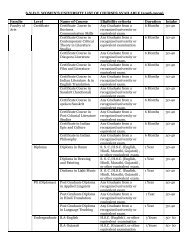
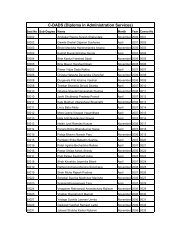
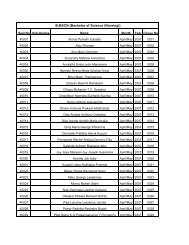
SNDT Women's University Syllabus Master of Personnel Masters in ...
SNDT Women's University Syllabus Master of Personnel Masters in ...
SNDT Women's University Syllabus Master of Personnel Masters in ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>SNDT</strong> Women’s <strong>University</strong><br />
(Sndt.digitaluniversity.ac)<br />
<strong>Syllabus</strong><br />
<strong>Master</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Personnel</strong> <strong>Master</strong>s <strong>in</strong> Retail<br />
Management (MRM)<br />
<strong>SNDT</strong> Women’s <strong>University</strong><br />
1, Nathibai Thackersey Road,<br />
Mumbai 400 020<br />
Revised - 2008<br />
1 | P a g e
<strong>Master</strong>s <strong>in</strong> Retail Management<br />
Introduction :<br />
Gone are the days, when you had to run from one shop to other to buy your daily<br />
groceries, your clothes, your cosmetics, toys for your children etc. Now that hypermalls<br />
and supermarkets are here, shopp<strong>in</strong>g has become an adventure. Today, under one ro<strong>of</strong>,<br />
you can f<strong>in</strong>d everyth<strong>in</strong>g you want and <strong>in</strong> a very short period <strong>of</strong> time, the mall culture had<br />
spread. In the com<strong>in</strong>g years, the retail <strong>in</strong>dustry will be boom<strong>in</strong>g after sector like<br />
agriculture, IT, textile and tourism. With the boom <strong>in</strong> the retail <strong>in</strong>dustry, the demand for<br />
pr<strong>of</strong>essionals for this <strong>in</strong>dustry has also gone up<br />
Malls and big stores have revolutionized the whole retail sector, as it is now more<br />
organized and efficient. The revolution is not only limited to metros but had shifted to<br />
small towns and one can f<strong>in</strong>d stores like Big Bazar and Shopper’s Stop <strong>in</strong> these small<br />
towns. In this scenario, the demand for a retail manager is go<strong>in</strong>g to be phenomenal and a<br />
career <strong>in</strong> retail is go<strong>in</strong>g to be a lucrative one.<br />
A part from manager, one can also opt for positions like <strong>in</strong>ventory manager, shopp<strong>in</strong>g<br />
operational manager, floor manager and customer service. The options don’t end here and<br />
there are also opportunities <strong>in</strong> human resources, f<strong>in</strong>ance and system management. In fact,<br />
accord<strong>in</strong>g to an estimate, the retail sector will soon become one <strong>of</strong> the major employers.<br />
A comb<strong>in</strong>ation <strong>of</strong> big brands and corporate names <strong>in</strong> the retail <strong>in</strong>dustry are open<strong>in</strong>g their<br />
outlets <strong>in</strong> smaller towns.<br />
Objectives:<br />
Though graduates from any field can enter the retail sector, but preference is given to one<br />
who has done a specialized course <strong>in</strong> the field. MBA or equivalent degree holders or<br />
people do<strong>in</strong>g a retail management postgraduation course, can make a career for<br />
themselves <strong>in</strong> this sector.<br />
1) To give an opportunity to work<strong>in</strong>g women to upgrade & empower themselves with a<br />
management degree.<br />
2) Prepare the participants for pr<strong>of</strong>essional careers <strong>in</strong> the various streams <strong>of</strong><br />
management.<br />
3) Promote among the future women executives a scientific approach and capability to<br />
undertake senior management responsibilities <strong>in</strong> various management streams.<br />
ELIGIBILITY<br />
DURATIO<br />
ITAKE<br />
MEDIUM OF ISTRUCTIO:<br />
SELECTIO PROCEDURE:<br />
Graduation <strong>in</strong> any discipl<strong>in</strong>e with work<br />
experience <strong>of</strong> m<strong>in</strong>imum 2 years<br />
2 years<br />
60 students<br />
English<br />
Aptitude test followed by Personal Interview by<br />
the panel <strong>of</strong> experts.<br />
2 | P a g e
Course ame : MBA - Retail Management<br />
SCHEME: Semester I<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
1 Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Communication 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
2. Fundamentals <strong>of</strong> Accounts 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
3. Management Market<strong>in</strong>g 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
4. Organization Behavior 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
5. Fundamental <strong>of</strong> Retail 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
6. Retail Environment 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
7. Foreign Language (French) 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
8. Macro Economic Environment 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
9. Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Statistics 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
10. International Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Law 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Total 30 40 20 -- 750 250 1000<br />
SCHEME: Semester II<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
1. Management Account<strong>in</strong>g 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
2. Research Methodology 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
3. Introduction to IT 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
4. Enterprise Resource Plann<strong>in</strong>g (ERP) 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
5. Consumer Behavior 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
6. International Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Management<br />
7. International F<strong>in</strong>ancial Management 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
8. International Bus<strong>in</strong>ess 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
9. Summer Project Report -- 4 -- -- 100 -- -- 100<br />
Total 24 36 16 -- 700 200 -- 900<br />
3 | P a g e
SCHEME: Semester III<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
1 Retail Operation and Inventory 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
2. Bank<strong>in</strong>g 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
3. Culture Strategy & Behavior 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
4. Franchise Operations &<br />
3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Management<br />
5. Managerial Economics 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
6. Retail Laws & HR <strong>in</strong> Retail<strong>in</strong>g 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
7. F<strong>in</strong>ancial Strategy 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
8. Visual Merchandis<strong>in</strong>g and Sales 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Policy<br />
9. Supply Cha<strong>in</strong> Management 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Total 27 36 18 -- 675 225 900<br />
SCHEME: Semester IV<br />
Subject L P/T P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
1. Sell<strong>in</strong>g techniques 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
2. Entrepreneurship Management 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
3. Management Control System 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
4. Retail Brand Build<strong>in</strong>g and Product 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Management<br />
5. Corporate F<strong>in</strong>ance 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
6. IT <strong>in</strong> Retail 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
7. Market Research 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
8. Foreign Language (German) 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
9. Research Based Project : Year Long -- 8 -- -- 100 -- -- 100<br />
Total 24 40 16 -- 700 200 -- 900<br />
4 | P a g e
SCHEME: Semester I<br />
Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Communication<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
1 Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Communication 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
1. Introduction<br />
1. The Comprehensive communication model and its analysis<br />
2. The communication network<br />
3. Barriers to communication<br />
4. Types <strong>of</strong> communication and situation<br />
5. Fac<strong>in</strong>g today’s communication challenges<br />
2. Oral Communication<br />
1. Face to face<br />
2. Telephonic conversation<br />
3. Interview<br />
4. Instruction and dictation<br />
5. Oral presentation<br />
3. on Verbal Communication<br />
1. Body language<br />
2. S<strong>in</strong>gs and symbols<br />
3. Colours<br />
4. Written Communication<br />
1. Writ<strong>in</strong>g for bus<strong>in</strong>ess audiences<br />
2. Revis<strong>in</strong>g and pro<strong>of</strong> read<strong>in</strong>g bus<strong>in</strong>ess messages<br />
3. Rout<strong>in</strong>e letters<br />
4. Memorandums and e-mails<br />
5. Letters and memos that persuade<br />
6. Negative messages<br />
7. Goodwill and special messages<br />
8. Informal reports<br />
9. Proposals and formal reports<br />
10. The job search, resumes, & job application letters<br />
5. List<strong>in</strong>g<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
05 12<br />
1. Managerial implications<br />
2. Selective listen<strong>in</strong>g<br />
3. Selective comprehensive / retention<br />
4. Selective distortion<br />
6. Important Parameters <strong>in</strong> Communication 05 12<br />
5 | P a g e
(a) The Cross Cultural Dimensions <strong>of</strong> Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Communication<br />
(b) Technology and Communication<br />
(c) Ethical & Legal Issues <strong>in</strong> Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Communication<br />
(d) Mass Communication: Mass Communication & Promotion<br />
Strategies, Advertisements,<br />
Publicity, and Press Releases. Media Mix, Public Relations,<br />
Newsletters.<br />
7. Bus<strong>in</strong>ess egotiation<br />
Negotiation Process & its Management<br />
Term Work<br />
05 11<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
6 | P a g e
Fundamentals <strong>of</strong> Accounts<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
2. Fundamentals <strong>of</strong> Accounts 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
1. ature <strong>of</strong> Account<strong>in</strong>g Information: Scope <strong>of</strong> Account<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
Account<strong>in</strong>g concepts, Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples & Standards, Account<strong>in</strong>g Cycle,<br />
Journalisation, Subsidiary Books; Ledger Post<strong>in</strong>g, Preparation <strong>of</strong> Trial<br />
Balance, Rectification <strong>of</strong> Error. Classification <strong>of</strong> Capital and Revenue.<br />
Fixed Assets and Depreciation Account<strong>in</strong>g. Preparation <strong>of</strong> F<strong>in</strong>al<br />
Accounts, Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g Account; Trad<strong>in</strong>g Account, Pr<strong>of</strong>it and Loss<br />
Account; Balance Sheet (with adjustments), Reports to be Annexed.<br />
2. Cost Account<strong>in</strong>g: Objectives, Classification <strong>of</strong> Cost, Preparation <strong>of</strong><br />
Cost Sheet, Material Cost Account<strong>in</strong>g, Perpetual Inventory Control,<br />
Inventory Valuation, EOQ, ABC Analysis, Sett<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> Reorder Level,<br />
Maximum Level, M<strong>in</strong>imum Level, Labour Cost Account<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
Remuneration and Incentive Schemes. Overhead Cost Allocations,<br />
Over and under Absorption. Job and Contract Cost<strong>in</strong>g, Operat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Cost<strong>in</strong>g (Transportation, Powerhouse, Hospitals), Reconciliation <strong>of</strong><br />
F<strong>in</strong>ancial and Cost Account<strong>in</strong>g<br />
