LB2882MaternalNutriti+ - Mead Johnson Nutrition
LB2882MaternalNutriti+ - Mead Johnson Nutrition
LB2882MaternalNutriti+ - Mead Johnson Nutrition
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
The United States has not established recommended intakes for DHA. The US Dietary Guidelines for Americans<br />
2010, however, recognized the importance of DHA during pregnancy and lactation. 37 The Guidelines state,<br />
“Moderate evidence indicates that intake of omega-3 fatty acids, in particular DHA, from at least 8 ounces<br />
of seafood per week for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding is associated with improved infant health<br />
outcomes, such as visual and cognitive development. Therefore, it is recommended that women who are<br />
pregnant or breastfeeding consume at least 8 and up to 12 ounces of a variety of seafood per week, from<br />
choices that are lower in methyl mercury.”<br />
Cold water, ocean-faring fatty fish, such as salmon and tuna, are among the richest natural sources of DHA. DHA is<br />
present naturally in lesser amounts in organ meats, poultry and eggs and is found in DHA-fortified foods (Table 7).<br />
The presence of methyl mercury and other neurotoxic chemicals in fish and shellfish is a potential concern for women<br />
in their childbearing years. 36 The US Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010 state that women who are pregnant or<br />
breastfeeding should not eat tilefish, shark, swordfish and king mackerel because they are high in mercury. 37 Fortified<br />
foods and dietary supplements containing DHA, either derived from single-cell organisms or fish oil that have been<br />
processed to remove potential contaminants, are also sources of preformed DHA for pregnant and lactating women<br />
who do not eat enough DHA-rich foods.<br />
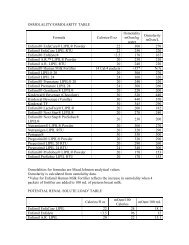
Table 7. Selected Food Sources of DHA<br />
Food<br />
DHA (mg)<br />
Salmon, coho, farmed, 3 oz, cooked 706<br />
Tuna, light, canned, drained, 3 oz 190<br />
Catfish, 3 oz, cooked 116<br />
Blue crab, 3 oz, cooked 57<br />
Fortified eggs, 1 large 57<br />
Chicken, roasted, dark meat, 3 oz 45<br />
Eggs, 1 large 29<br />
Sources: www.nal.usda.gov/fnic/foodcomp/search/. Accessed 09/12<br />
Fortified Eggs: www.egglandsbest.com. Accessed 09/12<br />
Vitamins<br />
Recommended intakes of several vitamins increase during pregnancy and lactation. Figure 1 compares<br />
recommended intakes of select vitamins for non-pregnant women (19 to 30 years old) with those of pregnant or<br />
lactating women of the same age.<br />
13