Critical Imaging Diagnoses: - Radiology
Critical Imaging Diagnoses: - Radiology
Critical Imaging Diagnoses: - Radiology
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
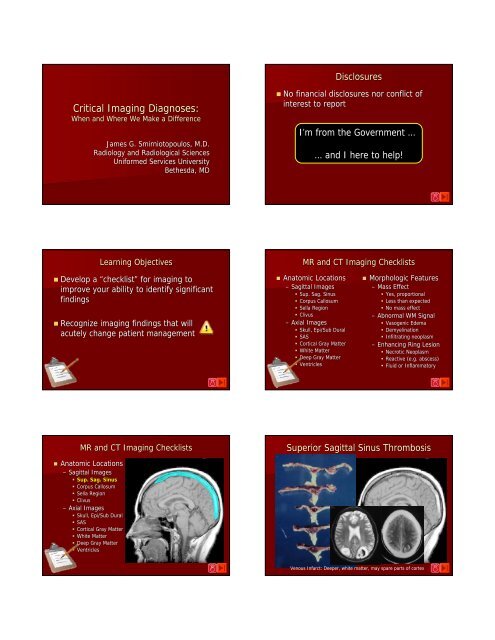
Disclosures<br />
<strong>Critical</strong> <strong>Imaging</strong> <strong>Diagnoses</strong>:<br />
When and Where We Make a Difference<br />
James G. Smirniotopoulos, M.D.<br />
<strong>Radiology</strong> and Radiological Sciences<br />
Uniformed Services University<br />
Bethesda, MD<br />
• No financial disclosures nor conflict of<br />
interest to report<br />
I’m from the Government …<br />
… and I here to help!<br />
Learning Objectives<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Develop a “checklist” for imaging to<br />
improve your ability to identify significant<br />
findings<br />
• Recognize imaging findings that will<br />
acutely change patient management<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Enhancing Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Superior Sagittal Sinus Thrombosis<br />
Venous Infarct: Deeper, white matter, may spare parts of cortex
Sup. Sag. Sinus Thrombosis<br />
• Dehydration<br />
• Paraneoplastic Syndromes w/hypercoag<br />
• Spinal Anesthesia<br />
• Post-partum<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Gliomatosis Cerebri<br />
Diffuse Astrocytoma of Corpus Callosum:<br />
“Butterfly Glioma”<br />
Gliomatosis cerebri: 2 or more lobes infiltrated by a diffuse astrocytoma<br />
Courtesy of R.D. Zimmerman, NY<br />
Diffuse Astrocytoma of Corpus Callosum:<br />
“Butterfly Glioma”<br />
Corpus Callosum Lesions<br />
Glioblastoma:<br />
Central Necrosis<br />
CNS Lymphoma:<br />
Hyperdense
Lymphoma: hyperdense<br />
PCNSL<br />
FLAIR<br />
Low water content … hyperattenuation<br />
T2W<br />
Low water content … restricted diffusion<br />
T1W Gd+<br />
CNS Lymphoma Micro Pathology<br />
Small * Round * Blue-Cell Tumor<br />
• DENSELY CELLULAR<br />
• Perivascular infiltration<br />
• Increased RETICULIN fibers<br />
• HIGH N/C (nuclear/cytoplasm)<br />
• Small Round Blue Cell Tumor<br />
• High attenuation/low signal intensity<br />
Perivascular<br />
Infiltrate<br />
Rimphoma<br />
RIM PHOMA
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Bitemporal Hemianopsia<br />
Mass Lesion Presentation<br />
Bitemporal Hemianopsia<br />
Met Hemoglobin in<br />
Sella Region<br />
Macroadenoma<br />
Pituitary Adenoma<br />
• Adult Patient<br />
• Microadenoma<br />
– < 10 mm<br />
– entirely within gland<br />
– Endocrine Sx.<br />
• Prolactinoma F<br />
• Acromegaly<br />
• Gigantism<br />
• Cushing Disease<br />
• Macroadenoma<br />
– > 10 mm<br />
– balloon sella<br />
– Visual Sx<br />
• if >6 mm above sella<br />
• bitemporal hemianopsia<br />
Pituitary MACRO-Adenoma<br />
Adenoma
Met Hemoglobin in<br />
Sella Region<br />
Macroadenoma<br />
Pituitary Apoplexy<br />
Pituitary Apoplexy<br />
David and Goliath<br />
• Did Goliath have Gigantism and/or<br />
Acromegaly?<br />
• He was a “Giant”<br />
• He was an Angry Giant from HA and ICP<br />
• Did he have a Macroadenoma?<br />
