Lecture 1: Introduction to Database - Nubacad.com
Lecture 1: Introduction to Database - Nubacad.com
Lecture 1: Introduction to Database - Nubacad.com
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
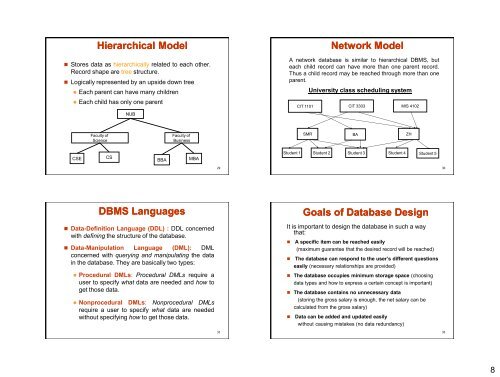
Hierarchical Model<br />
• S<strong>to</strong>res data as hierarchically related <strong>to</strong> each other.<br />
Record shape are tree structure.<br />
• Logically represented by an upside down tree<br />
• Each parent can have many children<br />
• Each child has only one parent<br />
NUB<br />
Network Model<br />
A network database is similar <strong>to</strong> hierarchical DBMS, but<br />
each child record can have more than one parent record.<br />
Thus a child record may be reached through more than one<br />
parent.<br />
University class scheduling system<br />
CIT 1101 CIT 3303 MIS 4102<br />
Faculty of<br />
Science<br />
Faculty of<br />
Business<br />
SMR BA ZH<br />
CSE<br />
CS<br />
BBA<br />
MBA<br />
Student 1 Student 2 Student 3 Student 4 Student 5<br />
29<br />
30<br />
DBMS Languages<br />
• Data-Definition Language (DDL) : DDL concerned<br />
with defining the structure of the database.<br />
• Data-Manipulation Language (DML): DML<br />
concerned with querying and manipulating the data<br />
in the database. They are basically two types:<br />
• Procedural DMLs: Procedural DMLs require a<br />
user <strong>to</strong> specify what data are needed and how <strong>to</strong><br />
get those data.<br />
• Nonprocedural DMLs: Nonprocedural DMLs<br />
require a user <strong>to</strong> specify what data are needed<br />
without specifying how <strong>to</strong> get those data.<br />
Goals of <strong>Database</strong> Design<br />
It is important <strong>to</strong> design the database in such a way<br />
that:<br />
• A specific item can be reached easily<br />
(maximum guarantee that the desired record will be reached)<br />
• The database can respond <strong>to</strong> the user’s different questions<br />
easily (necessary relationships are provided)<br />
• The database occupies minimum s<strong>to</strong>rage space (choosing<br />
data types and how <strong>to</strong> express a certain concept is important)<br />
• The database contains no unnecessary data<br />
(s<strong>to</strong>ring the gross salary is enough, the net salary can be<br />
calculated from the gross salary)<br />
• Data can be added and updated easily<br />
without causing mistakes (no data redundancy)<br />
31<br />
32<br />
8