Denition approach of learning new topics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
4 1 CARTESIAN COORDINATE SYSTEM<br />
Part I<br />
Lecture I<br />
We start are understanding dening the coordinate space. And further will use<br />
this to understand functions and physical implications <strong>of</strong> function, derivative<br />
and integration.<br />
1 Cartesian coordinate system<br />
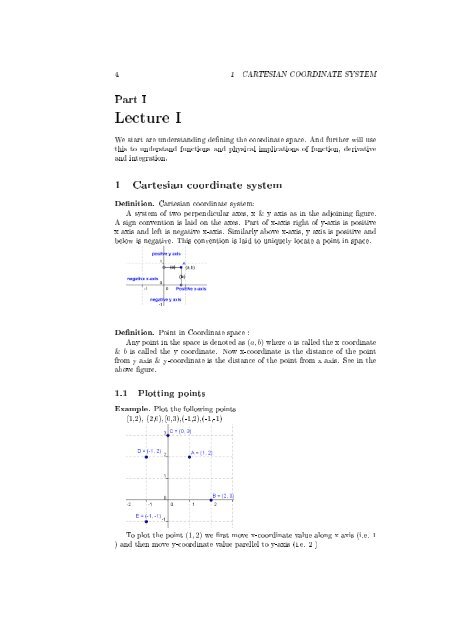
<strong>Denition</strong>. Cartesian coordinate system:<br />
A system <strong>of</strong> two perpendicular axes, x & y axis as in the adjoining gure.<br />
A sign convention is laid on the axes. Part <strong>of</strong> x-axis right <strong>of</strong> y-axis is positive<br />
x axis and left is negative x-axis. Similarly above x-axis, y axis is positive and<br />
below is negative. This convention is laid to uniquely locate a point in space.<br />
<strong>Denition</strong>. Point in Coordinate space :<br />
Any point in the space is denoted as (a, b) where a is called the x coordinate<br />
& b is called the y coordinate. Now x-coordinate is the distance <strong>of</strong> the point<br />
from y axis & y-coordinate is the distance <strong>of</strong> the point from x axis. See in the<br />
above gure.<br />
1.1 Plotting points<br />
Example. Plot the following points<br />
(1,2), (2,0),(0,3),(-1,2),(-1,-1)<br />
To plot the point (1, 2) we rst move x-coordinate value along x axis (i.e. 1<br />
) and then move y-coordinate value parellel to y-axis (i.e. 2 )