Replantation of Avulsed Tooth after Trauma: A One Year ... - IJMD
Replantation of Avulsed Tooth after Trauma: A One Year ... - IJMD
Replantation of Avulsed Tooth after Trauma: A One Year ... - IJMD
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Replantation</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Avulsed</strong> <strong>Tooth</strong> <strong>after</strong> <strong>Trauma</strong>: A<br />
<strong>One</strong> <strong>Year</strong> Follow-up Study<br />
Swaty Jhamb*, Lalit Bida**<br />
case report<br />
Abstract<br />
Clinical practice has shown that it avulsed teeth are replanted <strong>after</strong> a delayed extra-alveolar time it compromises the prognosis<br />
<strong>of</strong> replantation. In case <strong>of</strong> delayed replantation, the use <strong>of</strong> adequate media for storage and transportation <strong>of</strong> avulsed teeth may<br />
improve the prognosis considerably. The case reported in the study is <strong>of</strong> an accidentally avulsed maxillary right central incisor<br />
that was kept in milk from the moment <strong>of</strong> trauma until its replantation, 30 minutes later. <strong>One</strong> year follow-up revealed absence<br />
<strong>of</strong> root resorption, ankylosis or abnormal mobility, which demonstrates the feasibility <strong>of</strong> keeping avulsed teeth in milk.<br />
Key words: <strong>Replantation</strong>, root resorption, ankylosis, prognosis, avulsion<br />
Dentoalveolar traumas are most commonly<br />
observed in children and adolescents,<br />
particularly boys but may affect individuals <strong>of</strong><br />
any age. 1,2 Studies have demonstrated that replantation<br />
<strong>of</strong> avulsed teeth occurs most frequently between one<br />
and 4 hours <strong>after</strong> avulsion. 1,2 Despite the recognized<br />
therapeutic value <strong>of</strong> immediate tooth replantation,<br />
clinical practice has shown that most avulsed teeth are<br />
replanted <strong>after</strong> an extrabuccal time that extrapolates the<br />
adequate conditions for maintenance <strong>of</strong> the integrity <strong>of</strong><br />
periodontal ligament cells. 3 In such cases, wet storage is<br />
considered the best way to store avulsed teeth. 3,4 Some<br />
characteristics <strong>of</strong> storage medium i.e. pH, osmolarity 5,6<br />
and temperature should be compatible with the survival<br />
<strong>of</strong> periodontal ligament cells. 4,6 Storage media as Milk,<br />
Hanks balanced salt solution and Viaspan have been<br />
proved to maintain cell viability <strong>after</strong> long periods. 7<br />
Case Report<br />
A 20-year-old male patient was referred to Dept.<br />
<strong>of</strong> Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics <strong>after</strong><br />
falling from a motorbike and sustaining dental<br />
trauma.<br />
Routine protocol for management <strong>of</strong> trauma patients<br />
was carried out. On arrival, the patient was examined<br />
for extraoral signs <strong>of</strong> injury, including swelling and<br />
asymmetry <strong>of</strong> face and head. Inspection <strong>of</strong> facial bones<br />
revealed normal mouth opening. No area <strong>of</strong> ecchymosis,<br />
crepitus or pain on palpation was observed, which<br />
removed the suspicion <strong>of</strong> underlying fractures.<br />
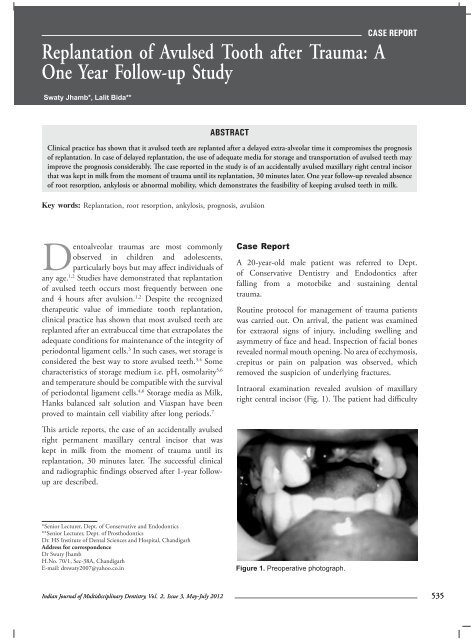
Intraoral examination revealed avulsion <strong>of</strong> maxillary<br />
right central incisor (Fig. 1). The patient had difficulty<br />
This article reports, the case <strong>of</strong> an accidentally avulsed<br />
right permanent maxillary central incisor that was<br />
kept in milk from the moment <strong>of</strong> trauma until its<br />
replantation, 30 minutes later. The successful clinical<br />
and radiographic findings observed <strong>after</strong> 1-year followup<br />
are described.<br />
