Global Update on Nutrition Labelling - The European Food ...
Global Update on Nutrition Labelling - The European Food ...
Global Update on Nutrition Labelling - The European Food ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
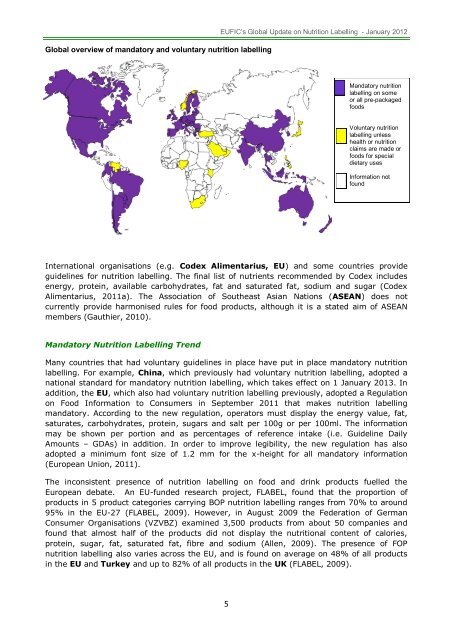
<str<strong>on</strong>g>Global</str<strong>on</strong>g> overview of mandatory and voluntary nutriti<strong>on</strong> labelling<br />
EUFIC’s <str<strong>on</strong>g>Global</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>Update</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong> Nutriti<strong>on</strong> <strong>Labelling</strong> - January 2012<br />
Mandatory nutriti<strong>on</strong><br />
labelling <strong>on</strong> some<br />
or all pre-packaged<br />
foods<br />
Voluntary nutriti<strong>on</strong><br />
labelling unless<br />
health or nutriti<strong>on</strong><br />
claims are made or<br />
foods for special<br />
dietary uses<br />
Informati<strong>on</strong> not<br />
found<br />
Internati<strong>on</strong>al organisati<strong>on</strong>s (e.g. Codex Alimentarius, EU) and some countries provide<br />
guidelines for nutriti<strong>on</strong> labelling. <strong>The</strong> final list of nutrients recommended by Codex includes<br />
energy, protein, available carbohydrates, fat and saturated fat, sodium and sugar (Codex<br />
Alimentarius, 2011a). <strong>The</strong> Associati<strong>on</strong> of Southeast Asian Nati<strong>on</strong>s (ASEAN) does not<br />
currently provide harm<strong>on</strong>ised rules for food products, although it is a stated aim of ASEAN<br />
members (Gauthier, 2010).<br />
Mandatory Nutriti<strong>on</strong> <strong>Labelling</strong> Trend<br />
Many countries that had voluntary guidelines in place have put in place mandatory nutriti<strong>on</strong><br />
labelling. For example, China, which previously had voluntary nutriti<strong>on</strong> labelling, adopted a<br />
nati<strong>on</strong>al standard for mandatory nutriti<strong>on</strong> labelling, which takes effect <strong>on</strong> 1 January 2013. In<br />
additi<strong>on</strong>, the EU, which also had voluntary nutriti<strong>on</strong> labelling previously, adopted a Regulati<strong>on</strong><br />
<strong>on</strong> <strong>Food</strong> Informati<strong>on</strong> to C<strong>on</strong>sumers in September 2011 that makes nutriti<strong>on</strong> labelling<br />
mandatory. According to the new regulati<strong>on</strong>, operators must display the energy value, fat,<br />
saturates, carbohydrates, protein, sugars and salt per 100g or per 100ml. <strong>The</strong> informati<strong>on</strong><br />
may be shown per porti<strong>on</strong> and as percentages of reference intake (i.e. Guideline Daily<br />
Amounts – GDAs) in additi<strong>on</strong>. In order to improve legibility, the new regulati<strong>on</strong> has also<br />
adopted a minimum f<strong>on</strong>t size of 1.2 mm for the x-height for all mandatory informati<strong>on</strong><br />
(<strong>European</strong> Uni<strong>on</strong>, 2011).<br />
<strong>The</strong> inc<strong>on</strong>sistent presence of nutriti<strong>on</strong> labelling <strong>on</strong> food and drink products fuelled the<br />
<strong>European</strong> debate. An EU-funded research project, FLABEL, found that the proporti<strong>on</strong> of<br />
products in 5 product categories carrying BOP nutriti<strong>on</strong> labelling ranges from 70% to around<br />
95% in the EU-27 (FLABEL, 2009). However, in August 2009 the Federati<strong>on</strong> of German<br />
C<strong>on</strong>sumer Organisati<strong>on</strong>s (VZVBZ) examined 3,500 products from about 50 companies and<br />
found that almost half of the products did not display the nutriti<strong>on</strong>al c<strong>on</strong>tent of calories,<br />
protein, sugar, fat, saturated fat, fibre and sodium (Allen, 2009). <strong>The</strong> presence of FOP<br />
nutriti<strong>on</strong> labelling also varies across the EU, and is found <strong>on</strong> average <strong>on</strong> 48% of all products<br />
in the EU and Turkey and up to 82% of all products in the UK (FLABEL, 2009).<br />
5