3. Performance Evaluation Techniques: Introduction to Budget<strong>in</strong>g<br />
and Budgetary Control;<br />
Performance Budget<strong>in</strong>g; Classification <strong>of</strong> Budget; Standard Cost<strong>in</strong>g<br />
and Variance Analysis;<br />
Balanced Scorecard; Responsibility Account<strong>in</strong>g<br />
4. Decision Mak<strong>in</strong>g Techniques: Cost Volume Pr<strong>of</strong>it Analysis;<br />
Management Account<strong>in</strong>g for Decision Mak<strong>in</strong>g and Control; EVA and<br />
Performance Measurement; Introduction to Activity Base Cost<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
Target<strong>in</strong>g Cost<strong>in</strong>g, Life Cycle Cost<strong>in</strong>g; Uniform Cost<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Term Work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
08 15<br />
09 20<br />
09 20<br />
09 20<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
7 | P a g e
Management Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
3. Management Market<strong>in</strong>g 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
Introduction to Market<strong>in</strong>g : Mean<strong>in</strong>g, Nature and Scope <strong>of</strong><br />
Market<strong>in</strong>g; Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 15<br />
Philosophies; Market<strong>in</strong>g Management Process; Concept <strong>of</strong> Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Mix; Market Analysis: Understand<strong>in</strong>g Market<strong>in</strong>g Environment;<br />
Consumer and Organisation Buyer Behaviour; Market Measurement;<br />
Market Segmentation, Target<strong>in</strong>g and Position<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Strategic Market<strong>in</strong>g Plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Corporate and Division Strategic Plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Strategic Plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Develop<strong>in</strong>g the Market<strong>in</strong>g Strategy<br />
• Market<strong>in</strong>g Plann<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the 21 st Strategy<br />
The Market<strong>in</strong>g Environment<br />
• Environmental Forces and Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Micro environment<br />
• Macro environment<br />
• Analyz<strong>in</strong>g needs and trends identify<strong>in</strong>g respond<strong>in</strong>g to the major<br />
macro envt forces<br />
Analyz<strong>in</strong>g Market<strong>in</strong>g Opportunity<br />
• Nature <strong>of</strong> Market<strong>in</strong>g Research<br />
• Market<strong>in</strong>g Decision Mak<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Market<strong>in</strong>g Information System<br />
• Market<strong>in</strong>g Research Process<br />
• Sales Analysis and Forecast<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Consumer Behaviour<br />
• A model <strong>of</strong> Consumer Behaviour<br />
• Major features <strong>in</strong>fluenc<strong>in</strong>g Buyer behaviour<br />
• Buy<strong>in</strong>g Decision Process<br />
• Stages <strong>of</strong> Buy<strong>in</strong>g decision process<br />
• Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Market & buy<strong>in</strong>g behaviour<br />
Competition Analysis<br />
• Nature <strong>of</strong> competition and degree <strong>of</strong> competition<br />
• Competition analysis<br />
• Competitive Strategies<br />
Market Segmentation Target<strong>in</strong>g and Position<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Strategic Approaches to segmentation<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
8 | P a g e
• Market Target<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• How to differentiate<br />
• Basis for position<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Position<strong>in</strong>g Strategies<br />
• Product Life Cycle-Market<strong>in</strong>g Strategies<br />
Develop<strong>in</strong>g Market<strong>in</strong>g Strategy<br />
• Market Offer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Strategy Framework<br />
• Local VS Global Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Product Decision<br />
• New Product development – why and How?<br />
• Stages <strong>in</strong> the development process<br />
• Consumer Adoption Process<br />
• Product – Mean<strong>in</strong>g and Levels<br />
• Product Structure<br />
• Product Classification<br />
• Product mix decision<br />
• Product l<strong>in</strong>e decisions<br />
• Brand decisions<br />
• Brand<strong>in</strong>g Strategies<br />
• Packag<strong>in</strong>g & Strategy<br />
Market<strong>in</strong>g Organization and Control: Emerg<strong>in</strong>g Trends and Issues<br />
<strong>in</strong> Market<strong>in</strong>g – Consumerism, Rural Market<strong>in</strong>g, Social Market<strong>in</strong>g;<br />
Direct and Onl<strong>in</strong>e Market<strong>in</strong>g; Green Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Physical Distribution and Channel Management<br />
• Market<strong>in</strong>g Channels – Functions and flows<br />
• Channel levels<br />
• Channel Levels<br />
• Channels designs<br />
• Channel dynamics<br />
• Develop<strong>in</strong>g channel strategy<br />
Integrated Market<strong>in</strong>g Communication<br />
• Identify<strong>in</strong>g target audience<br />
• Determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g Communication objectives<br />
• Promotional tools<br />
• Advertis<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Sales promotion<br />
• Public relations<br />
Case : Swatch<br />
Term Work<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
9 | P a g e
Organization Behavior<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
4. Organization Behavior 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
1. What is organization behavior<br />
• Contribution towards social sciences<br />
Industrial Psychology<br />
Sociology<br />
Anthropology<br />
Political Science<br />
• Hawthorne Studies<br />
Implications for managers<br />
• Douglas Mac Gregor (Theory X Versus Theory Y)<br />
Relation between managers and employees with the<br />
organization<br />
2. Individual behavior <strong>in</strong> the organization<br />
• Theories <strong>of</strong> human behavior-a psychological<br />
approach<br />
Factors affect<strong>in</strong>g personality<br />
Cultural variables<br />
Greet H<strong>of</strong>stede’s Studies<br />
• The human sides <strong>of</strong> enterprise (D.McGregor)<br />
• Employ<strong>in</strong>g the whole man (P.Ducker)<br />
• Characteristics <strong>of</strong> achievers (D.C. McClelland)<br />
3. Motivation<br />
• A needs approach – maslow<br />
• McClellend’s acquired needs<br />
• Thematic apperception test (TAT)<br />
• Herzberg’s two-factor theory<br />
• Job design (Hackman and Oldman)<br />
• Equity <strong>of</strong> rewards <strong>in</strong> the work place<br />
• Expectancy, <strong>in</strong>strumentally, and advance<br />
• On the folly <strong>of</strong> reward<strong>in</strong>g “A”, While hopp<strong>in</strong>g for<br />
‘B” (S. Kerr)<br />
An exam<strong>in</strong>ation <strong>of</strong> piece rates (Pro & Con)<br />
4. Leadership<br />
• Historical review <strong>of</strong> the study <strong>of</strong> leadership<br />
• Trait theories<br />
• Ohio state studies<br />
• The Blanchard model<br />
• The vroom model<br />
Path-goal theory <strong>of</strong> leadership (House & Mitchell)<br />
5. Team<br />
• Teams def<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
• Reasons for jo<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g teams<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 10<br />
06 13<br />
06 13<br />
06 13<br />
06 13<br />
10 | P a g e
Selection criteria<br />
Goals (objectives)<br />
• Norms and roles<br />
Deviance<br />
Dysfunction behaviors<br />
Social loaf<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Group processes<br />
Communication<br />
Responsibility<br />
Accountability<br />
Respect<br />
Evaluation<br />
• Decision mak<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Consensus<br />
Cooperation<br />
Constructive conflict<br />
• Groupth<strong>in</strong>k<br />
6. Organization power and politics<br />
• Power def<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
• Sources <strong>of</strong> power<br />
• Power as a function <strong>of</strong> dependence<br />
• Political behavior <strong>in</strong> the organization<br />
• Coalition formation<br />
• Control <strong>of</strong> Information<br />
Pattern <strong>of</strong> political behavior <strong>in</strong> organizations (Farrell &<br />
Petersen)<br />
Term Work<br />
06 13<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
11 | P a g e
Fundamental <strong>of</strong> Retail<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
5. Fundamental <strong>of</strong> Retail 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
1. Fundamental’s<br />
• Intro to retail<br />
• Organized V/S unorganized<br />
• Types <strong>of</strong> retail<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Types <strong>of</strong> retailers<br />
• Non store<br />
• Store<br />
• F<strong>in</strong>ancial product retail<strong>in</strong>g<br />
3. Multi channel retail<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Introduction<br />
• Characteristics<br />
• Importance<br />
4. Customer buy<strong>in</strong>g behaviour<br />
• Layout<br />
• Experience<br />
• Moment magic/truth<br />
• ambiance<br />
5. Retail market strategy<br />
• Symert<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Pestron<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Penetration<br />
6. Retail locations<br />
• Importance<br />
• How is it done<br />
• Customer Pr<strong>of</strong>il<strong>in</strong>g<br />
7. Site selection<br />
• Space<br />
• V as for customer<br />
• accessibility<br />
8. CRM<br />
• Tools for the same<br />
• Importance and contribution to bus<strong>in</strong>ess<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
03 08<br />
03 08<br />
03 08<br />
03 08<br />
03 08<br />
05 08<br />
05 08<br />
05 09<br />
9. Manag<strong>in</strong>g the stores 05 10<br />
Term Work<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
12 | P a g e
Retail Environment<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
6. Retail Environment 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
1) Retail Industry pr<strong>of</strong>ile – a chronological evolution. 02 06<br />
2) Trends <strong>in</strong> e-commerce retail<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Identify<strong>in</strong>g factors lead<strong>in</strong>g to success <strong>of</strong> retail <strong>in</strong>dustry<br />
• Emergence <strong>of</strong> new channels <strong>of</strong> retail<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Mom and pop stores to 7 – 11 or 365* 24*7, catalogues –<br />
mail order – <strong>in</strong>ternet channels.<br />
04 08<br />
3) Retail sales and market economics figures and analysis for 03 07<br />
countries such as US, UK, Canada and India<br />
4) Environmental Changes impact<strong>in</strong>g retail bus<strong>in</strong>ess 02 06<br />
5) Emergence <strong>of</strong> growth <strong>of</strong> retail <strong>in</strong>dustry <strong>in</strong> Asia and South east<br />
asian countries such as Malaysia, Indonesia, Korea, Japan<br />
and Ch<strong>in</strong>a<br />
04 08<br />
6) Trends <strong>in</strong> retail Brand<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> different countries – a<br />
04 08<br />
comparative study.<br />
7) Emergence <strong>of</strong> Inventory management solutions <strong>in</strong> retail<strong>in</strong>g 04 08<br />
8) CRM <strong>in</strong> retail<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Customer Service trends<br />
b) Chang<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the Employee – customer relationship<br />
management.<br />
9) Trends <strong>in</strong> retail advertis<strong>in</strong>g – media trend.<br />
a) The changes <strong>in</strong> advertis<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the recent times.<br />
