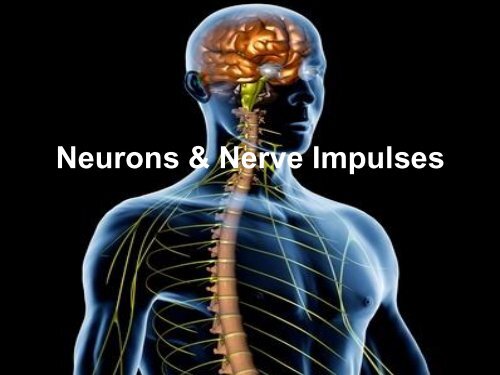
Neurons & Nerve Impulses - Fall River Public Schools
Neurons & Nerve Impulses - Fall River Public Schools
Neurons & Nerve Impulses - Fall River Public Schools
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Neurons</strong> & <strong>Nerve</strong> <strong>Impulses</strong>
Objectives<br />
• Explain the function of the nervous system<br />
• Contrast the three types of neurons<br />
• Identify the 4 main parts of a neuron<br />
• Identify where nerve impulses are transferred
Introduction<br />
• The nervous system controls<br />
and coordinates functions<br />
throughout the body and<br />
responds to internal and<br />
external stimuli<br />
• The nervous system is the<br />
communication system of<br />
the body<br />
• Messages carried by the<br />
nervous system are electrical<br />
signals called impulses
<strong>Neurons</strong><br />
• <strong>Neurons</strong> – cells that transmit<br />
nerve impulses<br />
• 3 Types of <strong>Neurons</strong><br />
– Sensory neurons carry<br />
impulses from sense organs to<br />
the spinal cord and brain<br />
– Motor neurons carry impulses<br />
from the brain and spinal cord<br />
to muscles and glands<br />
– Interneurons connect sensory<br />
and motor neurons and carry<br />
impulses between them
Parts of a Neuron<br />
• Cell body – the largest part of a neuron that<br />
contains the nucleus and most of the cytoplasm<br />
• Dendrites – short, branched extensions that carry<br />
impulses from the environment or from other<br />
neurons toward the cell body<br />
• Axon – long fibers that carry impulses away from<br />
the cell body<br />
– the ends of the axon are called axon terminals<br />
– Axons and dendrites are clustered into bundles of<br />
fibers called nerves
Parts of a Neuron<br />
• Some neurons have a myelin sheath, which is an insulating<br />
membrane that surrounds an axon<br />
• The myelin sheath has gaps in it called nodes which allow<br />
impulses to move quickly up the axon
The <strong>Nerve</strong> Impulse<br />
• An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another<br />
neuron or by the environment<br />
• An impulse is a sudden reversal of the membrane potential<br />
• Sodium channels open to allow Na + to flow into the cell<br />
• The inside of the membrane temporarily becomes more<br />
positive than the outside<br />
• Action potential – the reversal of charges across the cell<br />
membrane from negative to positive, also called a nerve<br />
impulse<br />
• As the impulse passes, potassium channels open, allowing K+<br />
to flow out, restoring resting potential<br />
• <strong>Nerve</strong> impulses at one point trigger an impulse at the next<br />
point, like a row of falling dominoes
The Synapse<br />
• Impulse reaches the end of a<br />
neuron at the axon terminal,<br />
where it makes contact with<br />
another cell<br />
– The neuron may pass the impulse<br />
to the second cell<br />
• Synapse – the location at which<br />
a neuron can transfer an impulse<br />
to another cell<br />
• Axon terminals contain vesicles<br />
with neurotransmitters<br />
• Neurotransmitter – chemicals<br />
used by a neuron to transmit an<br />
impulse across a synapse to<br />
another cell
Notes Review<br />
• Explain the function of the nervous system<br />
– The nervous system controls and coordinates<br />
functions throughout the body and responds to<br />
internal and external stimuli
Notes Review<br />
• Contrast the three types of neurons<br />
– Sensory neurons carry impulses from sense organs<br />
to the spinal cord and brain<br />
– Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and<br />
spinal cord to muscles and glands<br />
– Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons<br />
and carry impulses between them
Notes Review<br />
• Identify the 4 main parts of a neuron<br />
– Cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath
Notes Review<br />
• Identify where nerve impulses are transferred<br />
– <strong>Nerve</strong> impulses are transferred at the synapse.