Concentration of Solutions
Concentration of Solutions
Concentration of Solutions
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Name Class Date<br />
Problem Solving continued<br />
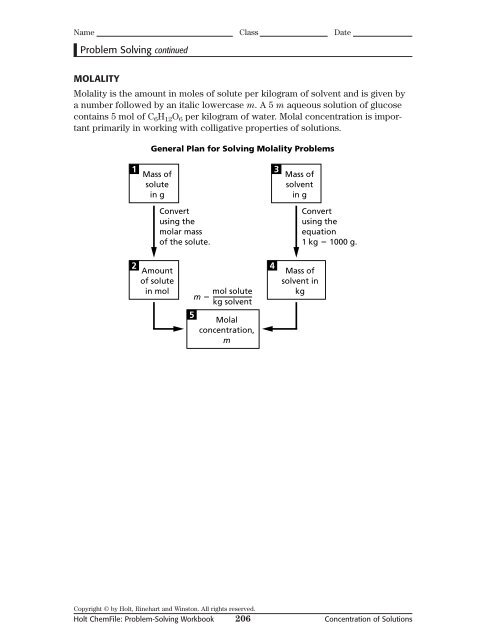
MOLALITY<br />
Molality is the amount in moles <strong>of</strong> solute per kilogram <strong>of</strong> solvent and is given by<br />
a number followed by an italic lowercase m. A 5 m aqueous solution <strong>of</strong> glucose<br />
contains 5 mol <strong>of</strong> C 6 H 12 O 6 per kilogram <strong>of</strong> water. Molal concentration is important<br />
primarily in working with colligative properties <strong>of</strong> solutions.<br />
General Plan for Solving Molality Problems<br />
1<br />
Mass <strong>of</strong><br />
solute<br />
in g<br />
3<br />
Mass <strong>of</strong><br />
solvent<br />
in g<br />
Convert<br />
using the<br />
molar mass<br />
<strong>of</strong> the solute.<br />
Convert<br />
using the<br />
equation<br />
1 kg 1000 g.<br />
2<br />
Amount<br />
<strong>of</strong> solute<br />
in mol<br />
m <br />
mol solute<br />
kg solvent<br />
4<br />
Mass <strong>of</strong><br />
solvent in<br />
kg<br />
5<br />
Molal<br />
concentration,<br />
m<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.<br />
Holt ChemFile: Problem-Solving Workbook 206 <strong>Concentration</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Solutions</strong>