b) Predict<strong>in</strong>g the future <strong>of</strong> retail advertis<strong>in</strong>g<br />
04 08<br />
10) Technological <strong>in</strong>tervention <strong>in</strong> retail<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Technologies <strong>of</strong> past<br />
b) E-convergence technologies<br />
c) Internet technologies<br />
11) Customer Pr<strong>of</strong>il<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> retail<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Demographic<br />
b) Educational<br />
c) Economic<br />
d) Socio – cultural<br />
04 08<br />
04 08<br />
12) Major failure <strong>in</strong> retail bus<strong>in</strong>ess such as K Mart.<br />
Term Work<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
13 | P a g e
Foreign Language (French)<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
7. Foreign Language (French) 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
1. Objectives:<br />
Topic<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
04 05<br />
To impart the basics <strong>of</strong> the French language.<br />
To teach basic conversation <strong>in</strong> French Language/Spanish<br />
Language/German Language.<br />
2. Scope<br />
Theory<br />
Basic nouns<br />
Th<strong>in</strong>gs around us.<br />
Items <strong>of</strong> daily use.<br />
Numbers<br />
0 -100<br />
Ord<strong>in</strong>al numbers.<br />
Colours<br />
Use them <strong>in</strong> complex sentences<br />
Change them accord<strong>in</strong>g to the nouns.<br />
Different materials<br />
eg. Silk, cotton………<br />
Grammer<br />
Def<strong>in</strong>ition & <strong>in</strong>def<strong>in</strong>ite articles.<br />
Prepositions<br />
S<strong>in</strong>gular – plural<br />
Adjectives<br />
Mascul<strong>in</strong>e- fem<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>e.<br />
Negation & <strong>in</strong>version <strong>of</strong> verbs.<br />
Verbs<br />
Basic verbes like etre, avoir………<br />
Conversation skills<br />
Understand simple sentences used <strong>in</strong> class.<br />
Formal & <strong>in</strong>formal greet<strong>in</strong>gs<br />
Understand & translate simple passages.<br />
Answer basic & complex “wh” type questions.<br />
Term Work<br />
04 10<br />
04 10<br />
04 10<br />
04 10<br />
04 10<br />
04 10<br />
07 10<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
14 | P a g e
Macro Economic Environment<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
8. Macro Economic Environment 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
Analysis <strong>of</strong> Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Environment, technological,<br />
political and economic – PEST, SWOT Analysis.<br />
Government <strong>in</strong>dustry <strong>in</strong>terface – Market <strong>in</strong>tervention,<br />
need for regulation and promotion monetary and fiscal<br />
policies.<br />
Consumerism, Consumer Protection, Labour issues –<br />
National and International.<br />
Analysis <strong>of</strong> Competitive Environment – Competitive<br />
policy & law.<br />
Role <strong>of</strong> Government <strong>in</strong> Industrial development .<br />
Mean<strong>in</strong>g and Rational for globalization from domestic<br />
market to global market, India – WTO and trade blocs,<br />
TRIPS, IPR.<br />
International Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Environment analysis.<br />
New Economic policy, Basic Economic trends and<br />
Bus<strong>in</strong>ess forecast<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Turnaround Management.<br />
Jo<strong>in</strong>t Ventures.<br />
Ecology and Susta<strong>in</strong>able Development.<br />
Corporate Governance.<br />
Term Work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
08 15<br />
08 20<br />
09 20<br />
10 20<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Statistics<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
9. Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Statistics 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
Basic Statistical Concepts.<br />
Summarization <strong>of</strong> Data : Frequency Distribution :<br />
Measures <strong>of</strong> central Tendency.<br />
Measure <strong>of</strong> Dispersion ; Relative Disperstion –<br />
Skewness, Kurtosis.<br />
Elementary Probability theory ; Marg<strong>in</strong>al and<br />
conditional probability ; Independence / Dependence <strong>of</strong><br />
Events.<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
08 15<br />
08 20<br />
15 | P a g e
Elementary Statistical Distribution ; B<strong>in</strong>omial,<br />
Poission, Normal, Estimation; Po<strong>in</strong>t and Interval,<br />
sampl<strong>in</strong>g, Distribution, Mean and Proportion.<br />
Test<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> Hypothesis.<br />
Simple Corelation and Regression ; Spearmans Rank<br />
Correlation.<br />
Types <strong>of</strong> Sampl<strong>in</strong>g – Simple and Random, Stratified<br />
sampl<strong>in</strong>g and Cluster sampl<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Time series – Components <strong>of</strong> time series, Estimation <strong>of</strong><br />
trends and seasonal components.<br />
Term Work<br />
09 20<br />
10 20<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
International Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Law<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
10. International Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Law 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
Introduction to International Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Law: (a) Development <strong>of</strong><br />
public and private <strong>in</strong>ternational law<br />
(b) Overview <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>ternational organizations, United Nations,<br />
International Court <strong>of</strong> Justice, International Monetary Fund, World<br />
Bank, World Intellectual Property Organization<br />
History <strong>of</strong> the European Common Market and European<br />
Union: (a) Structure <strong>of</strong> European Union, Harmonization pr<strong>in</strong>ciples<br />
<strong>of</strong> EU (b) Regulation <strong>of</strong> bus<strong>in</strong>ess under the EU, Monetary<br />
pr<strong>in</strong>ciples under the EU.<br />
Jurisdiction <strong>in</strong> International Disputes: (a) Collection <strong>of</strong> evidence<br />
<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>ternational litigation; enforcement <strong>of</strong><br />
foreign judgments <strong>in</strong> United States courts; enforcement <strong>of</strong> United<br />
States judgments <strong>in</strong> foreign nations;<br />
alternative dispute resolution <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>ternational conflicts (arbitration<br />
and mediation).<br />
U.S. and International law: Contracts and the sale <strong>of</strong> goods with<br />
special emphasis on the Convention for the International Sale <strong>of</strong><br />
Goods.<br />
Analysis <strong>of</strong> United States laws:<br />
a) Regulat<strong>in</strong>g trademarks, patents and copyrights<br />
b) licens<strong>in</strong>g Intellectual Property Rights (IPR's) <strong>in</strong> other nations;<br />
issues related to gray market goods<br />
c) Treaties affect<strong>in</strong>g IPR's, Grant back <strong>of</strong> IPR's<br />
International Trade F<strong>in</strong>anc<strong>in</strong>g:<br />
a) International Drafts, Trade Acceptances, Letters <strong>of</strong> Credit<br />
b) Uniform Customs and Practice (UCP) <strong>of</strong> Documentary Credits<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 10<br />
06 13<br />
06 13<br />
06 13<br />
06 13<br />
06 13<br />
16 | P a g e
and the Uniform Commercial Code<br />
c) Convertibility and other risks <strong>of</strong> foreign currency transactions.<br />
Term Work<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
17 | P a g e
SCHEME: Semester II<br />
Management Account<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
1. Management Account<strong>in</strong>g 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Time Value Money<br />
Topic<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 10<br />
• Future value <strong>of</strong> a s<strong>in</strong>gle Amount<br />
• Present Value <strong>of</strong> a S<strong>in</strong>gle Amount<br />
• Future Value <strong>of</strong> an Annuity<br />
• Present Value <strong>of</strong> an Annuity<br />
• Basic aspects <strong>of</strong> application <strong>of</strong> time value <strong>of</strong> money to NPV<br />
/ IRR situations.<br />
• Basics <strong>of</strong> RISK / Return Concepts<br />
• Valuation <strong>of</strong> Securities – An <strong>in</strong>troduction to the valuation <strong>of</strong><br />
Bonds / Equity Share etc.<br />
F<strong>in</strong>ancial Plann<strong>in</strong>g and Budget<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Forecast<strong>in</strong>g Process<br />
• Techniques <strong>of</strong> Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Forecast<strong>in</strong>g. Problems <strong>in</strong> Bus<strong>in</strong>ess<br />
Forecast<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Requirement or Sound Budget<strong>in</strong>g System<br />
• Budget<strong>in</strong>g Process<br />
• Budget Techniques<br />
• Problems <strong>in</strong> Budget<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Pro Forms Pr<strong>of</strong>it and Loss Account<br />
• Pro Forma Pr<strong>of</strong>it and Loss Account<br />
• Pro Forma Balance Sheet<br />
F<strong>in</strong>ancial Statements<br />
• Concept <strong>of</strong> Fund<br />
• Significance <strong>of</strong> F<strong>in</strong>ancial Statements<br />
• Preparation <strong>of</strong> the Funds Flow Statement<br />
• Preparation <strong>of</strong> the Cash Flow Statement<br />
F<strong>in</strong>ancial Statement Analysis (FSA)<br />
• Significance <strong>of</strong> FSA<br />
• Users <strong>of</strong> FSA<br />
• Ratio Analysis<br />
• Utility <strong>of</strong> Ratio Analysis<br />
• Cautions <strong>in</strong> Us<strong>in</strong>g Ratio Analysis<br />
Break Even Analysis and Leverages<br />
• Income Statement Relationship<br />
• Operat<strong>in</strong>g Leverage<br />
• Cost – Volume – Pr<strong>of</strong>it Analysis<br />
• F<strong>in</strong>ancial Leverage<br />
06 13<br />
06 13<br />
06 13<br />
06 13<br />
18 | P a g e
• Total Leverage<br />
Management <strong>of</strong> Work<strong>in</strong>g Capital<br />
• Ma<strong>in</strong> Elements <strong>of</strong> Work<strong>in</strong>g Capital<br />
• Purpose <strong>of</strong> Work<strong>in</strong>g Capital and the Nature <strong>of</strong> the Work<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Capital Cycle<br />
• Importance <strong>of</strong> Establish<strong>in</strong>g Policies for the Control<br />
Work<strong>in</strong>g Capital<br />
• Factors that have to be taken <strong>in</strong>to account when manag<strong>in</strong>g<br />
each element <strong>of</strong> work<strong>in</strong>g capitals.<br />
Term Work<br />
06 13<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
Research Methodology<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
2. Research Methodology 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
Relevance and scope <strong>of</strong> research <strong>in</strong> management.<br />
Steps <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> the research process.<br />
Identification <strong>of</strong> research problem<br />
Identification and types <strong>of</strong> research variables<br />
Research design.<br />
Data collection methodology, primary date collection methods /<br />
measurement techniques – characteristics <strong>of</strong> measurement<br />
techniques – reliability, validity etc. secondary data collection<br />
methods – library research, references – bibliography, abstracts etc.<br />
Analysis techniques – qualitative and quantitative analysis<br />
techniques – techniques <strong>of</strong> test<strong>in</strong>g hypothesis – chi-square, t-test,<br />
correlation and regression analysis, analysis <strong>of</strong> variance etc.<br />
