SNAKE LEMMA IN INCOMPLETE RELATIVE HOMOLOGICAL ...
SNAKE LEMMA IN INCOMPLETE RELATIVE HOMOLOGICAL ...
SNAKE LEMMA IN INCOMPLETE RELATIVE HOMOLOGICAL ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>SNAKE</strong> <strong>LEMMA</strong> <strong>IN</strong> <strong>IN</strong>COMPLETE <strong>RELATIVE</strong> <strong>HOMOLOGICAL</strong> CATEGORIES 89<br />
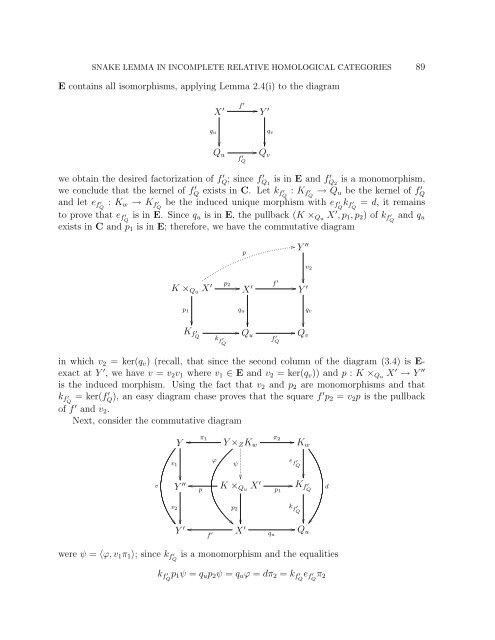
E contains all isomorphisms, applying Lemma 2.4(i) to the diagram<br />
X ′ f ′ Y ′ q v<br />
q u<br />
<br />
Q u<br />
f ′ Q<br />
Q v<br />
we obtain the desired factorization of f ′ Q ; since f ′ Q 1<br />
is in E and f ′ Q 2<br />
is a monomorphism,<br />
we conclude that the kernel of f ′ Q exists in C. Let k f ′ Q : K f ′ Q → Q u be the kernel of f ′ Q<br />
and let e f ′<br />
Q<br />
: K w → K f ′<br />
Q<br />
be the induced unique morphism with e f ′<br />
Q<br />
k f ′<br />
Q<br />
= d, it remains<br />
to prove that e f ′<br />
Q<br />
is in E. Since q u is in E, the pullback (K × Qu X ′ , p 1 , p 2 ) of k f ′<br />
Q<br />
and q u<br />
exists in C and p 1 is in E; therefore, we have the commutative diagram<br />
p<br />
Y ′′ v 2<br />
K × Qu X ′<br />
p 2 X ′ f ′ <br />
Y ′ q v<br />
p 1<br />
<br />
q u<br />
<br />
K f ′<br />
Q<br />
kf ′<br />
Q<br />
Q u<br />
f ′ Q<br />
Q v<br />
in which v 2 = ker(q v ) (recall, that since the second column of the diagram (3.4) is E-<br />
exact at Y ′ , we have v = v 2 v 1 where v 1 ∈ E and v 2 = ker(q v )) and p : K × Qu X ′ → Y ′′<br />
is the induced morphism. Using the fact that v 2 and p 2 are monomorphisms and that<br />
k f ′<br />
Q<br />
= ker(f Q ′ ), an easy diagram chase proves that the square f ′ p 2 = v 2 p is the pullback<br />
of f ′ and v 2 .<br />
Next, consider the commutative diagram<br />
Y<br />
π 1<br />
Y × Z K w<br />
π 2<br />
K w<br />
ϕ<br />
ψ<br />
v<br />
v 1<br />
<br />
Y ′′<br />
p<br />
K × Qu X ′<br />
p 1<br />
e f ′<br />
Q<br />
<br />
K f ′<br />
Q<br />
d<br />
v 2<br />
<br />
p 2<br />
<br />
Y ′ X ′<br />
f ′<br />
q u<br />
k f ′<br />
Q<br />
<br />
Q u<br />
were ψ = 〈ϕ, v 1 π 1 〉; since k f ′<br />
Q<br />
is a monomorphism and the equalities<br />
k f ′<br />
Q<br />
p 1 ψ = q u p 2 ψ = q u ϕ = dπ 2 = k f ′<br />
Q<br />
e f ′<br />
Q<br />
π 2