– David was able to sneak up to him<br />
• bitemporal hemianopsia<br />
• “Tunnel Vision”<br />
– One stone to the head killed him<br />
• Pituitary Apoplexy<br />
• Hemorrhage into a macroadenoma<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Craniopharyngioma – Bright T1W<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Bilateral Abducens (CNN6) Palsy
Chordoma<br />
Bulky Clival Mass<br />
Chordoma<br />
Midline Bone<br />
Destruction<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Depressed Skull Fx<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Small EDH, no herniation, can be<br />
managed with observation<br />
☺<br />
Smile of the Quadrigeminal Cistern
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
2 y.o. with Lethargy<br />
Child Abuse?<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Headache, Kernig & Brudzinski+<br />
History<br />
• 42 y.o. . woman with acute onset of:<br />
– “the worst headache of my life”<br />
• No papilledema<br />
• Kernig Sign +<br />
• Brudzinski Sign +<br />
Kernig sign: Pain elicited by<br />
straightening the knee with the<br />
hip/thigh flexed.<br />
Brudzinski sign: Pain and/or rigidity<br />
with simultaneous neck and knee/hip<br />
flexion.<br />
ICA Aneurysm<br />
ICA Aneurysm
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Fever, Kernig +, Brudzinski +<br />
Subarachnoid Space Enhancement<br />
Leptomeningeal Enhancement - Pneumococcal Meningitis<br />
Bacterial glycopeptides cause Breakdown in the BBB<br />
and contrast leaks into CSF in the SAS<br />
Zulmarie Roig, , MD and Gil Gonzalez, MD, MGH<br />
CSF Spread - Zuckerguss<br />
Serpentine - Cortical Gyral<br />
Carcinomatous Meningitis<br />
Meningitis<br />
Encephalitis<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Hx: 23 y.o. w/confusion<br />
HSV Encephalitis
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Hx: 53 y.o. left sided weakness<br />
CVA: Progression Over 3 Days<br />
Day 1 Day 3<br />
No Sulci<br />
Low attenuation<br />
“Insular Ribbon” Sign<br />
Cerebral Infarction<br />
Cerebral Infarction<br />
MCA<br />
MCA<br />
2 hrs of Sx 4 hrs of Sx<br />
2 hrs of Sx 4 hrs of Sx<br />
DWI<br />
ADC<br />
Chronic Infarct<br />
DWI<br />
ADC<br />
Hemorrhagic Transformation<br />
• Reperfusion Injury<br />
– Restoration of Systemic pressure into dead<br />
brain<br />
• Function of Ischemic Volume<br />
– Entire MCA vs. branch<br />
• Function of Time<br />
– IV TPA up to 3 hrs<br />
– IA up to 6 hrs<br />
– Desmoteplase up to 9 hrs<br />
Anterior Cerebral Artery
PCA Infarct<br />
DWI<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Hx: 13 y.o. w/ Seizures<br />
Another Cortical Wedge Lesion<br />
Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor (DNET)<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
65 y.o. HT had TAH/BSO<br />
Proton Density<br />
T1W<br />
Anoxia During Surgery<br />
Anoxia During Surgery<br />
Diffuse patchy abnormal loss of normal attenuation in cortical gray-matter.<br />
Ischemic gray-matter, cortical (ACA & MCA) and basal ganglia (caudate).<br />
