EEG source analysis.pdf - Clinical Neurophysiology
EEG source analysis.pdf - Clinical Neurophysiology
EEG source analysis.pdf - Clinical Neurophysiology
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
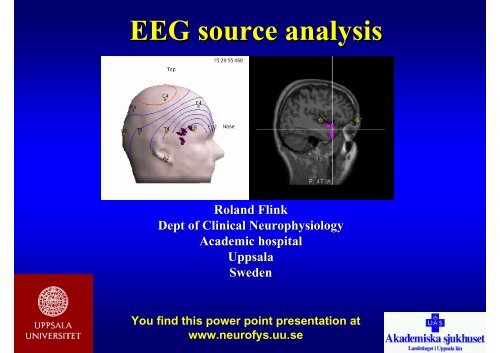
<strong>EEG</strong> <strong>source</strong> <strong>analysis</strong><br />
Roland Flink<br />
Dept of <strong>Clinical</strong> <strong>Neurophysiology</strong><br />
Academic hospital<br />
Uppsala<br />
Sweden<br />
You find this power point presentation at<br />
www.neurofys.uu.se
Dipole<br />
sink<br />
<strong>source</strong>
Dipole<br />
Homogeneous volume conductor
Dipole<br />
Radial dipole with<br />
magnetic field
Dipole<br />
Tangential dipole with<br />
magnetic filed
Multiple Source Analysis<br />
Spherical spline maps
FOCUS <strong>source</strong> montage<br />
Spatiotemporal Multiple Source Analysis, only accepting solutions<br />
continuous over time, increase and decrease smoothly
Sequential dipole fitting strategy (1)<br />
Residual waveforms
Sequential dipole fitting strategy (2)<br />
The inverse problem – iterative calculations<br />
Spike<br />
Residual<br />
Tre-dipol lösning<br />
Dipol 4-6 ej över brusnivå
Sequential dipole fitting strategy (3)
Sequential dipole fitting strategy (4)<br />
Global field power
Sequential dipole fitting strategy (5)
Sequential dipole fitting strategy (6)
Conduction or propagation<br />
Multiple <strong>source</strong><br />
<strong>analysis</strong>
Distributed Source Estimation<br />
LORETA (Low resolution Electromagnetic Tomography)<br />
Estimates the current density of the full brain volume<br />
Select the solutions with the smoothest distribution in space<br />
LORETA suggests a widespread <strong>source</strong> activating neighbouring areas
Interictal spike activity
Frequency Domain Source Localization
Semispherical helmet with 64 probes
Polhemus Digitizer
Polhemus Digitizer<br />
Reference nodes<br />
Reciever stylus<br />
Transmittor of magnetic field
Polhemus Digitizer
EETrak
Markers
MR segmentation
MR segmentation
Three shell realistic head model<br />
Calculating matrix
Dipole location is affected by the<br />
relative conductivity of the bone
Surface recording<br />
R Ave H Ave L Ave<br />
Subdural recording<br />
R Ave H Ave L Ave<br />
1 s<br />
1 s
Dipole location of interictal spike activity<br />
Comparing extrakranial and intracranial recordings
”Moving<br />
dipole” R<br />
L<br />
L<br />
R
Potential field mapping
Potential field mapping and dipoles
Single dipoles in MRI model
Source <strong>analysis</strong> with <strong>EEG</strong><br />
• Anatomic head model<br />
• Multi shell model – relative conductans<br />
• Matematical algorithms – clinical<br />
relevance<br />
• Epilepsy surgery - strategy for<br />
intracranial recording<br />
Ref:<br />
<strong>EEG</strong> Source Modeling, ed J Ebersole, J Clin Neurophysiol,<br />
Vol. 16:3, 1999.
Bilat synchronous interictal activity
Lateralised interictal activity
Equivalent Current Dipole
MUSIC<br />
Multiple Signal Classification
Lateralised interictal activity
Single Dipole <strong>analysis</strong>
MUSIC <strong>analysis</strong><br />
LORETA <strong>analysis</strong>
fMRI Activation in Continuous and<br />
Spike-triggered <strong>EEG</strong>-fMRI Studies<br />
of Epileptic Spikes<br />
A Al-Asmi, C-G Bénar, DW Gross,<br />
Y Agha Khani, F Andermann, B<br />
Pike, F Dubeau and J Gotman<br />
Epilepsia 44(10):1328-1339, 2003
fMRI<br />
• Activation studies<br />
• Deoxyhemoglobinconcentrationen on venous<br />
side<br />
• Distance to active neurons - < 1 cm<br />
• BOLD (blood oxygenation level-dependent)<br />
• Increased signal when seizure activity –<br />
movement artefacts<br />
• Interictal activity – <strong>EEG</strong>-fMRI
Spike triggered <strong>EEG</strong>-fMRI (SfMRI)
Continuous <strong>EEG</strong>-fMRI<br />
(C-fMRI)
Case 10: Cryptogenic epilepsy. MRI normal. <strong>EEG</strong> bilat occipital<br />
spike aktivity
Case 12: Headtrauma. MRI<br />
shows perisylvian atrophy dx,<br />
arachnoidal cyst in middle<br />
fossa
Case 16: Perinatal encephalopathy. MRI shows porencephalic cyst left hemisphere
Case 18: Cortical dysplasia. MRI shows perisylvian polymicrogyria bilat