Denition approach of learning new topics
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
18 3 EXAMPLES OF WHAT IS A LIMIT?<br />
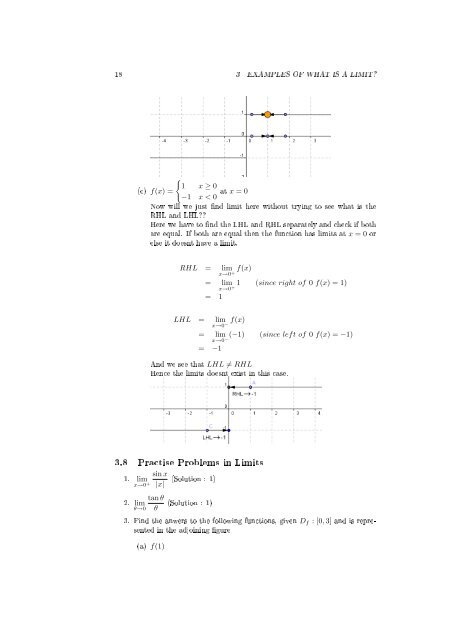
{<br />
1 x ≥ 0<br />
(c) f(x) =<br />
−1 x < 0 at x = 0<br />
Now will we just nd limit here without trying to see what is the<br />
RHL and LHL??<br />
Here we have to nd the LHL and RHL separately and check if both<br />
are equal. If both are equal then the function has limits at x = 0 or<br />
else it doesnt have a limit.<br />
RHL = lim<br />
x→0 + f(x)<br />
= lim 1<br />
x→0 +<br />
(since right <strong>of</strong> 0 f(x) = 1)<br />
= 1<br />
LHL = lim<br />
x→0 − f(x)<br />
= lim (−1)<br />
x→0 − (since left <strong>of</strong> 0 f(x) = −1)<br />
= −1<br />
And we see that LHL ≠ RHL<br />
Hence the limits doesnt exist in this case.<br />
3.8 Practise Problems in Limits<br />
1. lim<br />
x→0 + sin x<br />
|x|<br />
2. lim<br />
θ→0<br />
tan θ<br />
θ<br />
(Solution : 1)<br />
(Solution : 1)<br />
3. Find the anwers to the following functions, given D f : [0, 3] and is represented<br />
in the adjoining gure<br />
(a) f(1)