*Senior Lecturer, Dept. <strong>of</strong> Conservative and Endodontics<br />
**Senior Lecturer, Dept. <strong>of</strong> Prosthodontics<br />
Dr. HS Institute <strong>of</strong> Dental Sciences and Hospital, Chandigarh<br />
Address for correspondence<br />
Dr Swaty Jhamb<br />
H.No. 70/1, Sec-38A, Chandigarh<br />
E-mail: drswaty2007@yahoo.co.in<br />
Figure 1. Preoperative photograph.<br />
Indian Journal <strong>of</strong> Multidisciplinary Dentistry, Vol. 2, Issue 3, May-July 2012<br />
535
Case Report<br />
Figure 2. <strong>Tooth</strong> stored in milk.<br />
Figure 4. Working length radiograph.<br />
Figure 3a. Replanted tooth in socket.<br />
Figure 5. Post-obturation radiograph.<br />
Figure 3b. Preoperative radiograph with splinted tooth.<br />
Figure 6. Postoperative radiograph <strong>after</strong> 1-year <strong>of</strong><br />
restoration.<br />
in keeping the tooth in the oral cavity so was instructed<br />
to keep the tooth in milk (Fig. 2). The total time elapsed<br />
from the moment <strong>of</strong> trauma until tooth replantation<br />
was half an hour.<br />
The treatment consisted <strong>of</strong> replantation <strong>of</strong> 11 into<br />
socket <strong>after</strong> meticulous inspection and irrigation <strong>of</strong> the<br />
avulsed tooth with saline (Fig. 3a). Splinting was carried<br />
from tooth 12 to 11 using resin composite (Fig. 3b).’<br />
536<br />
Indian Journal <strong>of</strong> Multidisciplinary Dentistry, Vol. 2, Issue 3, May-July 2012
Case Report<br />
Antibiotics were administered for 7 days and 0.12%<br />
chlorhexidine mouth rinses daily were prescribed for<br />
7 days. <strong>One</strong> week <strong>after</strong> replantation, the root canal<br />
<strong>of</strong> 11 was biomechanically prepared using step back<br />
technique (Fig. 4). A Calcium Hydroxide paste was<br />
used as an intracanal dressing and was changed 14 days<br />
later, when splinting was removed. Radiographs were<br />
taken and intracanal medication was changed at 30 and<br />
60 days <strong>after</strong> replantation. The root canal <strong>of</strong> the tooth<br />
was obturated at 90 days with Gutta-percha points<br />
and Sealapex that is a Calcium Hydroxide based sealer<br />
(Fig 5). The patient wanted restoration <strong>of</strong> aesthetics so,<br />
a fixed bridge <strong>of</strong> metal –ceramic was given. The patient<br />
was kept on continuous recall.<br />
The clinical and radiographic findings <strong>after</strong> 1-year<br />
follow-up revealed absence <strong>of</strong> root radiolucency,<br />
absence <strong>of</strong> root resorption, ankylosis and abnormal<br />
mobility <strong>of</strong> the replanted tooth (Fig. 6).<br />
Discussion<br />
Milk is mostly used as a storage medium for accidentally<br />
avulsed teeth and therefore, the case reported is<br />
important in the clinical routine or management <strong>of</strong><br />
tooth replantation.<br />
Lack <strong>of</strong> knowledge and possibility <strong>of</strong> immediate<br />
replantation and unawareness <strong>of</strong> ideal conditions and<br />
storage media for exarticulated teeth have contributed<br />
to a poor prognosis. Both, the length <strong>of</strong> extra-alveolar<br />
time and type <strong>of</strong> storage are significant factors that<br />
can affect the long-term survival <strong>of</strong> replanted teeth.<br />
Immersion <strong>of</strong> avulsed teeth in milk at room temperature<br />
preserves the viability <strong>of</strong> periodontal ligament cells<br />
for upto one hour; whereas, storage in refrigerated<br />
milk is reported to maintain cell viability for additional<br />
45 minutes. 4,8<br />
Irrespective <strong>of</strong> the type <strong>of</strong> root surface treatment,<br />
there is consensus in the literature that replanted teeth<br />
should be endodontically treated because the necrotic<br />
pulp and its toxins affect the periodontal ligament<br />