NOTE: Relative sparing of the PCA (occipital lobes and thalami)
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
34 y.o. woman w/Coma<br />
34 yo comatose woman, psychiatric pt.<br />
Courtesy Aimee Hawley, M.D. MGAFMC<br />
Findings<br />
• Intraaxial<br />
• Diffuse Bilateral abnormalities<br />
– Low attenuation in Cortical Gray Matter<br />
– Low attenuation in basal ganglia<br />
• “Edema”<br />
– What Kind?<br />
• Interstitial<br />
• Cytotoxic<br />
• Hydrostatic<br />
Lab: Serum Na+ 121<br />
• Psychogenic polydipsia<br />
• Overhydration<br />
Water Intoxication<br />
– Athletes drinking too much water<br />
• Iatrogenic<br />
– D5W w/o salts<br />
• Treatment<br />
– Fluid restriction<br />
– Ringer’s s Lactate or Hypertonic Saline<br />
• 1.8% saline (not 4%NS and NOT D5W)<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Woman w/confusing symptoms<br />
Multiple Sclerosis<br />
Small Ovoid Lesions perpendicular to lateral ventricle
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Acute Pure Motor Hemiplegia<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
14 yo girl with congenital HIV<br />
TOXOPLASMOSIS<br />
14 yo AA girl with congenital HIV and CD4 count of 50 presents with<br />
mental status change, high fever, and two weeks of watery diarrhea<br />
Toxoplasmosis<br />
Left thalamic<br />
mass –low<br />
attenuation with<br />
hyperdense rim;<br />
hypointense T2<br />
rim (collagen<br />
capsule); smooth,<br />
round rim<br />
enhancement,<br />
surrounding<br />
vasogenic<br />
edema, restricted<br />
diffusion<br />
Typical deep gray matter paracentral abscesses with rim<br />
enhancement and surrounding edema<br />
Toxoplasmosis: Calcification after Treatment<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
71 yo man with HIV/AIDS<br />
Lesions shrinks, vasogenic edema resolves, calcification
1° CNS Lymphoma<br />
71 yo AA man with a history of<br />
HIV/AIDS presented with gait instability<br />
Low SI mass<br />
lesions in the<br />
right MCP, left<br />
insula, and left<br />
thalamus<br />
with<br />
surrounding<br />
vasogenic<br />
edema<br />
The T1-<br />
weighted post<br />
gadolinium<br />
images show<br />
predominantly<br />
ring<br />
enhancement<br />
with areas of<br />
central<br />
necrosis<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Coma at home after Ice Storm<br />
Medial Lenticular – Globus Pallidus<br />
Toxic and Metabolic<br />
•Intrinsic<br />
–Diabetic<br />
Ketoacidosis<br />
–Hypoglycemic Coma<br />
CO Poisoning: Selective for Globus Pallidus<br />
•Extrinsic<br />
Toxic Exposure<br />
–CO<br />
–Methanol, Ethylene Glycol<br />
–Solvent<br />
Leukoencephalopathy<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Bruns Syndrome – Positional HA<br />
Chronic HA – Acutely Worse<br />
Hydrocephalus: Vents > Sulci
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Positional Headaches<br />
3 rd Ventricle Cysticercosis<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Intraventricular Meningioma<br />
McCain - Palin - Smirniotopoulos<br />
John … How did<br />
we Lose?
