Chapter 4 - UCSB HEP
Chapter 4 - UCSB HEP
Chapter 4 - UCSB HEP
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
WORK AND ENERGY<br />
I_ I -1<br />
into a boron nucleus and a neutron. The collision is inelastic, and the<br />
final kinetic energy is less than EO by 2.8 MeV. (1 MeV = 10s eV =<br />
1.6 X 10-la J), The relative masses of the particles are: helium, mass<br />
4; lithium, mass 7; boron, mass 10; neutron, mass I. The reaction can<br />
be sym bollzed<br />
7Li + 4He t I0B + ln - 2.8 MeV.<br />
a. What is EO,thrsahold, the minimum value of Eo for which neutrons<br />
can be produced What is the energy of the neutrons at this threshold<br />
Ans. Neutron energy = 0.15 MeV<br />
6. Show that if the incident energy falls in the range Eo,thremhold <<br />
EO < E o , + 0.27 ~ MeV, ~ the ~ neutrons ~ ~ ejected ~ ~ in the forward direction<br />
do not all have the same energy but must have either one or the<br />
other of two possible energies. (You can understand the origin of the<br />
two groups by looking at the reaction in the center of mass system.)<br />
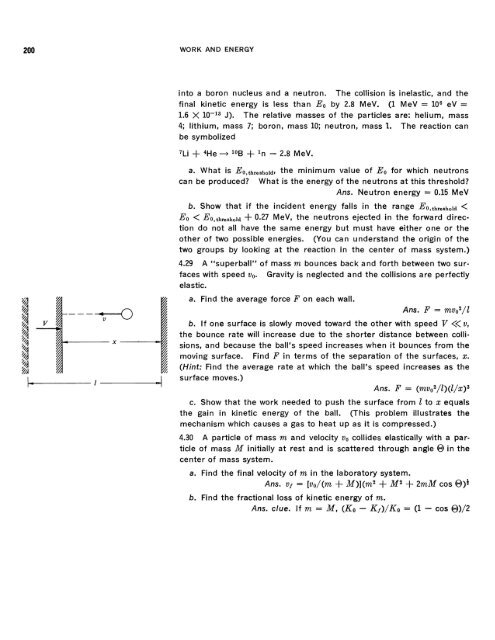
4.29 A "superball" of mass m bounces back and forth between two surfaces<br />
with speed 00. Gravity is neglected and the collisions are perfectly<br />
elastic.<br />
a. Find the average force F on each wall.<br />
Ans. F = rnvovl<br />
b. If one surface is slowly moved toward the other with speed V