cells through the dentinal tubules and play a decisive<br />
role in the resorption process. 3,9,10 In this case, calcium<br />
hydroxide is the most recommended material for root<br />
canal filling <strong>of</strong> teeth to be replanted because <strong>of</strong> its<br />
well-known capacity <strong>of</strong> controlling the progression <strong>of</strong><br />
inflammatory resorption. 11,12<br />
Another aspect <strong>of</strong> dental replantation is the preparation<br />
<strong>of</strong> socket, which consists <strong>of</strong> removal <strong>of</strong> destructions as<br />
blood clots and bone fragments in order to facilitate<br />
the replantation. 12-15<br />
Contention <strong>of</strong> replanted teeth is another variable<br />
that might affect the prognosis <strong>of</strong> tooth replantation.<br />
Basically, it should not interfere with oral hygiene,<br />
allow physiological mobility and remain for a short<br />
time in order to reduce the incidence <strong>of</strong> ankylosis. 2,16<br />
The goal <strong>of</strong> antibiotic therapy is to avoid bacterial<br />
proliferation in the area <strong>of</strong> ongoing process and<br />
contribute to the prevention <strong>of</strong> inflammatory<br />
resorption. Ideally a broad-spectrum antibiotic should<br />
be administered for seven days. 17<br />
Nevertheless, in the case presented in this paper,<br />
the 1-year clinical and radiographic controls showed<br />
maintainence <strong>of</strong> root integrity, intact Lamina dura<br />
periradicularly and absence <strong>of</strong> abnormal mobility,<br />
which are indicative <strong>of</strong> successful replantation.<br />
Certain precautions were taken while planning the<br />
replantation procedure. The tooth was immersed<br />
in saline prior to replantation to eliminate cell lysis<br />
products resulting from traumatic injury on root<br />
surface, as well as debris and bacteria from saliva. 18-20<br />
Systemic antibiotic therapy was administered and tooth<br />
was endodontically treated to prevent inflammatory<br />
resorption. 21<br />
Root resorption and ankylosis are frequently observed<br />
complications post-replantation. Therefore, despite<br />
the positive results observed <strong>after</strong> 1-year, clinical and<br />
radiographic follow-up <strong>of</strong> tooth replanted under the<br />
condition hereby described should be carried for a<br />
longer period.<br />
References<br />
1.<br />
2.<br />
3.<br />
4.<br />
Grossman LI, Ship II. Survival rate <strong>of</strong> replanted teeth.<br />
Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1970;29(6):899-906.<br />
Andreasan JO, Andreason FM. Textbook and Color Atlas<br />
<strong>of</strong> <strong>Trauma</strong>tic Injuries to Teeth. 3rd edition, Munksgaard:<br />
Copenhagen 1994:p.771.<br />
Andreasen JO, Borum MK, Jacobsen HL, Andreasen<br />
FM. <strong>Replantation</strong> <strong>of</strong> 400 avulsed permanent incisors. 4.<br />
Factors related to periodontal ligament healing. Endod<br />
Dent <strong>Trauma</strong>tol 1995;11(2):76-89.<br />
Lekic P, Kenny D, Moe HK, Barretti E, McCulloch CA.<br />
Relationship <strong>of</strong> clonogenic capacity to plating efficiency<br />
and vital dye staining <strong>of</strong> human periodontal ligament<br />
cells: implications for tooth replantation. J Periodontal<br />
Res 1996;31(4):294-300.<br />
Indian Journal <strong>of</strong> Multidisciplinary Dentistry, Vol. 2, Issue 3, May-July 2012<br />
537
Case Report<br />
5.<br />
6.<br />
7.<br />
8.<br />
9.<br />
10.<br />
11.<br />
12.<br />
Blomlöf L, Otteskog P, Hammarström L. Effect <strong>of</strong> storage<br />
in media with different ion strengths and osmolalities on<br />
human periodontal ligament cells. Scand J Dent Res<br />
1981;89(2):180-7.<br />
Sigalas E, Regan JD, Kramer PR, Witherspoon DE,<br />
Opperman LA. Survival <strong>of</strong> human periodontal ligament<br />
