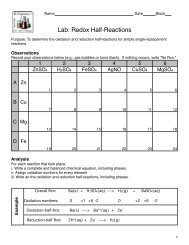
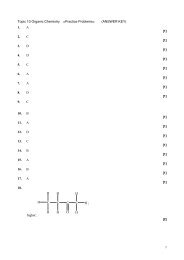
Hess's Law Practice
Hess's Law Practice
Hess's Law Practice
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Hessʼs <strong>Law</strong> (Page 509-511)<br />
A theoretical way to determine ΔH for a chemical reaction is provided by Hessʼs law, which states<br />
that if two or more thermochemical equations can be added to produce a final equation for a<br />
reaction, then the enthalpy change for the final reaction equals the sum of the enthalpy changes<br />
for the individual reactions.<br />
<strong>Practice</strong> Problems<br />
Use the given thermochemical equations a and b to determine ΔH for each of the the following<br />
reactions.<br />
1.) # # # # CuO(s)# +# H2(g)# # ---># Cu(s)# # +! H2O(g) , !! ΔH = <br />
# # # a. # # # # # # CuO(s)# ---># Cu(s) +! ! ½ O2(g)! , ! ΔH = 155 kJ<br />
! ! ! b. !! H2(g)# +# ½ O2(g)# ---># H2O(g) , ! ! ! ! ! ΔH = -242 kJ<br />
2.) # # # 2CO(s)# +# O2(g)# # ---># 2CO2(g), !! ΔH = <br />
# # # a. # # # # # CO(g)#---># C(s)# +! ! ½ O2(g) , ! ΔH = 110. kJ<br />
! ! ! b. !! C(s)# +# O2(g)# # ---># CO2(g) , ! ! ! ! ! ! ΔH = -394 kJ<br />
(over)
3.) # # # # S(s)# +# O2(g)# # # ---># SO2(g), ! ! ΔH = <br />
# # # a. # # 2SO2(g)# +# O2(g)# # ---># 2SO3(g), !! ! ! ΔH = -196. kJ<br />
! ! ! b. !! 2S(s)# +# 3O2(g)# # ---># 2SO3(g), !! ! ! ΔH = -790. kJ<br />
4.) # # # # CS2(l)## +# 2H2O(l)# # ---># CO2(g)# +! 2H2S(g) , ! ΔH = <br />
3 2<br />
# # # a. ## H2S(g)# +# # O2(g)# # ---># H2O(l)## +! SO2(g),! ! ΔH = -563 kJ<br />
! ! ! b. !! CS2(l)## +# 3O2(g)# # ---># CO2(g)# +! 2SO2(g),! ! ΔH = -1075 kJ