Aerosol Guide - AARC.org
Aerosol Guide - AARC.org
Aerosol Guide - AARC.org
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
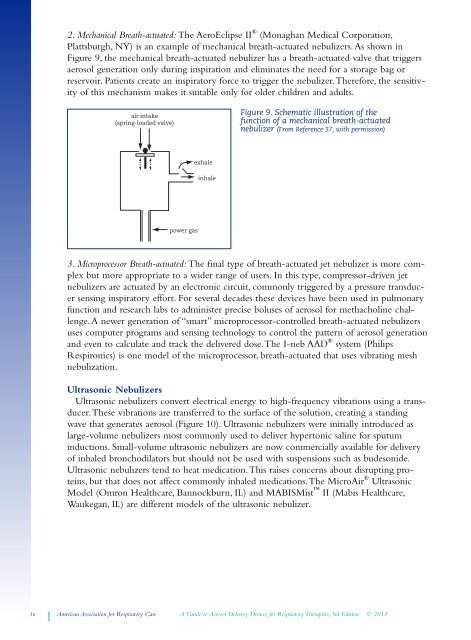
2. Mechanical Breath-actuated: The AeroEclipse II ® (Monaghan Medical Corporation,<br />
Plattsburgh, NY) is an example of mechanical breath-actuated nebulizers. As shown in<br />
Figure 9, the mechanical breath-actuated nebulizer has a breath-actuated valve that triggers<br />
aerosol generation only during inspiration and eliminates the need for a storage bag or<br />
reservoir. Patients create an inspiratory force to trigger the nebulizer. Therefore, the sensitivity<br />
of this mechanism makes it suitable only for older children and adults.<br />
air intake<br />
(spring-loaded valve)<br />
Figure 9. Schematic illustration of the<br />
function of a mechanical breath-actuated<br />
nebulizer (From Reference 37, with permission)<br />
exhale<br />
inhale<br />
power gas<br />
3. Microprocessor Breath-actuated: The final type of breath-actuated jet nebulizer is more complex<br />
but more appropriate to a wider range of users. In this type, compressor-driven jet<br />
nebulizers are actuated by an electronic circuit, commonly triggered by a pressure transducer<br />
sensing inspiratory effort. For several decades these devices have been used in pulmonary<br />
function and research labs to administer precise boluses of aerosol for methacholine challenge.<br />
A newer generation of “smart” microprocessor-controlled breath-actuated nebulizers<br />
uses computer programs and sensing technology to control the pattern of aerosol generation<br />
and even to calculate and track the delivered dose. The I-neb AAD ® system (Philips<br />
Respironics) is one model of the microprocessor, breath-actuated that uses vibrating mesh<br />
nebulization.<br />
Ultrasonic Nebulizers<br />
Ultrasonic nebulizers convert electrical energy to high-frequency vibrations using a transducer.<br />
These vibrations are transferred to the surface of the solution, creating a standing<br />
wave that generates aerosol (Figure 10). Ultrasonic nebulizers were initially introduced as<br />
large-volume nebulizers most commonly used to deliver hypertonic saline for sputum<br />
inductions. Small-volume ultrasonic nebulizers are now commercially available for delivery<br />
of inhaled bronchodilators but should not be used with suspensions such as budesonide.<br />
Ultrasonic nebulizers tend to heat medication. This raises concerns about disrupting proteins,<br />
but that does not affect commonly inhaled medications. The MicroAir ® Ultrasonic<br />
Model (Omron Healthcare, Bannockburn, IL) and MABISMist II (Mabis Healthcare,<br />
Waukegan, IL) are different models of the ultrasonic nebulizer.<br />
16 American Association for Respiratory Care A <strong>Guide</strong> to <strong>Aerosol</strong> Delivery Devices for Respiratory Therapists, 3rd Edition © 2013