Heating Coil or Dry Cooling Coil - Commissioning-hvac.org
Heating Coil or Dry Cooling Coil - Commissioning-hvac.org
Heating Coil or Dry Cooling Coil - Commissioning-hvac.org
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Heating</strong> <strong>Coil</strong> <strong>or</strong> <strong>Dry</strong> <strong>Cooling</strong> <strong>Coil</strong><br />
Jean Lebrun<br />
University of Liège<br />
The model proposed here can be used in both heating and cooling regime, providing that<br />
the coil stays dry.<br />
The secondary fluid is called “refrigerant”, but the heat flow rate is taken as positive in<br />
heating mode.<br />
The coil is supposed to behave as a counter-flow heat exchanger.<br />
Laminar and turbulent regimes are considered on air and “refrigerant” sides respectively.<br />
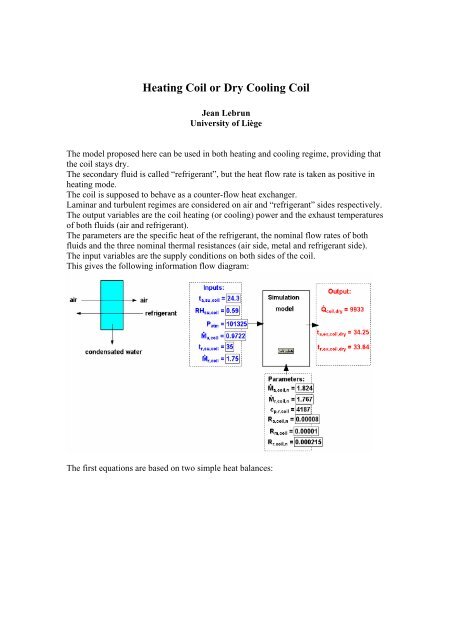
The output variables are the coil heating (<strong>or</strong> cooling) power and the exhaust temperatures<br />
of both fluids (air and refrigerant).<br />
The parameters are the specific heat of the refrigerant, the nominal flow rates of both<br />
fluids and the three nominal thermal resistances (air side, metal and refrigerant side).<br />
The input variables are the supply conditions on both sides of the coil.<br />
This gives the following inf<strong>or</strong>mation flow diagram:<br />
The first equations are based on two simple heat balances:
Then, the effectiveness is defined as f<strong>or</strong> a classical counter-flow heat exchanger:<br />
The thermal resistances are calculated by reference to their values in nominal conditions: