HYDRAULIC FLUIDS, CUTTING OILS, QUENCHING ... - K-Patents
HYDRAULIC FLUIDS, CUTTING OILS, QUENCHING ... - K-Patents
HYDRAULIC FLUIDS, CUTTING OILS, QUENCHING ... - K-Patents
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
METALS AND MINING<br />
APPLICATION NOTE 7.01.01_REV1<br />
METALWORKING AND MACHINING 1 (2)<br />
w w w . k p a t e n t s . c o m<br />
<strong>HYDRAULIC</strong> <strong>FLUIDS</strong>, <strong>CUTTING</strong> <strong>OILS</strong>, <strong>QUENCHING</strong> <strong>OILS</strong><br />
COOLING LUBRICANTS, WASHING LIQUIDS<br />
Typical end products<br />
Metal components and parts e.g. engines, drill bits, washers,<br />
beverage cans, steel coils, turbine blades, knives, blades, scissors,<br />
bearings etc.<br />
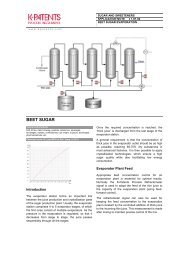
Chemical curve: R.I.per BRIX b.w. at Ref. Temp. of 20˚C<br />
Introduction<br />
Metal machining is the process of converting metal<br />
blanks into finished components or parts. All<br />
metalworking operations involve the contact of two<br />
solids, a tool and the work-piece, to create the<br />
finished piece. The process involves high friction,<br />
high temperatures and high stresses, resulting in tool<br />
wear. It is the function of the lubricant, or<br />
metalworking fluid, to minimize or dissipate these<br />
effects. Metalworking fluids accomplish this by<br />
providing cooling, lubrication and corrosion<br />
resistance.<br />
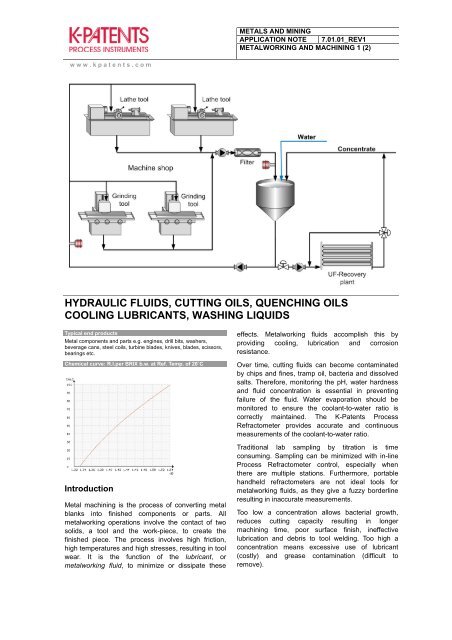
Over time, cutting fluids can become contaminated<br />
by chips and fines, tramp oil, bacteria and dissolved<br />
salts. Therefore, monitoring the pH, water hardness<br />
and fluid concentration is essential in preventing<br />
failure of the fluid. Water evaporation should be<br />
monitored to ensure the coolant-to-water ratio is<br />
correctly maintained. The K-<strong>Patents</strong> Process<br />
Refractometer provides accurate and continuous<br />
measurements of the coolant-to-water ratio.<br />
Traditional lab sampling by titration is time<br />
consuming. Sampling can be minimized with in-line<br />
Process Refractometer control, especially when<br />
there are multiple stations. Furthermore, portable<br />
handheld refractometers are not ideal tools for<br />
metalworking fluids, as they give a fuzzy borderline<br />
resulting in inaccurate measurements.<br />
Too low a concentration allows bacterial growth,<br />
reduces cutting capacity resulting in longer<br />
machining time, poor surface finish, ineffective<br />
lubrication and debris to tool welding. Too high a<br />
concentration means excessive use of lubricant<br />
(costly) and grease contamination (difficult to<br />
remove).
METALS AND MINING<br />
APPLICATION NOTE 7.01.01_REV1<br />
METALWORKING AND MACHINING 2 (2)<br />
w w w . k p a t e n t s . c o m<br />
Figure 1: Quenching Process:<br />
Figure 2: Induction Hardening Process:<br />
Application<br />
The K-<strong>Patents</strong> Process Refractometer applications<br />
can be divided into four areas:<br />
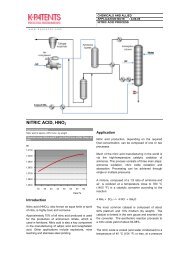
1. Quenching / Tempering Process<br />
The physical property of the metal is changed<br />
through quenching. The metal is heat-treated and<br />
then cooled rapidly (quenched) with a fluid in order<br />
to increase the surface hardness (Figure 1). The<br />
metal can also be heat-treated through magnetic<br />
induction heating (Figure 2).<br />
The concentration of the fluid is one important<br />
parameter, which affects the final quality. Fluids are<br />
also used in the casting process. When the<br />
concentration levels are correct, the surface<br />
properties of the finished parts are within the<br />
specifications. Typical liquids used in induction<br />
hardening are PAGs (Poly alkylene glycols).<br />
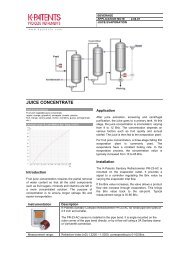
2. Cooling / Cutting<br />
During machining metal has to be cooled and<br />
lubricated. Coolants are often supplied through a<br />
centralized system but also by local systems at the<br />
point of use. The K-<strong>Patents</strong> refractometers are<br />
used in both the feed and recycling lines serving<br />
machine tools.<br />
3. Washing<br />
The primary goal of washing is to clean the<br />
machine parts thoroughly of residual oil and dirt.<br />
The washing fluid is sprayed onto the parts at high<br />
pressure. The fluid forms a film that protects the<br />
parts from corrosion during storage.<br />
The K-<strong>Patents</strong> refractometer detects the correct<br />
concentration to ensure that the excess grease and<br />
oil have been completely removed by the washing<br />
process.
METALS AND MINING<br />
APPLICATION NOTE 7.01.01_REV1<br />
METALWORKING AND MACHINING 2 (2)<br />
w w w . k p a t e n t s . c o m<br />
4. Rinsing<br />
If the parts and components are destined for<br />
welding, the protective film must be completely<br />
removed as residual wash solution affects the<br />
quality of welds. The film is removed in water<br />
rinsing baths.<br />
As the water picks up the residual wash liquid, the<br />
bath must be replenished as the concentration<br />
value reaches its saturation limit. The acceptable<br />
limit varies from plant to plant, but typically it is<br />
around 0.5 Brix.<br />
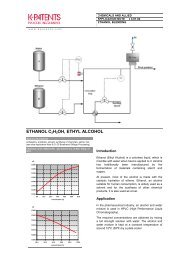
Instrumentation<br />
The K-<strong>Patents</strong> Sanitary Probe Refractometer<br />
PR-23-AP is the recommend system for larger<br />
pipes or vessels. The Sanitary Compact<br />
Refractometer PR-23-AC with a flow-cell is suitable<br />
for smaller pipes. An automatic prism cleaning<br />
system is recommended in cases, when dirty<br />
liquids are being processed.<br />
Instrumentation<br />
Description<br />
K-<strong>Patents</strong> Sanitary Compact Refractometer PR-23-AC for small pipe line sizes of<br />
2.5 inch and smaller.<br />
The PR-23-AC sensor is installed in the pipe bend. It is angle mounted in the outer<br />
corner of the pipe bend directly or through a flow cell and 3A Sanitary clamp or<br />
Varivent® connection.<br />
K-<strong>Patents</strong> Sanitary Probe Refractometer PR-23-AP for installations in large pipes,<br />
tanks, cookers, crystallizers and kettles and for higher temperatures up to 150°C<br />
(300 °F). Installation through a 3A Sanitary clamp.<br />
Automatic prism wash:<br />
Measurement range:<br />
Prism wash with high pressure water is recommended for dirty liquids.<br />
Refractive Index (nD) 1.3200 – 1.5300, corresponding to 0-100 Brix.