Covalent bond worksheet
Covalent bond worksheet
Covalent bond worksheet
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
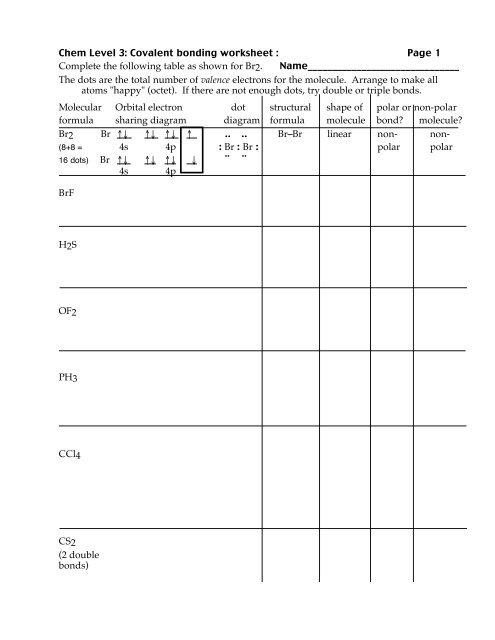
Chem Level 3: <strong>Covalent</strong> <strong>bond</strong>ing <strong>worksheet</strong> : Page 1<br />
Complete the following table as shown for Br2. Name_______________________________<br />
The dots are the total number of valence electrons for the molecule. Arrange to make all<br />
atoms "happy" (octet). If there are not enough dots, try double or triple <strong>bond</strong>s.<br />
Molecular Orbital electron dot structural shape of polar or non-polar<br />
formula sharing diagram diagram formula molecule <strong>bond</strong> molecule<br />
Br2 Br !" !" !" ! .. .. Br–Br linear non- non-<br />
(8+8 = 4s 4p : Br : Br : polar polar<br />
16 dots) Br !" !" !" " ¨ ¨<br />
4s 4p<br />
BrF<br />
H2S<br />
OF2<br />
PH3<br />
CCl4<br />
CS2<br />
(2 double<br />
<strong>bond</strong>s)
Worksheet: Dot Diagram Practice Page 2<br />
1. Complete the following dot diagrams and write the structural formula for each compound.<br />
( Hint: Carbon always makes a total of 4 <strong>bond</strong>s (4 single, 2 single and 1 double, etc. )<br />
CH4<br />
methane<br />
(4+4 =<br />
8 dots)<br />
C2H6<br />
ethane<br />
C2H4, ethene<br />
(1 double <strong>bond</strong>)<br />
H<br />
..<br />
H : C : H<br />
..<br />
H<br />
H H<br />
H C C H<br />
H H<br />
H H<br />
H C C H<br />
H<br />
|<br />
H - C - H<br />
|<br />
H<br />
ClCHF2<br />
freon<br />
CH2O<br />
formaldehyde<br />
(1 double <strong>bond</strong>)<br />
CH3OH<br />
methanol<br />
F<br />
H C Cl<br />
F<br />
H<br />
H C O<br />
H<br />
H C O H<br />
H<br />
C2H2<br />
acetylene<br />
(1 triple <strong>bond</strong>)<br />
H C C H<br />
HCOOH<br />
formic acid<br />
(1 double <strong>bond</strong>)<br />
H C O H<br />
O<br />
2. Draw the dot diagrams and write the structural formula for these compounds and polyatomic ions.<br />
Same principle: Dots = total number of valence electrons. Negative ions add extra elctron(s), Positive<br />
ions take away electron(s) Watch out for double and triple <strong>bond</strong>s!<br />
OH –<br />
hydroxide<br />
ion (6+1+1<br />
= 8 dots)<br />
NH2 –<br />
amide ion<br />
BrO2 –<br />
bromite ion<br />
CN -<br />
cyanide ion<br />
..<br />
: O : H<br />
˙˙<br />
H N H<br />
O Br O -<br />
[ C N ] -<br />
[ O - H ] -<br />
NH4 +<br />
ammonium<br />
ion<br />
SO3 –2<br />
sulfite ion<br />
N2O<br />
O<br />
O S O<br />
O<br />
H<br />
H N H<br />
H<br />
N N<br />
-2<br />
CO carbon<br />
monoxide<br />
POCl<br />
O<br />
O<br />
C<br />
P Cl<br />
NO3 –<br />
nitrate ion<br />
O N O<br />
O<br />
-
Level 2 Chemistry Name _________________________page 3<br />
<strong>Covalent</strong> <strong>bond</strong>ing <strong>worksheet</strong> (use your VSEPR chart to answer the following)<br />
1. Calculate the <strong>bond</strong> energy of the following molecules (add up the <strong>bond</strong> energies).<br />
a. NH3 b. Br c. H<br />
| |<br />
Br– C – Cl<br />
H – C = O<br />
|<br />
Cl<br />
2. Which of the following molecules is the most stable (highest <strong>bond</strong> energy) The least stable<br />
(lowest <strong>bond</strong> energy)<br />
H – F H – Br H – I H – Cl<br />
3. Calculate the electronegativity difference for the follwoing <strong>bond</strong>s. Then identify each as<br />
non-polar, polar or ionic . If Polar or ionic, identify the + and – or !+ and !– element in each.<br />
(The negative atom has the higher electronegativity).<br />
a. H – I e. O – O<br />
b. Li – I f. C – Cl<br />
c. Ca – Cl g. H – O<br />
d. I – I h. Na – O<br />
4. What is the shape of the following molecules Is each molecule polar or non-polar For<br />
polar molecules, identify the ! + and ! – part of each molecule.<br />
.. .. .. .. .. .. ..<br />
a. : I : I : c. : Cl : O : Cl : e. : Br : F :<br />
˙˙ ˙˙ ˙˙ ˙˙ ˙˙ ˙˙ ˙˙<br />
.. .. .. ..<br />
..<br />
: F :<br />
.. .. ..<br />
b. : Cl : P : Cl : d. H : C : : O : f. : F : C : F :<br />
˙˙ ˙˙ ˙˙ ˙˙ ˙˙ ˙˙ ˙˙<br />
: Cl : H : F:<br />
˙˙<br />
˙˙
Level 2 Chemistry page 4<br />
Review sheet for <strong>Covalent</strong> Bonding<br />
1. a. What are two differeneces between ionic <strong>bond</strong>ing and covalent <strong>bond</strong>ing<br />
b. What are two similarities between ionic <strong>bond</strong>ing and covalent <strong>bond</strong>ing<br />
2. Write the orbital notation electron sharing diagram for the covalent compound Cl2S.<br />
3. Fill in the following chart for these covalent compounds.<br />
ClF<br />
Dot structural shape type of molecule<br />
diagram formula (polar or non-polar)<br />
H2Se<br />
CH2Cl2<br />
ClO -<br />
4. H–Br Is the <strong>bond</strong> polar, non-polar or ionic<br />
5. Acetylene, H–C"C–H, is a linear molecule. Is this molecule polar or non-polar Why