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
Obtunded w/blown pupil<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
Brain Herniation Syndromes<br />
t<br />
f<br />
t<br />
Brain Herniation Syndromes<br />
Pupillary Reaction<br />
f<br />
C<br />
t<br />
U<br />
M<br />
t<br />
T<br />
T<br />
Blown Pupil:<br />
CNN3 (Oculomotor) nerve<br />
ipsilateral to the mass<br />
lesion. Note CNN4
Pupil - Intrinsic Ocular Muscle<br />
“Blown Pupil”<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
BP 180/135, HA, Hemiplegia<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
Long-standing Headache (yrs)<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
Two Pts: Compare Mass Effect<br />
Long-standing Headache (yrs)<br />
New onset Seizures<br />
AVM – No Mass Effect<br />
GBM – Has Mass Effect
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
Vasogenic Edema<br />
• A type of interstitial edema produced by<br />
abnormally increased capillary permiability<br />
• Spreads from site of abnormal vessels at<br />
~7-10 mm/week<br />
• May reach a steady-state<br />
state – can’t t estimate<br />
age of lesion from extent of edema<br />
• Spreads along association tracts > cortico-<br />
spinal tracts >>> commissures<br />
• Finger-like<br />
pseudopods of watery white<br />
matter<br />
Meningioma with extensive Edema<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
Glioblastoma Multiforme<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
T1-gad<br />
Neoplastic cells<br />
extend into the<br />
edema … and<br />
beyond, into the<br />
“normal” WM<br />
T2
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
Seizure and Obtundation<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• More than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
Hemorrhage into a Pre-existing existing mass<br />
Acute hemiplegia and confusion in a 68 year old man<br />
NOTE: Vasogenic Edema<br />
Courtesy Doug Phillips, UVA<br />
GBM<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
Variable and Confusing Sx<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
Courtesy Doug Phillips, UVA<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
Severe HA, HIV+<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
Lesion w/o Mass Effect - PML
T2W – Geographic hyperintensity<br />
FLAIR Geographic hyperintensity, no mass<br />
Looks like vasogenic edema<br />
Courtesy Jacqueline Bello, M.D.<br />
Looks like vasogenic edema …<br />
but, affects the corpus<br />
callosum<br />
Courtesy Jacqueline Bello, M.D.<br />
T1 w/Gd – No enhancement<br />
PML<br />
Looks like vasogenic edema …<br />
but, no enhancement !<br />
Courtesy Jacqueline Bello, M.D.<br />
No Mass, No Enhancement<br />
Courtesy Jacqueline Bello, M.D.<br />
Progressive<br />
Multifocal<br />
Leukoencephalopathy<br />
• WM Disease - JC Papova/Polyoma Virus<br />
– Initials of first patient cultured (1)<br />
• John<br />
Cunningham<br />
• Tx for Hodgkins, , died from PML in 1971<br />
• Lysis of Oligodendrocytes<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Geographic and Peripheral<br />
– Little or No Mass Effect<br />
– Little or No Enhancement<br />
• Poor Survival of 2-62<br />
6 months reported<br />
• Improved survival w/ HAART - up to 3-43<br />
4 years<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
Severe HA, HIV+<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory
PML<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
WHO Gr 2 Astrocytoma (“gliomatosis<br />
gliomatosis cerebri”)<br />
(“edema” w/o contrast enhancement)<br />
Gliomatosis Cerebri:<br />
Diffuse Astrocytoma – 2 lobes<br />
NOTE: Although this looks like “vasogenic edema” – there is no enhancement.<br />
Vasogenic edema often spares the internal capsule. This is NOT edema secondary to<br />
a lesion. This is the tumor itself infiltrating through the white-matter.<br />
T2<br />
T1-gad<br />
Infiltrates through White Matter Tracts<br />
Gliomatosis Cerebri<br />
CHO<br />
Cr<br />
NAA ?<br />
{
T1W Gd+ + in Two Astrocytomas<br />
Without Contrast Enhancement, it<br />
can’t be “vasogenic” edema?<br />
Why does it look like like interstitial<br />
vasogenic edema? Microcystic change<br />
Gr 4 Astrocytoma<br />
Neovascularity w/BBB causes<br />