Mak<strong>in</strong>g choice <strong>of</strong> an appropriate analysis technique.<br />
Research report writ<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Computer aided research methodology.<br />
Term Work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
08 18<br />
09 19<br />
09 19<br />
09 19<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
19 | P a g e
Introduction to IT<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
3. Introduction to IT 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
Overview <strong>of</strong> computer system :<br />
• What is Inside Mach<strong>in</strong>e<br />
• S<strong>of</strong>tware : Br<strong>in</strong>g<strong>in</strong>g the Mach<strong>in</strong>e To Life<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 12<br />
Types <strong>of</strong> Computers and Comput<strong>in</strong>g Devices<br />
Input-output Devices<br />
Input Device<br />
Keyboard<br />
Mouse<br />
Variants <strong>of</strong> Mouse<br />
Devices for the hand<br />
Optical Input devices<br />
Auto visual <strong>in</strong>put devices<br />
Output Devices<br />
Monitors<br />
PC Projectors<br />
Sound Systems<br />
Pr<strong>in</strong>ters<br />
Plotters<br />
Storage Devices<br />
Categorized Storage Devices<br />
Magnetic Storage Devices<br />
Optical Storage Devices<br />
Operat<strong>in</strong>g Systems<br />
The User Interface<br />
Runn<strong>in</strong>g Programs<br />
Manag<strong>in</strong>g Files<br />
Manag<strong>in</strong>g Hardware<br />
Utility S<strong>of</strong>tware<br />
Data Representation and Process<strong>in</strong>g<br />
How Computers Represent Data<br />
How a Computer Process Data<br />
Factors Affect<strong>in</strong>g Process<strong>in</strong>g Speed<br />
Extend<strong>in</strong>g the Processor’s Power to other Devices<br />
Office Application (Open Office 1.10rg)<br />
Calc<br />
Introduction to Calc<br />
Work<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Calc<br />
Perform<strong>in</strong>g Calculation <strong>in</strong> Calc<br />
Manag<strong>in</strong>g the layout <strong>of</strong> a Worksheet<br />
Manipulat<strong>in</strong>g the Worksheet<br />
06 12<br />
20 | P a g e
Word Process<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Gett<strong>in</strong>g Started with Write<br />
Edit<strong>in</strong>g Documents <strong>in</strong> Writer<br />
Formatt<strong>in</strong>g a document<br />
Advanced tools and features <strong>of</strong> writer<br />
Network and date Communication Concepts :<br />
The Uses <strong>of</strong> Network<br />
How Networks are structures<br />
Network Topologies for LAN<br />
Network Media and Hardware<br />
IT technologies DSL etc<br />
Data Communication over standard telephone l<strong>in</strong>es<br />
Us<strong>in</strong>g Digital telephone l<strong>in</strong>es<br />
Internet and Onl<strong>in</strong>e Resources<br />
The Internet : Than and Now<br />
How the Internet works<br />
Major Features <strong>of</strong> the Internet<br />
Onl<strong>in</strong>e Services<br />
Internet-related features <strong>in</strong> application<br />
Access<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>in</strong>ternet<br />
Work<strong>in</strong>g on the <strong>in</strong>ternet<br />
Commerce on the world wide web<br />
Database Concepts<br />
Database and Database Management Systems<br />
Work<strong>in</strong>g with database<br />
Creat<strong>in</strong>g Database Tables<br />
View<strong>in</strong>g Records<br />
Sort<strong>in</strong>g Records<br />
Query<strong>in</strong>g a Database<br />
Generat<strong>in</strong>g Reports<br />
Introduction to Programm<strong>in</strong>g<br />
What is Computer Program<br />
Hardware / S<strong>of</strong>tware Interaction<br />
Mach<strong>in</strong>e Code Programm<strong>in</strong>g Languages<br />
Compliers and Interpreters<br />
How Programmes solve Problem<br />
Program Control Flow<br />
Algorithms<br />
Variables and Functions<br />
Advantages and Limitations <strong>of</strong> High Level Languages<br />
Object-oriented Programm<strong>in</strong>g Languages<br />
Examples <strong>of</strong> Some High Level Languages<br />
Examples <strong>of</strong> OOPs<br />
Characteristics <strong>of</strong> good programm<strong>in</strong>g language<br />
Select<strong>in</strong>g a language for cod<strong>in</strong>g an application<br />
Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> ’C’<br />
Introduction<br />
Decision Statements<br />
Loop<strong>in</strong>g Statements<br />
06 12<br />
06 13<br />
06 13<br />
06 13<br />
21 | P a g e
Term Work<br />
Functions<br />
Structure and Unions<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
Enterprise Resource Plann<strong>in</strong>g (ERP)<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
4. Enterprise Resource Plann<strong>in</strong>g (ERP) 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
Introduction<br />
Information System overview<br />
a. Contemporary Info System<br />
i. Why use <strong>in</strong>formation System<br />
1. IS for automation<br />
2. IS for Organizational learn<strong>in</strong>g<br />
3. IS for support<strong>in</strong>g strategy<br />
b. Information system for competitive advantage<br />
a. Sources <strong>of</strong> competitive<br />
advantage<br />
b. Is and Value Cha<strong>in</strong> Analysis<br />
c. Mak<strong>in</strong>g the bus<strong>in</strong>ess case for<br />
a system<br />
d. Present<strong>in</strong>g the bus<strong>in</strong>ess case<br />
c. Competitive Advantages be<strong>in</strong>g at Cutt<strong>in</strong>g Edge<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 12<br />
d. Database Management Concepts<br />
i. Database Management for Strategic advantage<br />
ii. Key Database activities<br />
iii. How organization get most from their Data<br />
e. Ecommerce Management Solutions<br />
i. Intranet System Architecture<br />
ii. Intranet Applications<br />
iii. Extranet System Architecture<br />
iv. Extranet Applications<br />
v. Formula for E-commerce Success<br />
vi. Ecommerce bus<strong>in</strong>ess strategy<br />
vii. Bus<strong>in</strong>ess to Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Ecommerce<br />
viii. Enterprise Portals<br />
f. Organizational Information System<br />
i.Decision mak<strong>in</strong>g level <strong>of</strong> an organization<br />
ii.General type <strong>of</strong> IS<br />
iii.IS that spans organizational Boundaries<br />
iv.Collaboration Technologies<br />
22 | P a g e
v.Functional Area IS<br />
g. Enterprise wise <strong>in</strong>formation system<br />
i. Enterprise Systems<br />
ii. Type <strong>of</strong> Enterprise Systems<br />
h. Information System Development & Acquisition<br />
i. Need for Structure System Development<br />
ii. Step for System Development Phase<br />
iv. Other Approaches to Design<strong>in</strong>g and Build<strong>in</strong>g<br />
v. Need for alternatives to build<strong>in</strong>g System <strong>in</strong>-house<br />
Common alternative to <strong>in</strong>-house Systems<br />
Overview <strong>of</strong> ERP Modules (any product)<br />
a. HRMS<br />
b. F<strong>in</strong>ancial<br />
Supply Cha<strong>in</strong><br />
Overview <strong>of</strong> Architecture<br />
a. How ERP Architecture difference from Legacy<br />
Applications<br />
b. Key Components<br />
Manag<strong>in</strong>g Enterprise architecture<br />
Build<strong>in</strong>g basis for Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Development<br />
a. Plann<strong>in</strong>g for Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Case<br />
b. Determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g bus<strong>in</strong>ess drivers<br />
c. Identify<strong>in</strong>g various ERP Implementations Cost<br />
d. Def<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g Success for the project<br />
e. Creat<strong>in</strong>g an effective bus<strong>in</strong>ess case to support the project<br />
Communicat<strong>in</strong>g Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Case<br />
Plann<strong>in</strong>g and Communication<br />
a. A look at what organizational alignment is and how it<br />
affects the implementations<br />
b. What to do to better prepare the organization for the<br />
changes the project will br<strong>in</strong>g<br />
c. How to get the project started on the right foot<br />
d. What characteristics on should look <strong>in</strong> Project Manager<br />
e. What a project Charter is how to create one for the project<br />
f. What <strong>in</strong>dividual and Role required for a successful<br />
implementation<br />
g. What appropriate Project Infrastructure need to be <strong>in</strong> place<br />
for successful implementation<br />
How to create the right project plan and budget to ensure that goal<br />
and objectives for this <strong>in</strong>itiative is met<br />
Survey<strong>in</strong>g the Infrastructure<br />
a. A look at the key technical <strong>in</strong>frastructure components<br />
b. What technical resources are required to support Technical<br />
<strong>in</strong>frastructure<br />
What key policies and procedures should have <strong>in</strong> place to support<br />
technical needs<br />
Analyz<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>in</strong>frastructure<br />
a. What are bus<strong>in</strong>ess requirements anyway and who should<br />
identify them<br />
06 12<br />
06 12<br />
23 | P a g e
. Sponsorship – key support for requirements<br />
c. The 80 / 20rules<br />
d. Build<strong>in</strong>g Consensus<br />
e. Impact on s<strong>of</strong>tware<br />
f. Identify<strong>in</strong>g, Read<strong>in</strong>g and Prioritiz<strong>in</strong>g requirements<br />
g. Perform<strong>in</strong>g a Gap Analysis<br />
h. F<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g the right Solution<br />
i. Chang<strong>in</strong>g bus<strong>in</strong>ess requirements and processes not the<br />
s<strong>of</strong>tware<br />
j. Impact <strong>of</strong> decision and deal<strong>in</strong>g with the changes<br />
Design<strong>in</strong>g a Solution<br />
a. Alternative approaches to design<strong>in</strong>g a solution<br />
b. How to handle high impact changes to the applications<br />
c. Manag<strong>in</strong>g and track<strong>in</strong>g system and design changes<br />
d. Effect <strong>of</strong> changes, both Local and Global<br />
06 13<br />
How to track version control to track a change it’s made<br />
Prepar<strong>in</strong>g Organization for implementation<br />
a. Putt<strong>in</strong>g together a high power Implementation Team<br />
b. Develop<strong>in</strong>g a proper implementation Plan and approach<br />
c. Ensure Read<strong>in</strong>ess <strong>of</strong> People<br />
d. Look<strong>in</strong>g at the process<strong>in</strong>g support requirements<br />
e. Putt<strong>in</strong>g the proper technology <strong>in</strong> place to support<br />
f. Look<strong>in</strong>g at organizational changes and gett<strong>in</strong>g the right<br />
executive sponsorship<br />
Determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g the require communication flow <strong>in</strong> place<br />
Prototyp<strong>in</strong>g & Conference Room Pilot<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a. What is Prototyp<strong>in</strong>g<br />
b. Prototyp<strong>in</strong>g Techniques – Conference room pilot<strong>in</strong>g<br />
c. Why to prototype?<br />
d. CRP Tips<br />
e. Best time to prototype<br />
f. What to <strong>in</strong>clude <strong>in</strong> prototype<br />
Gett<strong>in</strong>g Feedback and leverag<strong>in</strong>g it<br />
Convert<strong>in</strong>g Data & Creat<strong>in</strong>g Interface<br />
a. What data to convert<br />
b. How much historical data to convert<br />
c. Available tools for conversion<br />
d. What to know about <strong>in</strong>terfaces<br />
e. What type <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>terfaces are encountered dur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
implementation<br />
Determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g format for <strong>in</strong>terface<br />
Technical Implementation Issues<br />
