 : Finding Corresponding Parts <strong>of</strong> Similar Triangles <br />
Unit 13 : Properties <strong>of</strong> Quadrilaterals and Parallelograms <br />
13‐1 : Finding Parts <strong>of</strong> Quadrilaterals and Parallelograms <br />
Unit 14 : Properties <strong>of</strong> Trapezoids and Rectangles <br />
14‐1 : Finding Parts <strong>of</strong> Rectangles <br />
14‐2 : Finding Parts <strong>of</strong> Trapezoids <br />
Unit 15 : Properties <strong>of</strong> Rhombi <br />
15‐1 : Finding Parts <strong>of</strong> Rhombi <br />
Unit 16 : Geometric Transformations <br />
16‐1 : Performing One Transformation <br />
16‐2 : Performing Two Transformations <br />
16‐3 : Performing Three Transformations <br />
Unit 17 : Exponential Modeling <br />
17‐1 : Modeling Equations with a Starting Point <strong>of</strong> One <br />
17‐2 : Modeling Equations with a Starting Point other than One <br />
17‐3 : Using Regression Models <br />
Unit 18 : Linear and Exponential Transformations <br />
18‐1 : Shifting Vertically <br />
18‐2 : Reflecting and Dilating using Graphs <br />
18‐3 : Shifting Horizontally <br />
18‐4 : Transforming using <strong>Table</strong>s <strong>of</strong> Values <br />
18‐5 : Using Multiple Transformations <br />
© Copyright 2009 Carnegie Learning, Inc.
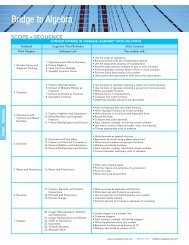
Unit 19 : Properties <strong>of</strong> Exponents <br />
19‐1 : Using the Product Rule <br />
19‐2 : Using the Quotient Rule <br />
19‐3 : Using the Power to a Power Rule <br />
19‐4 : Using the Product to a Power Rule <br />
19‐5 : Using the Quotient to a Power Rule <br />
19‐6 : Using Properties <strong>of</strong> Exponents with Whole Number Powers <br />
19‐7 : Simplifying Expressions with Negative Exponents <br />
19‐8 : Using Properties <strong>of</strong> Exponents with Integer Powers <br />
Unit 20 : Logarithmic and Exponential Equations <br />
20‐1 : Solving Base 10 Equations (No Type In) <br />
20‐2 : Solving Base 10 Equations (Type In) <br />
20‐3 : Solving Base e Equations (No Type In) <br />
20‐4 : Solving Base e Equations (Type In) <br />
20‐5 : Solving Any Base Equations (No Type In) <br />
20‐6 : Solving Any Base Equations (Type In) <br />
20‐7 : Solving Appreciation and Depreciation Equations (No Type In) <br />
20‐8 : Solving Appreciation and Depreciation Equations (Type In) <br />
Unit 21 : Quadratic Models in Factored Form <br />
21‐1 : Modeling Area as Product <strong>of</strong> Monomial and Binomial <br />
21‐2 : Modeling Area as Product <strong>of</strong> Two Binomials <br />
21‐3 : Maximizing Area <br />
Unit 22 : Linear and Quadratic Transformations <br />
22‐1 : Shifting Vertically <br />
22‐2 : Reflecting and Dilating using Graphs <br />
22‐3 : Shifting Horizontally <br />
22‐4 : Transformations using <strong>Table</strong>s <strong>of</strong> Values <br />
22‐5 : Using Multiple Transformations <br />
Unit 23 : Quadratic Models and Area <br />
23‐1 : Modeling Area <strong>of</strong> Rectangles <br />
© Copyright 2009 Carnegie Learning, Inc.
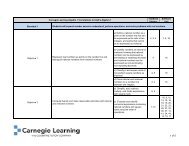
Unit 24 : Quadratic Expression Factoring <br />
24‐1 : Factoring Trinomials with Positive Constants and Coefficients <strong>of</strong> One <br />
24‐2 : Factoring Trinomials with Negative Constants and Coefficients <strong>of</strong> One <br />
24‐3 : Factoring Trinomials with Positive Constants and Coefficients Other than One <br />
24‐4 : Factoring Trinomials with Negative Constants and Coefficients Other than One <br />
24‐5 : Factoring using Difference <strong>of</strong> Squares <br />
24‐6 : Factoring Quadratic Expressions <br />
Unit 25 : Quadratic Equation Solving <br />
25‐1 : Solving Quadratic Equations <br />
Unit 26 : Quadratic Models in General Form <br />
26‐1 : Using Regression Models <br />
26‐2 : Modeling Projectile Motion from Ground <br />
26‐3 : Modeling Projectile Motion from Above Ground <br />
26‐4 : Modeling Projectile Motion <br />
Unit 27 : Cubic Models <br />
27‐1 : Modeling Volume <strong>of</strong> Cylinders <br />
27‐2 : Modeling Volume <strong>of</strong> Closed Prisms <br />
27‐3 : Modeling Volume <strong>of</strong> Open Prisms <br />
27‐4 : Using Given Cubic Models <br />
Unit 28 : Linear, Quadratic, Exponential, Cubic, and Square Root Transformations <br />
28‐1 : Transforming using Verbal Statements, Graphs, and Equations <br />
28‐2 : Transforming using <strong>Table</strong>s <strong>of</strong> Values <br />
Unit 29 : Polynomial Operations <br />
29‐1 : Adding Polynomials <br />
29‐2 : Adding Polynomials with Higher Orders <br />
29‐3 : Subtracting Polynomials <br />
29‐4 : Setting up a Factor <strong>Table</strong> <br />
29‐5 : Multiplying Polynomials using a Factor <strong>Table</strong> <br />
© Copyright 2009 Carnegie Learning, Inc.
<br />
<br />
Unit 30 : Rational Expressions <br />
30‐1 : Simplifying Rational Expressions <br />
30‐2 : Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions <br />
30‐3 : Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions <br />
Unit 31 : Systems <strong>of</strong> Linear Equations Modeling C <br />
31‐1 : Modeling Systems <strong>of</strong> Linear Equations <br />
© Copyright 2009 Carnegie Learning, Inc.