cells in media proposed for transport <strong>of</strong> avulsed teeth.<br />
Dent <strong>Trauma</strong>tol 2004;20(1):21-8.<br />
Hiltz J, Trope M. Vitality <strong>of</strong> human lip fibroblasts in<br />
milk, Hanks balanced salt solution and Viaspan storage<br />
media. Endod Dent <strong>Trauma</strong>tol 1991;7(2):69-72.<br />
Blomlöf L, Lindskog S, Hammarström L. Periodontal<br />
healing <strong>of</strong> exarticulated monkey teeth stored in milk or<br />
saliva. Scand J Dent Res 1981;89(3):251-9.<br />
Andreasen JO. Relationship between cell damage in the<br />
periodontal ligament <strong>after</strong> replantation and subsequent<br />
development <strong>of</strong> root resorption. A time-related study in<br />
monkeys. Acta Odontol Scand 1981;39(1):15-25.<br />
Ehnevid H, Jansson L, Lindskog S, Weintraub A,<br />
Blomlöf L. Endodontic pathogens: propagation <strong>of</strong><br />
infection through patent dentinal tubules in traumatized<br />
monkey teeth. Endod Dent <strong>Trauma</strong>tol 1995;11(5):<br />
229-34.<br />
Trope M, Moshonov J, Nissan R, Buxt P, Yesilsoy C.<br />
Short vs. long-term calcium hydroxide treatment <strong>of</strong><br />
established inflammatory root resorption in replanted<br />
dog teeth. Endod Dent <strong>Trauma</strong>tol 1995;11(3):124-8.<br />
Flores MT, Andreasen JO, Bakland LK, Feiglin B,<br />
Gutmann JL, Oikarinen K, et al; International<br />
Association <strong>of</strong> Dental <strong>Trauma</strong>tology. Guidelines for the<br />
evaluation and management <strong>of</strong> traumatic dental injuries.<br />
Dent <strong>Trauma</strong>tol 2001;17(5):193-8.<br />
13.<br />
14.<br />
15.<br />
16.<br />
17.<br />
18.<br />
19.<br />
20.<br />
21.<br />
Trope M, Hupp JG, Mesaros SV. The role <strong>of</strong> the socket<br />
in the periodontal healing <strong>of</strong> replanted dogs’ teeth stored<br />
in ViaSpan for extended periods. Endod Dent <strong>Trauma</strong>tol<br />
1997;13(4):171-5.<br />
Trope M. Clinical management <strong>of</strong> the avulsed tooth:<br />
present strategies and future directions. Dent <strong>Trauma</strong>tol<br />
2002;18(1):1-11.<br />
Andreasen JO. The effect <strong>of</strong> removal <strong>of</strong> the coagulum<br />
in the alveolus before replantation upon periodontal and<br />
pulpal healing <strong>of</strong> mature permanent incisors in monkeys.<br />
Int J Oral Surg 1980;9(6):458-61.<br />
von Arx T, Filippi A, Buser D. Splinting <strong>of</strong> traumatized<br />
teeth with a new device: TTS (Titanium <strong>Trauma</strong> Splint).<br />
Dent <strong>Trauma</strong>tol 2001;17(4):180-4.<br />
Sae-Lim V, Wang CY, Trope M. Effect <strong>of</strong> systemic<br />
tetracycline and amoxicillin on inflammatory root<br />
resorption <strong>of</strong> replanted dogs’ teeth. Endod Dent<br />
<strong>Trauma</strong>tol 1998;14(5):216-20.<br />
Andreasen JO. Effect <strong>of</strong> extra-alveolar period and<br />
storage media upon periodontal and pulpal healing <strong>after</strong><br />
replantation <strong>of</strong> mature permanent incisors in monkeys.<br />
Int J Oral Surg 1981;10(1):43-53.<br />
Loe H, Waerhaug J. Experimental replantation <strong>of</strong> teeth<br />
in dogs and monkeys. Arch Oral Biol 1961;3:176-84.<br />
Cvek M, Granath LE, Hollender L. Treatment <strong>of</strong> nonvital<br />
permanent incisors with calcium hydroxide. 3.<br />
Variation <strong>of</strong> occurrence <strong>of</strong> ankylosis <strong>of</strong> reimplanted<br />
teeth with duration <strong>of</strong> extra-alveolar period and storage<br />
environment. Odontol Revy 1974;25(1):43-56.<br />
Hammarström L, Blomlöf L, Feiglin B, Andersson<br />
L, Lindskog S. <strong>Replantation</strong> <strong>of</strong> teeth and antibiotic<br />
treatment. Endod Dent <strong>Trauma</strong>tol 1986;2(2):51-7.<br />
538<br />
Indian Journal <strong>of</strong> Multidisciplinary Dentistry, Vol. 2, Issue 3, May-July 2012