a. A look at various technical environments needed to support<br />
the project<br />
b. Decid<strong>in</strong>g between two tier and three tier architecture<br />
c. What type <strong>of</strong> standards should be <strong>in</strong> place – Development,<br />
Nam<strong>in</strong>g, Configuration Standards<br />
06 13<br />
24 | P a g e
Special Need <strong>of</strong> the users may need to support technically<br />
(report<strong>in</strong>g, Web enabl<strong>in</strong>g work flow etc.)<br />
Security<br />
a. Overview <strong>of</strong> security components<br />
b. What user security and permission lists are and how to<br />
configure these features<br />
c. What object security is and why it should be used<br />
d. A look at how query security is set up<br />
e. What process security it<br />
f. Use <strong>of</strong> field level security<br />
Product specific Security<br />
Test<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a. A detail look at what test<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>volves and what the key<br />
components are <strong>in</strong> a successful test<strong>in</strong>g effort<br />
b. Creat<strong>in</strong>g an effective Test<strong>in</strong>g efforts<br />
c. Track<strong>in</strong>g result <strong>of</strong> test<strong>in</strong>g efforts<br />
d. Types <strong>of</strong> Test<strong>in</strong>g<br />
e. Support<strong>in</strong>g Resources for Test<strong>in</strong>g<br />
f. Environment to Support Test<strong>in</strong>g<br />
g. How to accelerate Test<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Document<strong>in</strong>g Tast<strong>in</strong>g method<br />
Go Live<br />
a. A look at various cutover plann<strong>in</strong>g models might consider<br />
dur<strong>in</strong>g go live<br />
b. What it cut over plan, Why to have cut over plan<br />
c. Sett<strong>in</strong>g adequate user expectations<br />
d. Operational process<br />
e. Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and its role <strong>in</strong> successful rollout<br />
Post implementation support plann<strong>in</strong>g and its impact on rollout<br />
Post Implementation Support<br />
a. Creat<strong>in</strong>g new support services<br />
b. Help Desk structure and format<br />
c. Shift<strong>in</strong>g from a project to a production environment<br />
d. Conduct<strong>in</strong>g go live activities<br />
Knowledge transfer<br />
Organizational Changes<br />
Gett<strong>in</strong>g “E” for ERP<br />
a. How to use ERP for more Revenues (Earn<strong>in</strong>gs)<br />
Convergence <strong>of</strong> Back <strong>of</strong>fice & Front Office<br />
Enterprise Performance Management<br />
i. Balance Scorecard<br />
ii. Workflow analytics<br />
Data Warehous<strong>in</strong>g, Data m<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g<br />
Term Work<br />
06 13<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
25 | P a g e
Consumer Behavior<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
5. Consumer Behavior 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
A. To acqua<strong>in</strong>t with the conceptual issues models <strong>of</strong> consumer<br />
behaviour from the published literature.<br />
B. To develop an appreciation and understand<strong>in</strong>g about how these<br />
behavioural science based concepts & theories can be applied to<br />
expla<strong>in</strong> or understand consumer action (before, dur<strong>in</strong>g and after<br />
the purchase) <strong>in</strong> the Indian context.<br />
C. To help the participants’ to know the diversity <strong>of</strong> Indian market<br />
(with the help <strong>of</strong> an group assignment) and further, enrich their<br />
analytical skills (eg. Through preparation <strong>of</strong> a questionnaire<br />
with appropriate scal<strong>in</strong>g techniques to study specific aspects <strong>of</strong><br />
consumer action)<br />
D. F<strong>in</strong>ally, to understand how market<strong>in</strong>g strategies are evolved <strong>in</strong><br />
case <strong>of</strong> specific products / services or particular companies <strong>in</strong><br />
the Indian market, given the diversity with respect to<br />
demographics, psychology and behavioural patterns <strong>of</strong> Indian<br />
market.<br />
Term Work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
09 15<br />
09 20<br />
09 20<br />
08 20<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
26 | P a g e
International Market<strong>in</strong>g Management<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
6. International Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Management<br />
Topic<br />
Introduction to International Market<strong>in</strong>g :<br />
a)Mean<strong>in</strong>g, nature and scope <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>ternational market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
b) International market<strong>in</strong>g dist<strong>in</strong>guished from domestic market<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
Export<strong>in</strong>g, International trade and International bus<strong>in</strong>ess<br />
c) International market<strong>in</strong>g management process- an overview<br />
International Market<strong>in</strong>g Environment:<br />
a) Geographic, demographic, economic, political, legal, socio<br />
cultural environments- their nature and effects on <strong>in</strong>ternational<br />
market<strong>in</strong>g operations ,Tariff and non tariff barriers<br />
b) WTO, UNCTAD, Generalized system <strong>of</strong> preferences (GSP),<br />
Regional economic group<strong>in</strong>gs- European Union (EU), NAFTA,<br />
ASEAN, etc., Facilities and <strong>in</strong>centives schemes for exporters.<br />
International Product/ market Selection and Entry Modes:<br />
Select<strong>in</strong>g products, Select<strong>in</strong>g Market, Various modes <strong>of</strong> entry <strong>in</strong>to<br />
<strong>in</strong>ternational markets and their evaluation, Export licens<strong>in</strong>g/<br />
franchis<strong>in</strong>g, contract<strong>in</strong>g, Jo<strong>in</strong>t Venture, sett<strong>in</strong>g up wholly owned<br />
subsidiary.<br />
International Product Plann<strong>in</strong>g:<br />
a) Product <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>ternational context, standardization vs. adoption<br />
decision, other considerations<br />
b) Packag<strong>in</strong>g, Brand<strong>in</strong>g, after Sales Services, ISO 9001: 2000<br />
quality system standard<br />
International Pric<strong>in</strong>g: Factors <strong>in</strong>fluenc<strong>in</strong>g price, pric<strong>in</strong>g methods,<br />
Decisions and Pric<strong>in</strong>g process, Price quotations and related<br />
considerations<br />
International Distribution: Types and Functions <strong>of</strong> Foreign<br />
Distribution Channels, Selection <strong>of</strong> middlemen, Distribution<br />
logistics- transportation and warehous<strong>in</strong>g decisions<br />
International Promotion:<br />
International advertis<strong>in</strong>g- Standardization vs. Adaptation, Selection<br />
<strong>of</strong> Media, Selection <strong>of</strong> Agency, Measur<strong>in</strong>g Advertis<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Effectiveness<br />
Import and Export Procedures :<br />
a) ICD’s, Dry Port,Wet Port<br />
b) Domestic Procedures<br />
c) International Procedures (d) Procedures Specific <strong>of</strong> other<br />
country.<br />
Term Work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
06 15<br />
06 15<br />
08 15<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
27 | P a g e
International F<strong>in</strong>ancial Management<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
7. International F<strong>in</strong>ancial Management 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
International F<strong>in</strong>ancial Systems and Markets:<br />
a) The International Monetary Systems<br />
b)The Foreign Exchange Market – Spot, Forward, Futures and<br />
Options market<br />
Exchange Rate Determ<strong>in</strong>ants and Behaviour: Balance <strong>of</strong><br />
Payments, Relationships among <strong>in</strong>flation rates, <strong>in</strong>terest rates, and<br />
exchange rates and the parity conditions-International arbitrage and<br />
<strong>in</strong>terest rate parity.<br />
Exchange Rate Risk Management:<br />
a) Measur<strong>in</strong>g exposure to exchange rate fluctuations<br />
b) Manag<strong>in</strong>g exposure to exchange rate fluctuations.<br />
Asset and Liability Management:<br />
a) F<strong>in</strong>anc<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>ternational trade, International work<strong>in</strong>g capital<br />
management<br />
b) Corporate strategy and direct foreign <strong>in</strong>vestment, Political risk<br />
management<br />
c) International f<strong>in</strong>anc<strong>in</strong>g and equity issuance.<br />
Operation Control and Strategic Plann<strong>in</strong>g:<br />
a) Performance evaluation and control<br />
b) International tax plann<strong>in</strong>g, Cultural and ethical concern.<br />
Term Work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
10 25<br />
100<br />
28 | P a g e
International Bus<strong>in</strong>ess<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
8. International Bus<strong>in</strong>ess 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
International Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Environment:<br />
a) Globalization - Forces, Mean<strong>in</strong>g, dimensions and stages <strong>in</strong><br />
Globalization<br />
b) Trad<strong>in</strong>g Environment <strong>of</strong> International Trade - Tariff and Nontariff<br />
Barriers<br />
c) Trade Blocks - Rise <strong>of</strong> new economies like Japan, South East<br />
Asia and Ch<strong>in</strong>a.<br />
Country Risk Analysis:<br />
a) Political, Social and Economical - Cultural and Ethical practices<br />
(b) Responsibilities <strong>of</strong> International Bus<strong>in</strong>ess - Economic crisis <strong>of</strong><br />
Brazil, Mexico, India, South East Asia and Argent<strong>in</strong>a<br />
Manag<strong>in</strong>g Mult<strong>in</strong>ational Enterprises: Problems and Potential -<br />
Mult<strong>in</strong>ational Service Organizations, Indian companies becom<strong>in</strong>g<br />
mult<strong>in</strong>ationals - Potential, Need and Problems<br />
Introduction to International F<strong>in</strong>ancial Management:<br />
a) Balance <strong>of</strong> Trade and Balance <strong>of</strong> Payment<br />
b)International Monetary Fund, Asian Development Bank and<br />
World Bank , F<strong>in</strong>ancial Markets and its Instruments<br />
c) Introduction to Export and Import F<strong>in</strong>ance - Methods <strong>of</strong> payment<br />
<strong>in</strong> International Trade<br />
Bilateral and Multilateral Trade Laws:<br />
a) General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs, (GATT), World Trade<br />
Organization - Seattle and Doha round <strong>of</strong> talks<br />
b) Dispute settlement mechanism under WTO - Problems <strong>of</strong> Patent<br />
Laws - International convention on competitiveness<br />
Global sourc<strong>in</strong>g and its impact on Indian Industry -<br />
Globalization and <strong>in</strong>ternal reform process, India's competitive<br />
advantage <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>dustries like IT, Textiles, Gems & Jewellery etc. -<br />
Potential and threats<br />
Term Work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
06 15<br />
06 15<br />
08 15<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
Summer Project Report<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
9. Summer Project Report -- 4 -- -- 100 -- -- 100<br />
(100 marks, 90 hours)<br />
29 | P a g e
SCHEME: Semester III<br />
Retail Operation and Inventory<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
1 Retail Operation and Inventory 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
1. Information systems and supply cha<strong>in</strong> management<br />
• Strategic advantage ga<strong>in</strong>ed through supply cha<strong>in</strong><br />