contrast Enhancement and<br />
“vasogenic” edema<br />
Gr 2 Astrocytoma<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
Fever, HA, Recent Dental work<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
Abscess<br />
Mag. susceptibility from<br />
atomic oxygen in<br />
macrophages
Abscess<br />
Brain Abscess<br />
AA<br />
Peaks<br />
Inverted<br />
AA Peaks<br />
DWI<br />
Short TE MRS<br />
Long TE MRS<br />
Viscous Pus and Coagulation Necrosis<br />
MRS Courtesy of Mauricio Castillo - UNC<br />
DWI: Necrosis vs. PUS<br />
Ring Lesion Differences<br />
GBM<br />
Abscess<br />
“We conclude that viable cell density is the main biological parameter<br />
responsible for restricted diffusion in brain abscess, and it is not<br />
influenced by the etiological agents responsible for its causation.”<br />
Magn. reson. med. 2005, vol. 54, no4, pp. 878-885<br />
GBM<br />
Abscess - Toxo<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
Fluid Secreting Pilocytic Astrocytoma<br />
Nodule<br />
“Cyst”<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
5 min.<br />
Neoplasm + thin<br />
rim of enhancing<br />
gliosis
Fluid Secreting Tumor: Pilocytic Astrocytoma<br />
Fluid Secreting Tumor: Pilocytic Astrocytoma<br />
NOTE: Fluid has protein – not identical to CSF signal nor attenuation<br />
Fluid Secreting Tumor: Ganglioglioma<br />
Enhancement w/o Vasogenic Edema<br />
“open ring<br />
sign”<br />
Absent vasogenic edema … signal abnormality ends at<br />
edge of enhancement<br />
Open (Incomplete) Ring Sign<br />
• Demyelinating Disease<br />
• Fluid-secreting<br />
“Cystic” Neoplasms<br />
Inflammatory Breakdown of the blood-brain-barrier from<br />
Enhancement w/o Vasogenic Edema<br />
a Demyelinating Lesion<br />
Masdeau JC, Moreira J, Trasi S, Visintainer P, Cavaliere R, Grundman M:<br />
The open ring. A new imaging sign in demyelinating disease.<br />
J.Neuroimaging 1996; 6(2):104-107.<br />
Masdeu JC, Quinto C, Olivera C, Tenner M, Leslie D, Visintainer P: Openring<br />
imaging sign: highly specific for atypical brain demyelination.<br />
Neurology 2000; 54(7):1427-1433.<br />
“incomplete ring”<br />
Absent vasogenic edema … signal abnormality ends at<br />
edge of enhancement & incomplete ring
31 yo ♀- Multiple Sclerosis<br />
“open ring sign”<br />
Enhance for 3-8 weeks<br />
Summary<br />
Perivenular<br />
Absent vasogenic edema … signal abnormality ends at<br />
inflammation<br />
edge of enhancement & incomplete ring<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
• Morphologic Features<br />
– Mass Effect<br />
• Yes, proportional<br />
• Less than expected<br />
• No mass effect<br />
– Abnormal WM Signal<br />
• Vasogenic Edema<br />
• Demyelination<br />
• Infiltrating neoplasm<br />
– Enhancing Ring Lesion<br />
• Necrotic Neoplasm<br />
• Reactive (e.g. abscess)<br />
• Fluid or Inflammatory<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
2 y.o. with Lethargy<br />
Cerebral Infarction<br />
MCA<br />
2 hrs of Sx 4 hrs of Sx<br />
MR and CT <strong>Imaging</strong> Checklists<br />
• Anatomic Locations<br />
– Sagittal Images<br />
• Sup. Sag. Sinus<br />
• Corpus Callosum<br />
• Sella Region<br />
• Clivus<br />
– Axial Images<br />
• Skull, Epi/Sub Dural<br />
• SAS<br />
• Cortical Gray Matter<br />
• White Matter<br />
• Deep Gray Matter<br />
• Ventricles<br />
Coma at home after Ice Storm<br />
DWI<br />
ADC<br />
Medial Lenticular – Globus Pallidus
T1W Gd+ + in Two Astrocytomas<br />
Without Contrast Enhancement, it<br />
can’t be “vasogenic” edema …<br />
it must be tumor infiltration<br />
Two Pts: Compare Mass Effect<br />
Long-standing Headache (yrs)<br />
New onset Seizures<br />
Gr 4 Astrocytoma<br />
Neovascularity w/BBB causes<br />
contrast Enhancement and<br />
“vasogenic” edema<br />
Gr 2 Astrocytoma<br />
AVM – No Mass Effect<br />
GBM – Has Mass Effect<br />
Hemorrhage into a Pre-existing existing mass<br />
Acute hemiplegia and confusion in a 68 year old man<br />
NOTE: Vasogenic Edema<br />
Courtesy Doug Phillips, UVA<br />
Thank You!<br />
ありがとうございます。 Visit 感 謝 us いたします。 on the web:<br />
rad.usuhs.edu<br />
Muito Obrigado<br />
EUXAPIΣTΩ !<br />
Muchas<br />
Gracias<br />
Mahalo !<br />
Dank u wel !<br />
Go Raibh Maith Agat<br />
Merci Beaucoup<br />
Danke Schön !