Sample Assessment Schedule 2012
Sample Assessment Schedule 2012
Sample Assessment Schedule 2012
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
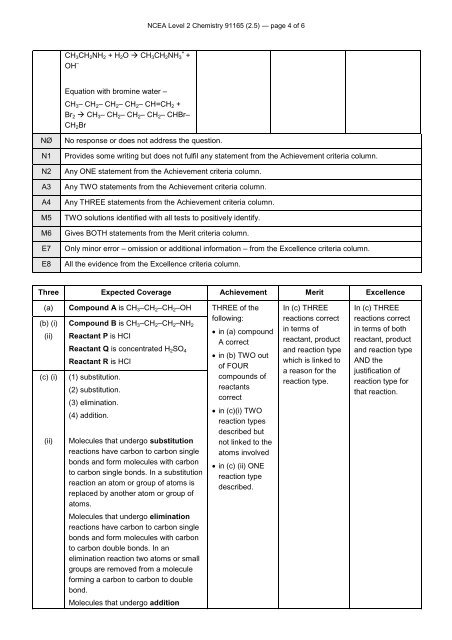
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry 91165 (2.5) — page 4 of 6<br />
CH 3 CH 2 NH 2 + H 2 O CH 3 CH 2 NH 3<br />
+<br />
+<br />
OH –<br />
Equation with bromine water –<br />
CH 3 – CH 2 – CH 2 – CH 2 – CH=CH 2 +<br />
Br 2 CH 3 – CH 2 – CH 2 – CH 2 – CHBr–<br />
CH 2 Br<br />
NØ<br />
N1<br />
N2<br />
A3<br />
A4<br />
M5<br />
M6<br />
E7<br />
E8<br />
No response or does not address the question.<br />
Provides some writing but does not fulfil any statement from the Achievement criteria column.<br />
Any ONE statement from the Achievement criteria column.<br />
Any TWO statements from the Achievement criteria column.<br />
Any THREE statements from the Achievement criteria column.<br />
TWO solutions identified with all tests to positively identify.<br />
Gives BOTH statements from the Merit criteria column.<br />
Only minor error – omission or additional information – from the Excellence criteria column.<br />
All the evidence from the Excellence criteria column.<br />
Three Expected Coverage Achievement Merit Excellence<br />
(a)<br />
(b) (i)<br />
Compound A is CH 3 –CH 2 –CH 2 –OH<br />
Compound B is CH 3 –CH 2 –CH 2 –NH 2<br />
THREE of the<br />
following:<br />
in (a) compound<br />
(ii) Reactant P is HCI<br />
A correct<br />
Reactant Q is concentrated H 2 SO 4<br />
in (b) TWO out<br />
Reactant R is HCl<br />
of FOUR<br />
(c) (i)<br />
(ii)<br />
(1) substitution.<br />
(2) substitution.<br />
(3) elimination.<br />
(4) addition.<br />
compounds of<br />
reactants<br />
correct<br />
in (c)(i) TWO<br />
reaction types<br />
described but<br />
not linked to the<br />
atoms involved<br />
Molecules that undergo substitution<br />
reactions have carbon to carbon single<br />
bonds and form molecules with carbon<br />
to carbon single bonds. In a substitution<br />
reaction an atom or group of atoms is<br />
replaced by another atom or group of<br />
atoms.<br />
Molecules that undergo elimination<br />
reactions have carbon to carbon single<br />
bonds and form molecules with carbon<br />
to carbon double bonds. In an<br />
elimination reaction two atoms or small<br />
groups are removed from a molecule<br />
forming a carbon to carbon to double<br />
bond.<br />
Molecules that undergo addition<br />
in (c) (ii) ONE<br />
reaction type<br />
described.<br />
In (c) THREE<br />
reactions correct<br />
in terms of<br />
reactant, product<br />
and reaction type<br />
which is linked to<br />
a reason for the<br />
reaction type.<br />
In (c) THREE<br />
reactions correct<br />
in terms of both<br />
reactant, product<br />
and reaction type<br />
AND the<br />
justification of<br />
reaction type for<br />
that reaction.