management<br />
• The flow <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
• The Physical flow management<br />
2. Customer relationship management<br />
• The CRM process<br />
• Collect<strong>in</strong>g customer data<br />
• Analysis customer data identify<strong>in</strong>g target customer<br />
• Develop<strong>in</strong>g CRM programs<br />
• Implementation <strong>of</strong> CRM<br />
3. Organis<strong>in</strong>g the buy<strong>in</strong>g process by categories<br />
4. Sett<strong>in</strong>g objectives for the merchandise plan<br />
5. Sales forecast<strong>in</strong>g<br />
6. The assortment plann<strong>in</strong>g process<br />
7. The assortment plan<br />
8. Staple merchandise buy<strong>in</strong>g system<br />
9. Merchandis<strong>in</strong>g budget plan for fashion<br />
10. Merchandise<br />
11. Open-to-buy<br />
12. Allocation merchandise performance<br />
13. Analyz<strong>in</strong>g merchandise performance<br />
14. Brand<strong>in</strong>g Strategies<br />
15. International Sourc<strong>in</strong>g decision<br />
16. Connection with vendors<br />
17. Negotiat<strong>in</strong>g with vendors<br />
18. Establish<strong>in</strong>g and Ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g Strategic relationship with<br />
vendor<br />
19. Store Management responsibility<br />
20. Recruitment and select<strong>in</strong>g store employees<br />
21. Socializ<strong>in</strong>g and Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g New store employees<br />
Term Work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
30 | P a g e
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
2. Bank<strong>in</strong>g 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
• Introduction, mean<strong>in</strong>g and objective <strong>of</strong> f<strong>in</strong>ancial services,<br />
banks NBFCs, <strong>in</strong>vestment bankers etc.<br />
• Bank<strong>in</strong>g, def<strong>in</strong>ition, mean<strong>in</strong>g, types, role, historical<br />
overview, role <strong>of</strong> globalization, Role Pf, IT, SWOT <strong>of</strong><br />
Indian public sector banks.<br />
• Consolidation <strong>in</strong> the bank<strong>in</strong>g sector through merger and<br />
acquisition. Discussion with three major cities.<br />
• NBFCs, Mean<strong>in</strong>g, objective, types, role played RBI<br />
guidel<strong>in</strong>es, SWOT <strong>of</strong> NBFC, Bank VS NBFCs. Discussion<br />
through case.<br />
• Investment bank<strong>in</strong>g mean<strong>in</strong>g, objective, scope, role, banks<br />
VS <strong>in</strong>vestment bank<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
• Plastic money<br />
• Case discussion<br />
Term Work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
06 15<br />
06 15<br />
08 15<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
31 | P a g e
Culture Strategy & Behavior<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
3. Culture Strategy & Behavior 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
Environmental Foundation<br />
Worldwide Developments the political, legal, technological<br />
environment And global competitiveness<br />
Integrative Cases :<br />
A. Brazil & Argent<strong>in</strong>a<br />
B. Israel : A unique member <strong>of</strong> the Global Community<br />
C. Colgate’s Distasteful Toothpaste<br />
The Role <strong>of</strong> Culture<br />
Mean<strong>in</strong>g, dimensions, manag<strong>in</strong>g across cultures, organizational<br />
cultures and <strong>in</strong>tercultural communication<br />
International Strategic Management<br />
Strategic Plann<strong>in</strong>g, Organiz<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>ternational operations, decisionmak<strong>in</strong>g<br />
and controll<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Integrative Cases :<br />
A. Cultural Differences Doom a Seem<strong>in</strong>gly Perfect Alliance<br />
B. Questionable Strategy at the pebble Beach Golf L<strong>in</strong>ks<br />
OB & HRM<br />
Motivation across cultures, leadership across cultures, global<br />
leadership project and competencies, perpetual differences and<br />
personality analysis. Human Resource Selection and repatriation<br />
and Development across cultures.<br />
Integrative Cases :<br />
A. Cultural Differences Doom a Seem<strong>in</strong>gly Perfect Alliance<br />
B. Questionable Strategy at the pebble Beach Golf L<strong>in</strong>ks<br />
Skill Build<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar on International Management and Cross cultural<br />
operations to be delivered by four groups. Case Discussion and<br />
Submission <strong>in</strong> the Session<br />
Plann<strong>in</strong>g Merchandise Assortments<br />
Organiz<strong>in</strong>g the buy<strong>in</strong>g process by categories sett<strong>in</strong>g objectives for<br />
the Merchandise Plan Sales Forecast<strong>in</strong>g Assortment Plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Process<br />
Buy<strong>in</strong>g Systems<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
06 15<br />
Staple merchandise buy<strong>in</strong>g systems Merchandise buy<strong>in</strong>g plan for<br />
fashion merchandise Open To buy (OTB) Allocat<strong>in</strong>g Merchandise<br />
to stores Analyz<strong>in</strong>g merchandise performance<br />
Buy<strong>in</strong>g Merchandise<br />
Brand<strong>in</strong>g strategy<br />
International sourc<strong>in</strong>g decisions<br />
32 | P a g e
Connect<strong>in</strong>g with vendors<br />
Pric<strong>in</strong>g :<br />
Pric<strong>in</strong>g strategies<br />
Approaches for sett<strong>in</strong>g prices<br />
Price adjustments<br />
Us<strong>in</strong>g price to stimulate retail sales<br />
Methodology<br />
Class room sessions<br />
Case studies<br />
Role Play<br />
Project assignments<br />
Work shop<br />
Location visit – on the spot study<br />
Interactions<br />
Team games<br />
Internet Surf<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Library references<br />
CD VHS PPT presentations<br />
Evaluation<br />
Written exam<strong>in</strong>ations<br />
Project presentations<br />
Store visit report<br />
Attendance & classroom participation<br />
Work shop results<br />
Team participation<br />
Submission <strong>of</strong> dissertation on retail Management<br />
Term Work<br />
06 15<br />
08 15<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
33 | P a g e
Franchise Operations & Management<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
4. Franchise Operations &<br />
3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Management<br />
Topic<br />
Franchis<strong>in</strong>g as Entrepreneurship<br />
The Franchise relationship model<br />
The wealth – creat<strong>in</strong>g power <strong>of</strong> franchis<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Service delivery system & Real Estate<br />
Select<strong>in</strong>g & Monitor<strong>in</strong>g Franchisees<br />
The Service Delivery System & Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Transaction Analysis<br />
F<strong>in</strong>ancial Analysis<br />
The Dynamics <strong>of</strong> the Franchiser, Franchisee Relationship<br />
Understand<strong>in</strong>g the basis <strong>of</strong> Franchise Laws<br />
International Franchis<strong>in</strong>g<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
15<br />
15<br />
15<br />
15<br />
15<br />
Harvest<br />
Term Work<br />
10 25<br />
100<br />
Managerial Economics<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
5. Managerial Economics 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
The mean<strong>in</strong>g, scope and methods <strong>of</strong> Managerial Economics.<br />
Economic concepts relevant to bus<strong>in</strong>ess; Demand and supply,<br />
production, distribution, consumption and consumption function;<br />
Cost, Price, Competition, Monopoly, Pr<strong>of</strong>its, Optimisation, Marg<strong>in</strong><br />
and Average, Elasticity, Macro and Micro Analysis<br />
Demand Analysis and Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Forecast<strong>in</strong>g, Market Structures,<br />
Factors <strong>in</strong>fluenc<strong>in</strong>g Demand, Elasticities and Demand levels.<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 20<br />
10 20<br />
34 | P a g e
Demand Analysis for various products and situations, Determ<strong>in</strong>ants<br />
<strong>of</strong> Demand, Durables and Non-durable goods. Long run and Short<br />
run Demand, Derived and Autonomous Demand, Industry and Firm<br />
Demand<br />
Cost and Production analysis – cost concepts, short term and long<br />
term, cost-output relationship, cost <strong>of</strong> multiple products,<br />
Economics <strong>of</strong> scale, production functions, Cost control, Cost and<br />
pr<strong>of</strong>it forecast<strong>in</strong>g, Break even analysis<br />
Market analysis, Competition, K<strong>in</strong>ds <strong>of</strong> Competitive situations,<br />
Oligopoly and monopoly, Measur<strong>in</strong>g concentration <strong>of</strong> economic<br />
power. Pric<strong>in</strong>g decisions, policies and practices, pric<strong>in</strong>g and output<br />
decisions under perfect and imperfect competition, oligopoly and<br />
monopoly : pric<strong>in</strong>g methods, product l<strong>in</strong>e pric<strong>in</strong>g, specific pric<strong>in</strong>g<br />
problems, price discrim<strong>in</strong>ation, price forecast<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Pr<strong>of</strong>it Management, role <strong>of</strong> pr<strong>of</strong>it <strong>in</strong> the economy, Nature and<br />
measurement <strong>of</strong> pr<strong>of</strong>it, Pr<strong>of</strong>it policies, policies on pr<strong>of</strong>it<br />
maximization, pr<strong>of</strong>its and control, pr<strong>of</strong>it plann<strong>in</strong>g and control<br />
Capital budget<strong>in</strong>g, demand for capital, supply <strong>of</strong> capital, capital<br />
ration<strong>in</strong>g, cost <strong>of</strong> capital, apprais<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> pr<strong>of</strong>itability <strong>of</strong> a project,<br />
risk and uncerta<strong>in</strong>ty, Economical probability analysis<br />
Macro economics and bus<strong>in</strong>ess, bus<strong>in</strong>ess cycle and bus<strong>in</strong>ess<br />
policies, economic <strong>in</strong>dicators, forecast<strong>in</strong>g for bus<strong>in</strong>ess, <strong>in</strong>put output<br />
analysis<br />
Term Work<br />
Total<br />
05 20<br />
05 05<br />
05 05<br />
05 05<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
35 | P a g e
Retail Laws & HR <strong>in</strong> Retail<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
6. Retail Laws & HR <strong>in</strong> Retail<strong>in</strong>g 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
Human Resource Management –<br />
a. Nature, mean<strong>in</strong>g, def<strong>in</strong>ition, scope & objectives<br />
b. Functions & Role <strong>of</strong> HR <strong>Personnel</strong><br />
c. HR Policies & Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples<br />
Human Resource Plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a. Mean<strong>in</strong>g & def<strong>in</strong>ition<br />
b. Importance, scope & objectives<br />
c. Factors affect<strong>in</strong>g HRP & Requisites for HRP<br />
d. Plann<strong>in</strong>g Process. (assess<strong>in</strong>g current, implications<br />
<strong>of</strong> demand & supply)<br />
e. Barriers to HRP<br />
f. Job Analysis (mean<strong>in</strong>g, process, methods,<br />
problems) – Job Description, Job specification.<br />
g. Job Design<br />
h. Job evaluation, job security<br />
i. Job load<strong>in</strong>g, job enlargements, job rotation,<br />
job enrichment, job shar<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Human Resource Acquisition<br />
a. Recruitment (mean<strong>in</strong>g, def<strong>in</strong>ition, purpose,<br />
importance, methods, process, cost, problems,<br />
barriers)<br />
b. Selection (mean<strong>in</strong>g, def<strong>in</strong>ition, purpose, methods,<br />
