Statistics and Hypothesis Testing
Statistics and Hypothesis Testing
Statistics and Hypothesis Testing
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
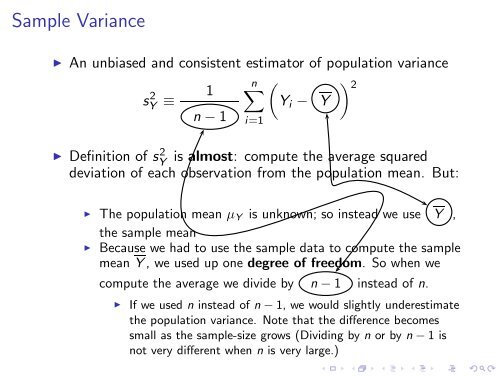
Sample Variance<br />
◮ An unbiased <strong>and</strong> consistent estimator of population variance<br />
sY 2 ≡ 1<br />
n∑<br />
( ) 2<br />
Y i − Y<br />
n − 1<br />
i=1<br />
◮ Definition of sY 2 is almost: compute the average squared<br />
deviation of each observation from the population mean. But:<br />
◮ The population mean µY is unknown; so instead we use Y ,<br />
the sample mean<br />
◮ Because we had to use the sample data to compute the sample<br />
mean Y , we used up one degree of freedom. So when we<br />
compute the average we divide by n − 1 instead of n.<br />
◮<br />
If we used n instead of n − 1, we would slightly underestimate<br />
the population variance. Note that the difference becomes<br />
small as the sample-size grows (Dividing by n or by n − 1 is<br />
not very different when n is very large.)