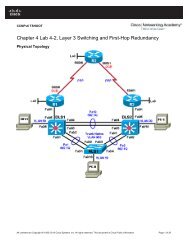
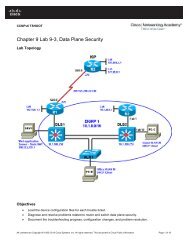
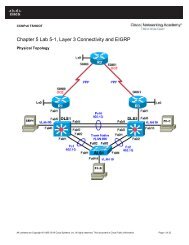
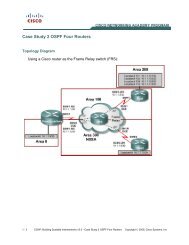
Lab 6.2 Configuring CBAC
Lab 6.2 Configuring CBAC
Lab 6.2 Configuring CBAC
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Why is this particularly important for UDP protocols<br />
On a per-protocol basis, there are other adjustable settings. For instance, you<br />
can manipulate <strong>CBAC</strong> to trigger logging messages based on the matched<br />
protocol. This is important for security accounting as well as for debugging<br />
purposes. View the options available on a per-protocol basis, using the <br />
character.<br />
FW(config)# ip inspect name myrules tcp <br />
alert<br />
Turn on/off alert<br />
audit-trail Turn on/off audit trail<br />
router-traffic Enable inspection of sessions to/from the router<br />
timeout<br />
Specify the inactivity timeout time<br />
<br />
In a secure network, you would likely set up a Syslog server to monitor security<br />
information including communication to external networks. Alert and audit trail<br />
messages allow holes in the firewall created by <strong>CBAC</strong> to be monitored and<br />
logged for later use. By default, <strong>CBAC</strong> logs alert messages to the console<br />
which can be configured on a per-protocol basis to override the global settings<br />
for the alert messages (as shown above). To change the global setting for<br />
alerts, use the command ip inspect alert-off. By default, alerts are on. To<br />
enable audit-trail messages, use the global command ip inspect audit-trail. By<br />
default, audit-trail messages are off. The timeout argument specifies a perprotocol<br />
connection timeout period. Add in Internet Control Message Protocol<br />
(ICMP) with a timeout time of 5 seconds, HTTP inspection without alerting, and<br />
FTP inspection with an audit-trail. ICMP inspection may not work on older IOS<br />
releases.<br />
FW(config)# ip inspect name myrules icmp timeout 5<br />
FW(config)# ip inspect name myrules http alert off<br />
FW(config)# ip inspect name myrules ftp audit-trail on<br />
To apply the rule set to an interface, use the interface level command ip<br />
inspect name direction. Apply “myrules” to the inside interface on FW with an<br />
inbound direction. This means that any traffic initiated from the inside interface<br />
going through the router will have IP inspection performed on it.<br />
FW(config)# interface serial0/0/0<br />
FW(config-if)# ip inspect myrules in<br />
In this scenario, you could also apply it outbound on the outside interface to<br />
achieve the same effect. When would this not apply<br />
4 - 8 CCNP: Implementing Secure Converged Wide-area Networks v5.0 - <strong>Lab</strong> 6-2 Copyright © 2007, Cisco Systems, Inc