Mathematical Models for Nano Science - Politecnico di Milano
Mathematical Models for Nano Science - Politecnico di Milano
Mathematical Models for Nano Science - Politecnico di Milano
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
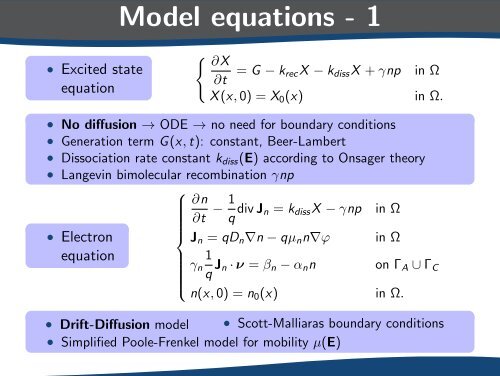
Model equations - 1<br />
• Excited state<br />
equation<br />
{ ∂X<br />
∂t = G − k recX − k <strong>di</strong>ss X + γnp in Ω<br />
X (x, 0) = X 0 (x) in Ω.<br />
• No <strong>di</strong>ffusion → ODE → no need <strong>for</strong> boundary con<strong>di</strong>tions<br />
• Generation term G(x, t): constant, Beer-Lambert<br />
• Dissociation rate constant k <strong>di</strong>ss (E) accor<strong>di</strong>ng to Onsager theory<br />
• Langevin bimolecular recombination γnp<br />
• Electron<br />
equation<br />
⎧<br />
∂n<br />
∂t − 1 q <strong>di</strong>v J n = k <strong>di</strong>ss X − γnp in Ω<br />
⎪⎨<br />
J n = qD n ∇n − qµ n n∇ϕ in Ω<br />
1<br />
γ n<br />
q J n · ν = β n − α n n on Γ A ∪ Γ C<br />
⎪⎩<br />
n(x, 0) = n 0 (x) in Ω.<br />
• Drift-Diffusion model • Scott-Malliaras boundary con<strong>di</strong>tions<br />
• Simplified Poole-Frenkel model <strong>for</strong> mobility µ(E)