devices, process, discrete, barriers)<br />
c. Orientation, placement, <strong>in</strong>duction<br />
d. Promotion, demotion, transfer, separation, turnover<br />
Human Resource Development<br />
a. Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g (nature, mean<strong>in</strong>g, purpose, importance,<br />
objectives, process, identify<strong>in</strong>g needs, methods,<br />
use, barriers, evaluation, effectiveness)<br />
b. Managerial Development<br />
c. Mentor<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Human Resource Utilization<br />
a. Productivity<br />
b. Performance Management<br />
c. Performance Appraisal (nature, mean<strong>in</strong>g, purpose,<br />
importance, objectiveness)<br />
d. Career development (dimensions, stages,<br />
<strong>in</strong>dividual role, organizational responsibility)<br />
e. Succession plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Human Relation Management<br />
A. Compensation<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
06 13<br />
06 12<br />
07 15<br />
06 15<br />
10 20<br />
36 | P a g e
I. Employee Remuneration<br />
a. Compensation (importance, theories, Components,<br />
challenges, remuneration plan)<br />
b. Wages, wage policy <strong>in</strong> India<br />
c. Incentives (mean<strong>in</strong>g, def<strong>in</strong>ition, scope, types,<br />
group <strong>in</strong>centive plans, <strong>in</strong>stall<strong>in</strong>g a <strong>in</strong>centive<br />
scheme)<br />
II. Executive Remuneration (components,<br />
Features, extent)<br />
III. Rewards (types, quality <strong>of</strong> rewards, criterion for reward<strong>in</strong>g)<br />
B. Employee Benefits & Services<br />
(mean<strong>in</strong>g, def<strong>in</strong>ition, types, pr<strong>in</strong>ciples, non-monetary rewards,<br />
adm<strong>in</strong>istration <strong>of</strong> benefits, group <strong>in</strong>centive<br />
plans, <strong>in</strong>stall<strong>in</strong>g a <strong>in</strong>centive scheme<br />
C. Participative management, empowerment goal<br />
Sett<strong>in</strong>g, quality <strong>of</strong> work life.<br />
Term Work<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
37 | P a g e
F<strong>in</strong>ancial Strategy<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
7. F<strong>in</strong>ancial Strategy 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
• Strategic Pr<strong>of</strong>it Model : An Overview<br />
The Pr<strong>of</strong>it Path<br />
Net Sales<br />
Gross Marg<strong>in</strong><br />
Expenses<br />
• The Turnover Path<br />
Current Assets<br />
Accounts Receivable<br />
Merchandise Inventory<br />
Cash and Other Current Assets<br />
Fixed Assets<br />
Assets Turnover<br />
Liabilities and Owner’s Equity<br />
• The Strategic Pr<strong>of</strong>it Model<br />
Return on Assets<br />
Term Work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
11 25<br />
12 25<br />
12 25<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
38 | P a g e
Visual Merchandis<strong>in</strong>g and Sales Policy<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
8. Visual Merchandis<strong>in</strong>g and Sales 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Policy<br />
Topic<br />
Plann<strong>in</strong>g Merchandise<br />
Assortments<br />
Organiz<strong>in</strong>g the buy<strong>in</strong>g process by categories<br />
Buy<strong>in</strong>g Systems<br />
Staple merchandise buy<strong>in</strong>g systems Merchandis<strong>in</strong>g buy<strong>in</strong>g plan for<br />
fashion merchandise<br />
Open to buy (OTB)<br />
Allocat<strong>in</strong>g Merchandise to stores<br />
Analyz<strong>in</strong>g Merchandise performance<br />
Buy<strong>in</strong>g Merchandise<br />
Brand<strong>in</strong>g strategy<br />
International Sourc<strong>in</strong>g decisions<br />
Connect<strong>in</strong>g with vendors<br />
Negotiation with vendors<br />
Establish<strong>in</strong>g & ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g strategic<br />
Relationship with vendors<br />
Pric<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Pric<strong>in</strong>g strategies<br />
Approaches for sett<strong>in</strong>g prices<br />
Price adjustments<br />
Us<strong>in</strong>g price to stimulate retail sales<br />
Term Work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
11 25<br />
12 25<br />
12 25<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
39 | P a g e
Supply Cha<strong>in</strong> Management<br />
Subject L Cr P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
9. Supply Cha<strong>in</strong> Management 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
1. Introduction to Supply Cha<strong>in</strong> Management<br />
- Fundamentals <strong>of</strong> SCM and basic def<strong>in</strong>ition<br />
- Major drivers <strong>of</strong> SC<br />
- SC components and need for <strong>in</strong>tegration<br />
- SC <strong>in</strong> various <strong>in</strong>dustries<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 10<br />
2.Strategic Decisions <strong>in</strong> Supply Cha<strong>in</strong><br />
- Bus<strong>in</strong>ess strategy<br />
- Core compete <strong>in</strong> SC<br />
- Trade <strong>of</strong>f <strong>in</strong> SC<br />
- CRM strategy <strong>in</strong> SC<br />
3. Manag<strong>in</strong>g a Supply Cha<strong>in</strong><br />
- Creat<strong>in</strong>g SC vision and adopt<strong>in</strong>g SC <strong>in</strong>itiative measures<br />
- Develop<strong>in</strong>g SC organization<br />
- Customer service dimensions and SC orientation<br />
- SC ‘Value Cha<strong>in</strong>’ & ‘Value Network<br />
4. Sub systems <strong>in</strong> SC<br />
- Procurement (Strategic sourc<strong>in</strong>g, partnership, vendor<br />
development)<br />
- Conversions (Flexible manufactur<strong>in</strong>g, facility plann<strong>in</strong>g)<br />
- Distribution (Network and logistic plann<strong>in</strong>g)<br />
- Warehous<strong>in</strong>g & Transportation <strong>in</strong> Supply cha<strong>in</strong><br />
- Align<strong>in</strong>g capabilities <strong>of</strong> SC partners<br />
5. Supply Cha<strong>in</strong> Mapp<strong>in</strong>g<br />
- Value and non value added activities<br />
- Waste identification and elim<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
- Techniques used <strong>in</strong> waste elim<strong>in</strong>ation (Kaizen, TQM, Six<br />
sigma)<br />
6. Information Technology <strong>in</strong> Supply Cha<strong>in</strong><br />
- Developments <strong>in</strong> E-commerce and E-bus<strong>in</strong>ess solutions<br />
- EDI, Bar Cord<strong>in</strong>g, RFID<br />
- Data m<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and warehous<strong>in</strong>g<br />
- E-supply Cha<strong>in</strong><br />
7. Supply cha<strong>in</strong> Information System<br />
- Computer based Information System<br />
- Feature and Evaluation <strong>of</strong> ERP, DRP, MRP systems<br />
- ERP & SCM<br />
- Organization Structure<br />
8. Supply Cha<strong>in</strong> Optimization<br />
- L<strong>in</strong>ear Programm<strong>in</strong>g model<strong>in</strong>g example<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
06 15<br />
06 15<br />
40 | P a g e
- Multiple objective optimization<br />
- Asset based and process based optimization<br />
9. Benchmark<strong>in</strong>g SC<br />
- What is benchmark<strong>in</strong>g<br />
- Benchmark<strong>in</strong>g SC process and its components<br />
- Sett<strong>in</strong>g benchmark<strong>in</strong>g priorities and performance <strong>in</strong>dicators<br />
Term Work<br />
08 15<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
41 | P a g e
SCHEME: Semester IV<br />
Sell<strong>in</strong>g techniques<br />
Subject L P/T P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
1. Sell<strong>in</strong>g techniques 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
1. The role <strong>of</strong> a personal sell<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> overall Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Framework<br />
2. personality Traits for Sales Success<br />
3. fundamentals <strong>of</strong> communication<br />
4. Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Creation and Prospect<strong>in</strong>g<br />
5. pre- approach preparation<br />
6. The sell<strong>in</strong>g process<br />
7. Negotiation skills<br />
8. positive Attitude Ma<strong>in</strong>tenance<br />
9. Sett<strong>in</strong>g Goals<br />
10. Time Management<br />
11. Territory Plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
12. Major Accounts Plann<strong>in</strong>g and Management<br />
13. Sell<strong>in</strong>g to different personality Types<br />
14. Telemarket<strong>in</strong>g<br />
15. Advanced Sell<strong>in</strong>g Methods<br />
Term Work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
42 | P a g e
Entrepreneurship Management<br />
Subject L P/T P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
2. Entrepreneurship Management 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
1. Concept or Entrepreneurship – How a Manager<br />
differentiated from an entrepreneur? Qualities <strong>of</strong> an<br />
Entrepreneur Characteristic. Risk tak<strong>in</strong>g Ability egotiation<br />
Skills etc. Develop<strong>in</strong>g Entrepreneurship and the theory <strong>of</strong><br />
Achievement Motivation.<br />
2. Generat<strong>in</strong>g and Screen<strong>in</strong>g the Bus<strong>in</strong>ess ideas and Identify<strong>in</strong>g<br />
the venture; Entrepreneurial Opportunities <strong>in</strong> Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
and Service <strong>in</strong>dustries <strong>in</strong> India .<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 10<br />
05 10<br />
3. Role <strong>of</strong> small and Ancillary Industries <strong>in</strong> ational Economy. 05 10<br />
4. Start<strong>in</strong>g and Management a new small or Ancillary Unit –<br />
Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Plan ; Procedures; <strong>Personnel</strong>, F<strong>in</strong>ancial Materials,<br />
Market<strong>in</strong>g and Distribution and R & D Management<br />
06 15<br />
5. Vendor Development programme – Organisation for vendor<br />
Development Programme ; Cost – Benefit Analysis <strong>of</strong> vendor<br />
Development programme.<br />
6. Entrepreneurial Development and the Indian Environment<br />
– Government Policies ; Government Agencies Support<strong>in</strong>g<br />
entrepreneurial Development ; Industries Estates F<strong>in</strong>ancial<br />
Assistance Schemes Tax Incentives Schemes for Educated<br />
unemployment etc.<br />
Term Work<br />
06 15<br />
08 15<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
43 | P a g e
Management Control System<br />
Subject L P/T P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
3. Management Control System 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
F<strong>in</strong>ancial goal sett<strong>in</strong>g – Analysis <strong>of</strong> Incremental ROI – Sensitivity<br />
Analysis – Develop<strong>in</strong>g f<strong>in</strong>ancial goals along organisation hierarchy<br />
– Concept and Technique <strong>of</strong> Responsibility Budget<strong>in</strong>g – Analytical<br />
framework for Develop<strong>in</strong>g Responsibility Budgets – Integrat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Responsibility Budgets – Budget<strong>in</strong>g with MBO Systems.<br />
ORGANISATION GROWTH ; Responsibility <strong>of</strong> pr<strong>of</strong>it centres –<br />
identification and creation <strong>of</strong> pr<strong>of</strong>it centres, Pr<strong>of</strong>it centres as a<br />
control systems – decentralisation and pr<strong>of</strong>it centres.<br />
Mechanics <strong>of</strong> determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>of</strong>it objectives <strong>of</strong> pr<strong>of</strong>it centres –<br />
Problems and perspectives <strong>of</strong> transfer pric<strong>in</strong>g – L<strong>in</strong>ear<br />
programm<strong>in</strong>g technique for determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g divisional goals <strong>in</strong> a multidivisional<br />
