Triangulation Framework for Local Service Delivery - Philippine ...
Triangulation Framework for Local Service Delivery - Philippine ...
Triangulation Framework for Local Service Delivery - Philippine ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
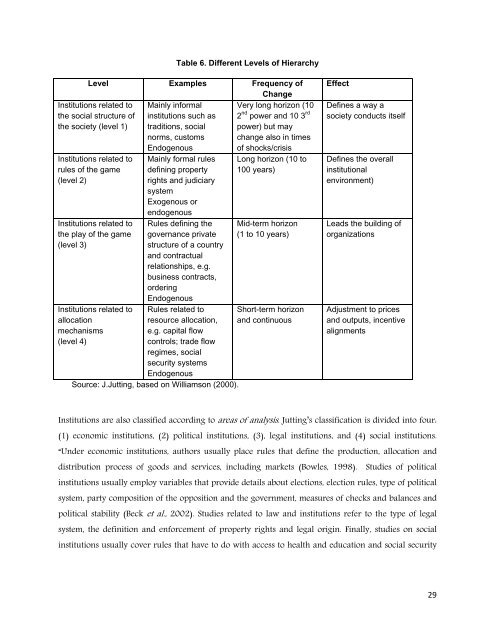
Table 6. Different Levels of Hierarchy<br />
Level Examples Frequency of<br />
Change<br />
Institutions related to Mainly in<strong>for</strong>mal Very long horizon (10<br />
the social structure of institutions such as 2 nd power and 10 3 rd<br />
the society (level 1) traditions, social power) but may<br />
norms, customs change also in times<br />
Endogenous<br />
of shocks/crisis<br />
Institutions related to<br />
rules of the game<br />
(level 2)<br />
Institutions related to<br />
the play of the game<br />
(level 3)<br />
Institutions related to<br />
allocation<br />
mechanisms<br />
(level 4)<br />
Mainly <strong>for</strong>mal rules<br />
defining property<br />
rights and judiciary<br />
system<br />
Exogenous or<br />
endogenous<br />
Rules defining the<br />
governance private<br />
structure of a country<br />
and contractual<br />
relationships, e.g.<br />
business contracts,<br />
ordering<br />
Endogenous<br />
Rules related to<br />
resource allocation,<br />
e.g. capital flow<br />
controls; trade flow<br />
regimes, social<br />
security systems<br />
Endogenous<br />
Source: J.Jutting, based on Williamson (2000).<br />
Long horizon (10 to<br />
100 years)<br />
Mid-term horizon<br />
(1 to 10 years)<br />
Short-term horizon<br />
and continuous<br />
Effect<br />
Defines a way a<br />
society conducts itself<br />
Defines the overall<br />
institutional<br />
environment)<br />
Leads the building of<br />
organizations<br />
Adjustment to prices<br />
and outputs, incentive<br />
alignments<br />
Institutions are also classified according to areas of analysis. Jutting’s classification is divided into four:<br />
(1) economic institutions, (2) political institutions, (3), legal institutions, and (4) social institutions.<br />
“Under economic institutions, authors usually place rules that define the production, allocation and<br />
distribution process of goods and services, including markets (Bowles, 1998). Studies of political<br />
institutions usually employ variables that provide details about elections, election rules, type of political<br />
system, party composition of the opposition and the government, measures of checks and balances and<br />
political stability (Beck et al., 2002). Studies related to law and institutions refer to the type of legal<br />
system, the definition and en<strong>for</strong>cement of property rights and legal origin. Finally, studies on social<br />
institutions usually cover rules that have to do with access to health and education and social security<br />
29