Thermocouple Circuit Thermocouple Thermometry
Thermocouple Circuit Thermocouple Thermometry
Thermocouple Circuit Thermocouple Thermometry
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
มว<br />
NIMT<br />
<strong>Thermocouple</strong> <strong>Thermometry</strong><br />
Theory<br />
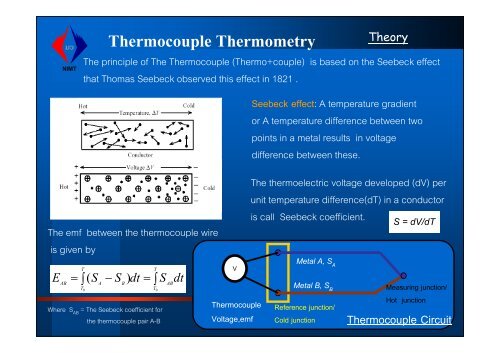
The principle of The <strong>Thermocouple</strong> (Thermo+couple) is based on the Seebeck effect<br />
that Thomas Seebeck observed this effect in 1821 .<br />
Seebeck effect: A temperature gradient<br />
or A temperature difference between two<br />
points in a metal results in voltage<br />
difference between these.<br />
The emf between the thermocouple wire<br />
is given by<br />
E<br />
AB<br />
T<br />
= ∫ ( S<br />
T<br />
0<br />
A<br />
− S<br />
B<br />
) dt<br />
T<br />
= ∫ S<br />
Where S AB = The Seebeck coefficient for<br />
the thermocouple pair A-B<br />
T<br />
0<br />
AB<br />
dt<br />
V<br />
<strong>Thermocouple</strong><br />
Voltage,emf<br />
The thermoelectric voltage developed (dV) per<br />
unit temperature difference(dT) in a conductor<br />
is call Seebeck coefficient. S = dV/dT<br />
Metal A, S A<br />
Metal B, S B<br />
Reference junction/<br />
Cold junction<br />
Measuring junction/<br />
Hot junction<br />
<strong>Thermocouple</strong> <strong>Circuit</strong>
Inhomogeneity Error In <strong>Thermocouple</strong><br />
•TC As Use<br />
“The variation of the thermocouple output along the used length.”<br />
E=S 12 (T1-T2)=small<br />
1 2 3 4<br />
TC emf,E<br />
E=S 23 (T2-T3)=largeE=S 34 (T3-T4)=small<br />
Un-Aged<br />
wire<br />
Transition<br />
wire<br />
Aged<br />
wire<br />
1 2<br />
3<br />
4<br />
•TC in calibration furnace<br />
Causes of inhomogeneity in thermocouple wire:<br />
-Cold work (bending, twisting,etc.)<br />
-Chemical (environment and in-use)<br />
-Heat treatment (above 250 o C for base-metal)<br />
- Change in immersionMeaningless results.<br />
Typical inhomogeneity for new <strong>Thermocouple</strong>;<br />
Pt thermocouple S R B ≈ ± 0.02%of E<br />
Base-metal thermocouple ≈ ± 0.1%of E<br />
(test by Thermal Scan)
<strong>Thermocouple</strong> Types<br />
TC In Use<br />
Standard Type<br />
(Letter-designed types)<br />
Non Standard Type<br />
(Special designed)<br />
Noble (Rare) Metal<br />
Type B, R ,S<br />
Base Metal<br />
Type E,J,K,N,T<br />
Pt/Pd, Au/Pt,<br />
W3-Re/W25-Re(Type C)<br />
General Range use :<br />
•Type R or Type S < 1300 o C , Type B > 1300 o C.<br />
•Type T,E and K At low temp / Room temp.<br />
•Type K (< 200 o C), Type N (300 – 600) o C.<br />
• Type K, N > 600 o C.
NIMT <strong>Thermocouple</strong> Calibration System<br />
ITS-90<br />
- Calibration Method-<br />
มว<br />
NIMT<br />
SPRT / HSPRT<br />
(-38.8344 o C to 961.78 o C )<br />
NIMT Fixed Point Cell<br />
Triple point of Mercury,Triple point of Water,Melting point<br />
of Galium, Freezing point of Tin,Freezing point of<br />
Zinc,Freezing point of Aluminum,Freezing point of Silver<br />
(-38.8344 o C to 961.78 o C )<br />
Nobel Metal TC<br />
NPL(UK), NMIA(Aus)<br />
Reference Standard <strong>Thermocouple</strong><br />
(Pt/Pd ,Au/Pt,Type B,Type R ,Type S)<br />
(0 o C to 1100 o C )<br />
1.Comparison with Fixed Point<br />
Range (0 o C-962 o C)<br />
Uncertainty 0.4 o C – 0.5 o C<br />
Calibration Laboratory<br />
SPRT<br />
IPRT<br />
<strong>Thermocouple</strong><br />
(All Type)<br />
DTM<br />
LIG<br />
USERS<br />
NIMT Traceability Chart(2006)<br />
2.Comparison with SPRT / Ref. TC<br />
Range (0 o C-1100 o C)<br />
Uncertainty 0.5 o C – 1.5 o C