company – problems <strong>of</strong> growth and corporate control.<br />
CONTROL IN SPECIAL SECTORS : Scrap Control <strong>of</strong> R & D –<br />
Project Control – Adm<strong>in</strong>istrative Cost Control – audit Efficiency<br />
Audit – Internal Audit – Government Cost Audit – Management<br />
Audit.<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
09 20<br />
09 20<br />
09 20<br />
F<strong>in</strong>ancial Report<strong>in</strong>g to Management Under Conditions <strong>of</strong> price<br />
level change : Objective and methodology.<br />
08 15<br />
Term Work<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
44 | P a g e
Retail Brand Build<strong>in</strong>g and Product Management<br />
Subject L P/T P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
4. Retail Brand Build<strong>in</strong>g and Product 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Management<br />
Topic<br />
Intro to ew product Management ; The ew Product Process<br />
Strategic plann<strong>in</strong>g for new products.The operation <strong>of</strong> product<br />
Management<br />
The Ideation Stage<br />
Concept Evaluation<br />
The Design Processes<br />
Customer Measurement<br />
Commercialization<br />
Market<strong>in</strong>g Plan<br />
Market<strong>in</strong>g Mix<br />
Post Launch Control<br />
• What is brand ?<br />
• Why a brand is much more than a logo<br />
• Ttypes <strong>of</strong> brand<strong>in</strong>g used today<br />
Strategic Implications <strong>of</strong> Brand<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Creat<strong>in</strong>g and susta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g Brand Equity<br />
• Creat<strong>in</strong>g a brand<br />
• Pyramid Model<br />
• Brand Extension<br />
• Brand Architecture<br />
• Brand portfolios<br />
• Global Brands<br />
Brand Position<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Brand Action<br />
• Deliver<strong>in</strong>g expectations<br />
• Campaign plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Why Brand Management ?<br />
• The importane to company value<br />
• Strategic implications<br />
• How brands drive growth<br />
• F<strong>in</strong>ancial evaluation <strong>of</strong> brands<br />
The Philosophy <strong>of</strong> Brand<strong>in</strong>g – Discussion<br />
The Role <strong>of</strong> Retailers<br />
Brand<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> service Bus<strong>in</strong>ess<br />
Term work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 12<br />
06 12<br />
06 15<br />
06 12<br />
06 12<br />
06 12<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
45 | P a g e
Corporate F<strong>in</strong>ance<br />
Subject L P/T P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
5. Corporate F<strong>in</strong>ance 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
1. ITRODUCTIO : Ma<strong>in</strong> corporate decisions. Balance<br />
Sheet model <strong>of</strong> firm Capital structure. Types <strong>of</strong><br />
organizations: proprietorship, Partnership,<br />
Corporation, Goals <strong>of</strong> corporate firm : Shareholders<br />
wealth maximization, Managerial Goals, Separation <strong>of</strong><br />
ownership and control, F<strong>in</strong>ancial markets.<br />
2. ACCOUTIG STATEMET AD CASH FLOWS :<br />
Balance sheet, et work<strong>in</strong>g capital, Statement <strong>of</strong> cash<br />
flow, F<strong>in</strong>ancial Statement analysis: Liquidity ratios,<br />
Activity ratios, F<strong>in</strong>ancial leverage ratios, Pr<strong>of</strong>itability<br />
ratios, Market ratios.<br />
3. VALUE AD CAPITAL BUDGETIG: The F<strong>in</strong>ancial<br />
Market Economy, Mak<strong>in</strong>g consumption choices over<br />
time, The competitive market.<br />
4. ET PRESET VALUE: The one period case, The<br />
multi-period case, Future value and compound<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
Present value and discount<strong>in</strong>g, Compound<strong>in</strong>g periods,<br />
Compound<strong>in</strong>g over many years, Cont<strong>in</strong>ious<br />
compound<strong>in</strong>g, Perpetuity, Growth perpetuity Anuity,<br />
Grow<strong>in</strong>g annuity, What is a firm worth.<br />
5. VALUIG STOCKS AD BODS: Valu<strong>in</strong>g bonds,<br />
Pure discountbonds, consols, Bond concepts, Interest<br />
rates and bond prices, Yield to maturity, Present value<br />
<strong>of</strong> common stocks, Dividends versus capital ga<strong>in</strong>s, Stock<br />
valuation, Dividend discount model, Growth<br />
opportunities, PVGO model, P/E ratio.<br />
CAPITAL BUDGETIG: Payback period, Discounted<br />
payback, Average account<strong>in</strong>g return, Internal rate <strong>of</strong> return,<br />
et present value, Pr<strong>of</strong>itability <strong>in</strong>dex, Independent and<br />
mutually exclusive projects, Example with net work<strong>in</strong>g<br />
capital, Inflation & capital budget<strong>in</strong>g, Investment <strong>in</strong><br />
unequal lives, Replacement cha<strong>in</strong>, Strategy and PV.<br />
6. WORKIG CAPITAL MAAGEMET :<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
07 15<br />
7. CAPITAL MARKET THEORY: Risk and return,<br />
Capital asset pric<strong>in</strong>g model, The efficient set <strong>of</strong> two<br />
assets, Covariance and correlation , Beta, Risk less<br />
borrow<strong>in</strong>g and lend<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
8. RISK, COST OF CAPITAL BUDGETIG : Cost <strong>of</strong> 07 15<br />
46 | P a g e
capital, Betas, Determ<strong>in</strong>ants <strong>of</strong> Beta, cost <strong>of</strong> equity &<br />
Debt, Determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g weighted average cost <strong>of</strong> capital,<br />
cost <strong>of</strong> equity and debt, Efficient capital markets.<br />
Different types <strong>of</strong> efficiency.<br />
9. LOG TERM FIACIG: Common stock and<br />
Corporate long term debt, Preferred stock, patterns <strong>of</strong><br />
F<strong>in</strong>anc<strong>in</strong>g, Capital structure, F<strong>in</strong>ancial leverage and<br />
firm value, Modigliani and Miller Proposition I & II<br />
, Bankruptcy Risk, Valuation <strong>of</strong> a levered firm.<br />
10. DIVIDED POLICY<br />
Term work 10 25<br />
45 100<br />
IT <strong>in</strong> Retail<br />
Subject L P/T P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
6. IT <strong>in</strong> Retail 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
Fundamentals <strong>of</strong> Information Technology.<br />
Hardware & s<strong>of</strong>tware<br />
Internet & Intranet<br />
etwork<strong>in</strong>g Fundamentals<br />
Manag<strong>in</strong>g Data Resource<br />
Management <strong>of</strong> Information Systems<br />
Types <strong>of</strong> MIS.<br />
Privacy, Ethical and Social issues <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>formation system<br />
Crime and legal aspects <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>formation system.<br />
Information system <strong>in</strong> Retail<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Bus<strong>in</strong>ess <strong>in</strong>formation systems<br />
E- commerce & E- Bus<strong>in</strong>ess<br />
Decision support system<br />
Executive Information system<br />
Expert systems<br />
Inventory Information system<br />
Market<strong>in</strong>g Information system<br />
Systems <strong>in</strong>tegration & analysis<br />
System design, implementation<br />
Retail Applications and ew paradigms<br />
Retail S<strong>of</strong>twares & Applications<br />
ew concepts and paradigms shifts <strong>in</strong> RIS design<br />
Value <strong>in</strong>novation through bus<strong>in</strong>ess web.<br />
Enterprise Resource systems<br />
Strategy and new economic <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Merchandis<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
09 18<br />
09 19<br />
09 19<br />
08 19<br />
47 | P a g e
Human centric comput<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Intelligent Techniques :<br />
Artificial Intelligence.<br />
eural etworks.<br />
Term work<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
48 | P a g e
Market Research<br />
Subject L P/T P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
7. Market Research 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
Fitt<strong>in</strong>g MR <strong>in</strong>to market<strong>in</strong>g framework.<br />
What is MR and not MR.<br />
Def<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g Problems and structure <strong>of</strong> survey.<br />
Primary data / Secondary data collection.<br />
Sample decision / Field work / Tabulation.<br />
Analysis and Interpretation <strong>of</strong> Data Analysis.<br />
Factor analysis – us<strong>in</strong>g computer based techniques like SPSS<br />
packages, special emphasis on cluster Analysis and Determ<strong>in</strong>ant<br />
Analysis.<br />
Application <strong>of</strong> MR to advertis<strong>in</strong>g research / Industrial market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
research.<br />
Term work<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs)<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
05 15<br />
10 15<br />
10 15<br />
10 30<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
Foreign Language (German)<br />
Subject L P/T P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
8. Foreign Language (German) 3 4 2 3 75 25 -- 100<br />
Topic<br />
Foreign Language Knowledge Related To:<br />
1. Listen<strong>in</strong>g: Understand Simple Questions and Instructions.<br />
Read<strong>in</strong>g: Understand S<strong>in</strong>gle Words and Sentences but also Signposts,<br />
Signs and Posters.<br />
Speak<strong>in</strong>g: Provide Short Information about the Job and the Person.<br />
Writ<strong>in</strong>g: Fill <strong>in</strong> Forms and Provide Information About Name, Address,<br />
Nationality etc.<br />
2. Listen<strong>in</strong>g: Understand Information about the Person and the Work.<br />
Read<strong>in</strong>g: Understand Simple Letters, Appo<strong>in</strong>tments, Invitations and<br />
Information <strong>in</strong> Short<br />
Texts.<br />
Speak<strong>in</strong>g: Answer Simple Questions About One's Work<strong>in</strong>g Field.<br />
Writ<strong>in</strong>g: Write Faxes and e-mails (10 Hours)<br />
3. Listen<strong>in</strong>g: Understand Standard Information Related to the Work<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Field.<br />
Read<strong>in</strong>g: Understand Standard Letters and Texts about Work<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Processes and Product<br />
o. <strong>of</strong><br />
Lectures<br />
(Hrs)<br />
Weight<br />
age (%)<br />
09 15<br />
09 20<br />
49 | P a g e
Descriptions.<br />
Speak<strong>in</strong>g: Provide Information about the Job, the Departments, the<br />
Company, the Products and<br />
Processes <strong>in</strong> a Conversation or on the Phone.<br />
Writ<strong>in</strong>g: Answer Standard Inquiries, Make Quotations, Write Short<br />
Texts with a Familiar<br />
Content, Possibly Give Some Explanation and Answer Simple<br />
Questions.<br />
4. Listen<strong>in</strong>g: Understand Complex Information Related to the<br />
Work<strong>in</strong>g Field <strong>in</strong> Meet<strong>in</strong>gs,<br />
Discussions and at Presentations.<br />
Read<strong>in</strong>g: Understand Reports and Contracts with a Company-related<br />
Content.<br />
Speak<strong>in</strong>g: Describe and Expla<strong>in</strong> Work Processes and Projects. Report<br />
on Meet<strong>in</strong>gs and<br />
Presentations. Expla<strong>in</strong> Concepts and Clarify Misunderstand<strong>in</strong>gs.<br />
Writ<strong>in</strong>g: Write Formal Standard Letters and Texts about One's Field<br />
<strong>of</strong> Expertise. Expla<strong>in</strong> a<br />
Graphic and Reflect the Content.<br />
Term work<br />
09 20<br />
08 20<br />
10 25<br />
45 100<br />
Research Based Project : Year Long<br />
Subject L P/T P/T D TP TW P/V T<br />
9. Research Based Project : Year Long -- 8 -- -- 100 -- -- 100<br />
(100 marks 90 hours)<br />
50 | P a g e